The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing. Inability to perform repetitive movements in a rapid rhythmic fashion is called dysdiadochokinesia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics an... | Coordination Examination; Dysdiadochokinesia | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 27 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Natural Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Wide-based, unsteady, irregular steps with lateral veering| ataxia is most prominent when sudden changes are needed such as turning, standing up or stopping. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics ... | Coordination Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 28 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 29 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Finger tapping, wrist rotation and front-to-back hand patting. Watch for the rapidity and rhythmical performance of the movements noting any right-left disparity. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediat... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 30 |
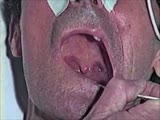 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 31 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Heel-to-shin (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient places her heel on the opposite knee then runs the heel down the shin to the ankle and back to the knee in a smooth coordinated fashion. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the O... | Coordination Examination; Heel-shin Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 32 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Versions (x2) | The first patient shown has incomplete abduction of her left eye from a 6th nerve palsy. The second patient has a left 3rd nerve palsy resulting in ptosis, dilated pupil, limited adduction, elevation, and depression of the left eye. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Lif... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 33 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 34 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 35 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 36 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Heel and Toe Walking | A good way to test balance as well as strength of the distal lower extremities is to have the patient heel and toe walk. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Un... | Gait Examination; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 37 |
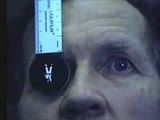 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Ductions | Each eye is examined with the other covered (this is called ductions). The patient is unable to adduct either the left or the right eye. If you watch closely you can see nystagmus upon abduction of each eye. When both eyes are tested together (testing versions) you can see the bilateral adduction de... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Ductions | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 38 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Introduction (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The principle area of the brain that is examined by the coordination exam is the cerebellum. The cerebellum is important for motor learning and timing of motor activity. It fine-tunes the force of agonist and antagonist muscle activity simultaneously and sequentially across multiple joints to produc... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 39 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 40 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Toe-to-finger (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Same as finger-to-nose except for the lower extremities. For both the upper and lower extremities, it is important to always compare right versus left. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and th... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 41 |
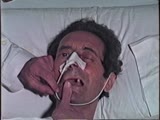 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Motor | The first patient shown has weakness of the pterygoids and the jaw deviates towards the side of the weakness. The second patient shown has a positive jaw jerk which indicates an upper motor lesion affecting the 5th cranial nerve. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. NeuroLogic Exam h... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 42 |
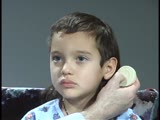 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 8 - Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests (x2) | This patient has decreased hearing acuity of the right ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the right ear and bone conduction is greater than air conduction on the right. He has a conductive hearing loss. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the Univ... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Weber Test; Rinne Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 43 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Versions | The first patient shown has incomplete abduction of her left eye from a 6th nerve palsy. The second patient has a left 3rd nerve palsy resulting in ptosis, dilated pupil, limited adduction, elevation, and depression of the left eye. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Lif... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 44 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 45 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 46 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 47 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Cerebrocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The 3rd subdivision of the cerebellum is the cerebrocerebellum. This system consists of connections from the cerebral cortex (predominantly motor) to the cerebellar hemispheres then back to the cerebral cortex. This system is important in motor planning. Dysfunction of the cerebellar hemispheres res... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 48 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Optokinetic Nystagmus (x2) | This patient has poor optokinetic nystagmus when the tape is moved to the right or left. The patient lacks the input from the parietal-occipital gaze centers to initiate smooth pursuit movements therefore her visual tracking of the objects on the tape is inconsistent and erratic. Patients who have a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 49 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements - Dysarthria (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Impaired speech articulation of cerebellar origin is characterized by being slow, indistinct, and scanning (scanning refers to decomposition of words into monosyllabic parts and loss of normal phrasing and intonation). NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 50 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Inspection & Ocular Alignment (x2) | This patient with ocular myasthenia gravis has bilateral ptosis, left greater then right. There is also ocular misalignment because of weakness of the eye muscles especially of the left eye. Note the reflection of the light source doesn't fall on the same location of each eyeball. NeuroLogic Exam ha... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
