The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 976 |
 |
Rosacea | Patients with rosacea often have eye involvement, which can consist of styes as shown here. Dr. Randy Olson at the University of Utah recommends treating these with intralesional injection of Kenalog 40 mg/cc. He points out it requires only 1 to 2 drops of this intralesionally, and the inflammatory ... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 977 |
 |
Keloid | Keloids can be injected with a Depo form of injectable steroid and/or silicone gel sheet. The corticosteroid reduces the production of all components of the keloid, which include ground substance, collagen, and elastin. The silicone gel is thought to act by increasing the temperature of the skin and... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 978 |
 |
Excision procedure | This demonstrates placement of the deep dermal suture that is secured to the underside of the dermis as far away from the wound edge as possible. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 979 |
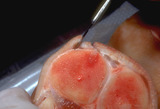 |
Scalpel | This shows the outward angle of the scalpel in a cross-sectional view. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 980 |
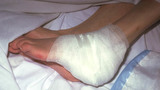 |
Wound dressing | This shows a bulky dressing applied on top of the non-adherent dressing to absorb the bleeding that will occur over the next hour or two after debridement. The wound should be gently cleansed once or twice daily with dilute Hibiclens (one part Hibiclens and three parts water), and then the Silvaden... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 981 |
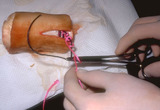 |
Suturing | The short arm of the suture is grasped. The throw is then tightened by pulling the hands back into their natural positions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 982 |
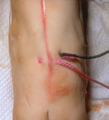 |
Suturing | This demonstrates the placement of the suture in a vertical mattress prior to tying. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 983 |
 |
Retin-A | During the first several weeks of use of Retin-A, some people experience a diffuse redness and scaling where it is applied, and acne lesions can become inflamed or more inflamed during that period of time. Simply reassure the patient that he/she should continue with the therapy and the inflammation ... | Retin-A; Drug Effects | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 984 |
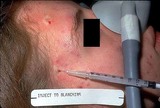 |
Kenalog | The solution should be injected directly into the lesion until there is slight blanching, which indicates saturation with the solution. You must warn the patient beforehand that there is some risk of atrophy of the skin and sometimes the underlying fat, and it can take 6 to 12 months for that to fil... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 985 |
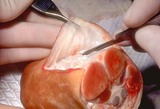 |
Excision procedure | Undermining on the opposite side of the wound. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 986 |
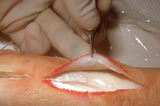 |
Suturing | The wound edges should pull together easily if wound has been properly undermined. The needle should be grasped two-thirds of the way from the point of the needle with the needle holders. This allows one to use a majority of the needle when suturing, but the needle is not grasped so far away from th... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 987 |
 |
Excision: suturing | The loops must be tightened by pulling and tightening along the long axis of the wound. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 988 |
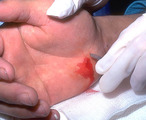 |
Puncture wounds | Puncture wounds often have to be enlarged in order to be explored. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 989 |
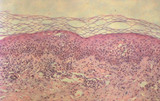 |
Dermatitis biopsy | This biopsy demonstrates basically what is happening within dermatitis. Lymphocytes (small purple dots) are attacking the epidermis (thick upper purple area), as well as the underlying dermis (fainter pink area at the base) and induce abnormal maturation of the epidermis (scaling), vasodilation (red... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 990 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | Stasis dermatitis (shown here) that is not oozing, is best treated with a support hose. The optimum ankle pressure is around 30 to 40 mm Hg, and generally a hose that comes to just below the knee is adequate. The hose should be worn at all times when the extremity is in the dependent position, such ... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 991 |
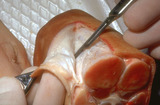 |
Excision procedure | Undermining is achieved by using scalpel or scissors to free the dermis from the fibrous septae that connect it to the underlying fascia. One undermines the wound until the wound edges pull together readily. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 992 |
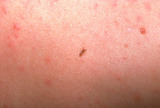 |
Body louse | This is a body louse on the same patient as shown in slide 78. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 993 |
 |
Keloid | Keloid. Keloids tend to form on areas where there is a significant amount of tension on the wound, and also in certain families, and in certain races, particularly those who are more darkly pigmented. A keloid is defined as scar tissue that extends beyond the boundaries of the original injury.(Summa... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 994 |
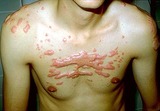 |
Keloids | Keloids. These are composed of excessive amounts of collagen, elastin, and ground substance. They occur generally on the upper chest and back, and also over areas of stretch such as the elbows and knees. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 995 |
 |
Excision: suturing | The non-dominant (left) hand crosses over the dominant (right) hand on the second throw. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 996 |
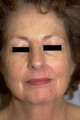 |
Periorificial dermatitis | Periorificial dermatitis. This eruption consists of erythema or sometimes discreet red papules with or without scale located on the eyelids, in a paranasal and paraoral distribution. In my experience, it most commonly occurs around the nose and mouth. The cause of this remains unknown, though it can... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 997 |
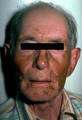 |
Vitiligo | This patient has vitiligo. The melanocytes within the epidermis are destroyed presumably by a lymphocytic cell-mediated process. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 998 |
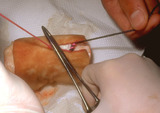 |
Suturing | The second throw is made by placing the needle holder in the inside of the long arm (needle bearing) of the V, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 999 |
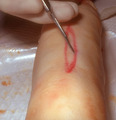 |
Scalpel | The other side of the ellipse is cut and the blade is angled outward. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1000 |
 |
Suturing | The needle holder is then placed on the inside of the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V, and a single loop is thrown around the needle holder. The short end of the suture is then grasped, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
