The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 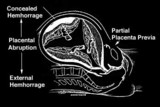 | Abruptio placenta | Abruptio placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 2 |  | Abruptio placenta - Gross | This large retroplacental blood clot is known as abruptio placenta. Such abnormal hemorrhage prior to delivery can lead to sudden onset of pain in the mother. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 3 |  | Abruptio Placenta - Microscopic | Microscopically, this abruptio placenta is seen to have extensive hemorrhage at thetop of the photograph at the decidual plate, with placental villi below. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 4 |  | Androgen insensitivity | Adapted with permission from Jaffe R.B. Disorders of Sexual Differentiation. In Yen SSC and Jaffe RB, eds, Reproductive Endocrinology, W.B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1986, p 300. An inability to respond to testosterone through a target organ receptor defect in 60-70% and a post-receptor signalling... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 5 | 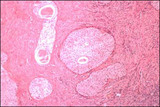 | Brenner tumor | Brenner tumors are comprised of solid to partly cystic epithelial nests surrounded by stroma composed of bundles of tightly packed spindle-shaped cells. The epithelial cells are polygonal and of squamoid type, with pale, eosinophilic cytoplasm and oval nuclei with distinct nucleoli and longitudinal ... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 6 | 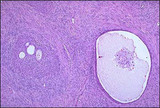 | Brenner tumor | Solid and partially cystic epithelial nests are surrounded by a stroma composed of bundles of tightly-packed spindle shaped cells. The epithelial cells are polygonal and of the squamoid type, with pale, eosinophilic cytoplasm and oval nuclei having distinct nuclei and longitudinal grooving, a coffee... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 7 |  | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia and clitoromegaly | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia and clitoromegaly | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 8 |  | Corpus luteum cyst | The corpus luteum secretes progesterone which induces a secretory endometrium. It normally regresses in 14 days unless it is rescued by increasing concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin from a pregnancy. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 9 | 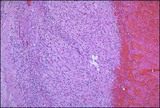 | Corpus luteum cysts exhibit a convoluted lining with luteinized granulosa and theca cells. | Corpus luteum of the ovary, medium power. The granulosa cells have undergone proliferation and alteration to lutein cells that produce progesterone. The lutein cells are large and polyhedral and the cytoplasm is foamy and eosinophilic. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 10 | 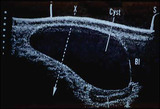 | Cystic ovarian mass | Ovarian cyst demonstrated by ultrasound. The ovarian cyst fills the abdominal cavity in this sagittal view and is seen overlying the uterus. The bladder is represented by Bl. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 11 | 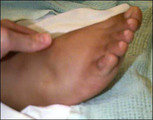 | Edema | PIH is characterized by hypertension, edema and proteinuria. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 12 |  | Endometrioma | Endometriosis. This is a section through an ovary to demonstrate several irregular hemorrhagic areas of endometriosis. Sometimes the blood is darker and gives the foci of endometriosis the gross appearance ofpowder burns. Typical locations for endometriosis include: ovaries, uterine ligaments, rect... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 13 |  | Epithelium of a follicular cyst | Low cuboidal cells are found in the lining of follicular cysts. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 14 | 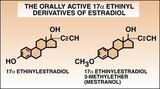 | Estradiol | The structure of ethinyl estradiol and mestranol. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 15 |  | Fibroid uterus | Smooth muscle tumors of the uterus. Smooth muscle tumors of the uterus are often multiple. Seen here are submucosal, intramural, and subserosal leiomyomata of the uterus. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 16 |  | Fibroma | This is the cut surface of a fibroma. Such neoplasms slowly enlarge over the years. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 17 |  | Follicular cyst | Benign ovarian cyst. Here is a benign cyst in an ovary. This is probably a follicular cyst. Occasionally such cysts may reach several centimeters in size and, if they rupture, can cause abdominal pain. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 18 | 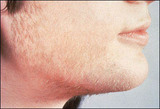 | Hirsutism | This woman has polycystic ovarian syndrome and hyperandrogenemia resulting in hirsutism. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 19 |  | Indications for intrauterine insemination | Indications for intrauterine insemination | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 20 | 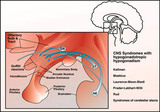 | Kallman's syndrome | In Kallman's Syndrome of the x linked variety a cell adhesion protein which participates in the migration of GnRH neurons from the medial olfactory bulb to the hypothalamus is absent. This protein is encoded by a gene on the short arm of the X chromosome. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 21 |  | Klinefelter's syndrome | Adapted with permission from Grumbach M.M. and Conte F.A.,Disorders of Sexual Differentation. In Williams R.H. ed, Textbook of Endocrinology, W. B.Squanders Co., Philadelphia, 1981, p 451. Males with an XXY karyotype characteristically have long extremities, aeunuchoidal habitus, and gynecomastia. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 22 | 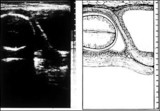 | Low lying posterior placenta | Low lying posterior placenta | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 23 |  | Mature cystic teratoma | Teratomas, often called dermoid tumors, represent 25% of all benign neoplasms. The most common elements are components of stratified squamous epithelium, hence their name: dermoid tumor. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 24 | 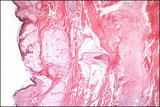 | Mature cystic teratoma - Microscopic | Ectodermal tissue is usually most abundant and represented by: squamous epithelium and appendages, brain tissue, glia, retina, choroid plexus, and ganglia. Mesodermal tissue is represented by bone and cartilage. Endodermal tissue is represented by gastrointestinal and bronchial epithelium and glands... | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 25 |  | Mature cystic teratoma-torsed with adenexal structures | Elements of all three germ layers are present: endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. They are classified as germ cell tumors and are thought to arise through parthenogenesis. They are found in the path of migration of the germ cells from the yolk sac to the primitive gonad. | Pathogenesis | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction |
