John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Identifier | Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
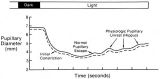 |
Figure-06 | The Normal Pupillary Light Reflex | The normal pupillary light reflex is initiated following exposure to light. After a brief latency, both the right (solid line) and left (broken line) pupil constrict, then undergo a small amount of redilation (escape), followed by oscillations (hippus) if the light is sustained. Hippus is not a path... | Reflex, Pupillary; Examination, Pupillary |
| 52 |
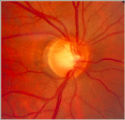 |
glaucoma notching | Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Glaucoma |
| 53 |
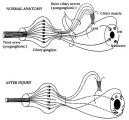 |
Figure-16 | Pathophysiology of Signs Associated with a Tonic Pupil | Pathophysiology of signs associated with a tonic pupil. Normally, all parasympathetic fibers of the third cranial nerve synapse in the ciliary ganglion (top). Most postganglionic fibers innervate the ciliary muscle (dashed lines). After injury to the ciliary ganglion, the pupil becomes denervated an... | Adie's Tonic Pupil; Pupil Disorders; Physiopathology, Iris; Pupil |
| 54 |
 |
Figure-17 | Pupil Signs in a 32-year-old Woman with Right-sided Adie's Pupil | Pupil signs in a 32-year-old woman with right-sided Adie's pupil. The right pupil is larger than the left pupil (top), reacts poorly to direct light stimulation (second panel), and better in response to near stimulation (third panel). The right pupil also shows a supersensitive response 30 minutes a... | Adie's Tonic Pupil; Innervation, Pupil; Drug Effects, Pupil; Physiology, Pupil |
| 55 |
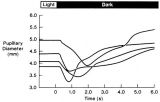 |
Figure-27 | Pupillogram Demonstrating Paradoxical Pupillary Constriction to Darkness | Pupillogram demonstrating paradoxical pupillary constriction to darkness in four patients with congenital achromatopsia. Note that the pupils initially constrict when the light is extinguished. (Price MJ, Thompson HS, Judisch GF et al: Pupillary constriction to darkness. Br J Ophthalmol 1981;69:205-... | Congenital, Color Vision Defects; Physiopathology, Color Vision Defects; Dark Adaptation; Flynn Phenomenon; Humans; Diagnostic Use, Infrared Rays; Congenital, Night Blindness; Physiopathology, Night Blindness; Physiopathology, Optic Nerve Diseases; Physiopathology, Pupil; Congenital, Retinal Disease... |
| 56 |
 |
Figure-08 | Pupillogram of a Healthy Young Subject | Pupillogram of a healthy young subject showing continuous pupillary oscillations of both pupils when light is sustained, indicated by the dark arrow at the top of the recording. Note that the oscillations of the pupils are synchronous and demonstrate variable amplitude and frequency. This pattern of... | Reflex, Pupillary; Pupillogram; Parasympathetic Pupil; Normal Pupillary Responses |
| 57 |
 |
Figure-07 | Relationship Between Age and Pupil Size | Relationship between age and pupil size, determined using an infrared flash photograph technique with subjects placed in darkness for 3 minutes. The numbers above the abscissa indicate the number of subjects tested in each age range. (Reprinted with permission of Loewenfeld IE: "Simple, central" ani... | Physiology, Pupil; Management of a Large or a Small Pupil; Normal Pupillary Responses; Pupil Size with Age |
| 58 |
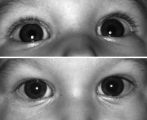 |
Figure-22 | Right-sided Pseudo-Horner's Syndrome | Right-sided pseudo-Horner's syndrome in an 8-month-old infant referred because her mother had noted a larger pupil on the left for a few months and her pediatrician thought the right upper lid was droopy. Both pupils reacted normally to light and darkness, the degree of anisocoria was similar in bot... | Infant; Diagnosis, Horner Syndrome; Etiology, Horner Syndrome; Horner's Syndrome |
| 59 |
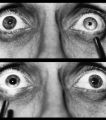 |
Figure-09 | Right-sided Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect | Right-sided relative afferent pupillary defect in a man with optic nerve glioma. When the unaffected left eye is stimulated by light, both pupils constrict (top). When the light is then swung over to the affected right eye, both pupils dilate (bottom). This indicates that pupillomotor conduction thr... | Pupil Disorders; Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect; RAPD; Afferent Pupillary Defect |
| 60 |
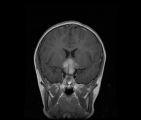 |
CorT1_with_11.jpg | See-saw Nystagmus MRI 1 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | See-saw Nystagmus |
| 61 |
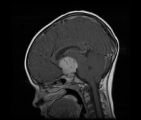 |
SagT1_with_11.jpg | See-saw Nystagmus MRI 2 | MRI; See-saw Nystagmus | See-saw Nystagmus |
| 62 |
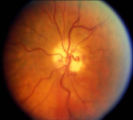 |
shunt vessel meningioma | Shunt Vessel Meningioma | RETINO-CHOROIDAL (OPTO-CILIARY) COLLATERAL VESSELS: (also known as Retinal-choroidal venous collaterals, opticociliary veins or ciliary shunt vessels) Retino-choroidal collaterals are potential telangiectatic connections between the retina and choroidal circulation. Although sometimes called "shunts... | Shunt Vessels (Meningioma) |
| 63 |
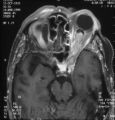 |
shunt vessel meningioma MRI | Shunt Vessel Meningioma - MRI | Meningiomas block venous egress and open potential venous channels known as retinochoroidal (optociliary) collateral vein. This meningioma extends from the back of the globe through the optic canal. | Shunt Vessels (Meningioma) |
| 64 |
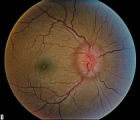 |
stage 2 | Stage 2 - Papilledema | Papilledema Stages; Raised Intracranial Pressure | |
| 65 |
 |
Figure-01 | Structures of the iris | Structures of the iris. The a indicates the anterior border layer that terminates at the pigmentary ruff of the pupillary border (b). The c indicates the iris sphincter muscle, which is oriented circumferentially within the stroma and located deep to the anterior border layer; d indicates vessels th... | Autonomic Anatomy; Iris |
| 66 |
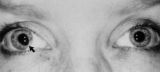 |
Figure-28 | Tadpole-shaped Pupil | Tadpole-shaped pupil in a 20-year-old women with frequent episodes of blurred vision and achiness of the right eye lasting several minutes. The patient took a photograph of her eyes during an attack to document the peaked, segmental dilation of her right pupil (black arow). (Thompson HS, Zackon DH, ... | Adult; Female; Humans; Complications, Iris Diseases; Diagnosis, Iris Diseases; Physiopathology, Iris Diseases; Pupil; Complications, Spasm; Diagnosis, Spasm; Physiopathology, Spasm; Tadpole Pupil |
