The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 2 & 3 - Pupillary Light Reflex | The swinging flashlight test is used to show a relative afferent pupillary defect or a Marcus Gunn pupil of the left eye. The left eye has perceived less light stimulus (a defect in the sensory or afferent pathway) then the opposite eye so the pupil dilates with the same light stimulus that caused c... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Marcus Gunn Pupil | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 102 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Heel-to-shin (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient with ataxia of the lower extremity will have difficulty placing the heel on the knee with a side-to-side irregular over- and undershooting as the heel is advanced down the shin. Dysmetria on heel-to-shin can be seen in midline ataxia syndromes as well as cerebellar hemisphere disease so ... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 103 |
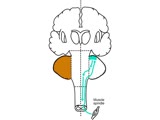 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 104 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Spinocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 2nd subdivision of the cerebellum is the spinocerebellum. This system consists of the connections between the cutaneous and proprioceptive information coming from the spinal cord to the vermis and paravermis regions with corrective feedback predominantly to the muscles of truncal stability and g... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Spinocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 105 |
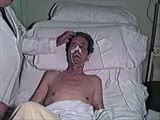 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Motor (x2) | The first patient has weakness of all the muscles of facial expression on the right side of the face indicating a lesion of the facial nucleus or the peripheral 7th nerve. The second patient has weakness of the lower half of his left face including the orbicularis oculi muscle but sparing the forehe... | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach | |
| 106 |
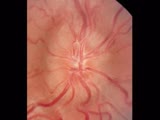 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Fundoscopy (x2) | The first photograph is of a fundus showing papilledema. The findings of papilledema include 1. Loss of venous pulsations 2. Swelling of the optic nerve head so there is loss of the disc margin 3. Venous engorgement 4. Disc hyperemia 5. Loss of the physiologic cup and 6. Flame shaped hemorrhages. Th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 107 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Normal Exam: Vergence | Vergence eye movements occur when the eyes move simultaneously inward (convergence) or outward (divergence) in order to maintain the image on the fovea that is close up or far away. Most often convergence is tested as part of the near triad. When a patient is asked to follow an object that is brough... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Vergence | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 108 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Motor | The first patient has weakness of all the muscles of facial expression on the right side of the face indicating a lesion of the facial nucleus or the peripheral 7th nerve. The second patient has weakness of the lower half of his left face including the orbicularis oculi muscle but sparing the forehe... | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach | |
| 109 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Heel-to-shin (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient with ataxia of the lower extremity will have difficulty placing the heel on the knee with a side-to-side irregular over- and undershooting as the heel is advanced down the shin. Dysmetria on heel-to-shin can be seen in midline ataxia syndromes as well as cerebellar hemisphere disease so ... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 110 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Finger-to-nose (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Under (hypometria) and over (hypermetria) shooting of a target (dysmetria) and the decomposition of movement (the breakdown of the movement into its parts with impaired timing and integration of muscle activity) are seen with appendicular ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 111 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Finger-to-nose (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient moves her pointer finger from her nose to the examiner's finger as the examiner moves his finger to new positions and tests accuracy at the furthest outreach of the arm. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Coordination Examination; Finger-to-nose Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 112 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 113 |
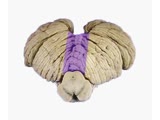 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 114 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Check Reflex (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Examiner pulls on actively flexed arm then suddenly releases. The patient should be able to check or stop the arm's movement when released. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of ... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 115 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 116 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 117 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 118 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Station | The patient should be able to stand still with her feet less then shoulder width apart. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Cent... | Gait Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 119 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Exam Tests (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The following tests of the neuro exam can be divided according to which system of the cerebellum is being examined: Vestibulocerebellum and spinocerebellum (midline): - Station - Walking - Tandem gait Cerebrocerebellum (appendicular): - Rapid alternating movements - Finger-to-nose - To... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 120 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 121 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Check Reflex (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is unable to stop flexion of the arm on sudden release so the arm may strike the chest and doesn't recoil to the initial position. This is most likely due to failure of timely triceps contraction. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at th... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 122 |
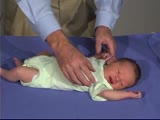 |
PediNeuroLogic Exam: Newborn: Normal: Tone - Arm Recoil (x2) | Arm recoil tests tone and action of the biceps. The arms are held in flexion against the chest for a few seconds, then are quickly extended and released. The arms should spring back to the flexed position. The hypotonic infant will have slow incomplete recoil. Asymmetry to this response with lack of... | PediNeuroLogic Exam | |
| 123 |
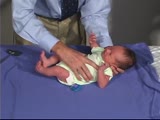 |
PediNeuroLogic Exam: Newborn: Normal: Primitive Reflexes - Galant | The Galant reflex (trunk incurvation) is obtained by placing the baby in ventral suspension, then stroking the skin on one side of the back. The baby's trunk and hips should swing towards the side of the stimulus. PediNeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developmen... | PediNeuroLogic Exam |
