The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 801 |
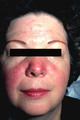 |
Rosacea | The typical appearance of a patient with rosacea. The patient usually has underlying erythema on the nose and cheeks, and generally has superimposed red papules and pustules on these areas. The first stage of rosacea consists of only erythema, and the second stage consists of the superimposed red pa... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 802 |
 |
Excision: suturing | A single loop is thrown around the needle holder. The short arm of the suture is then grasped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 803 |
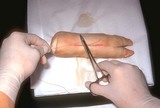 |
Suturing | This demonstrates a single loop of suture thrown around the needle holder. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 804 |
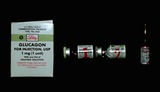 |
Epinephrine | If a patient is on beta-blockers and experiences severe urticaria or anaphylaxis, often epinephrine does not work. Glucagon can be used in lieu of epinephrine, and generally 1 mg (regardless of body size) is given in the subcutaneous fat | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 805 |
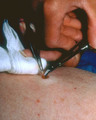 |
Punch biopsy | I gently lift the punch without pinching it and thereby creating damage to the specimen, and then snip the fatty strand that connects the skin to the underlying fat and muscle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 806 |
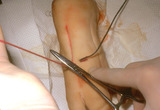 |
Suturing | With the needle holders placed inside the long arm (needle bearing end) of V, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 807 |
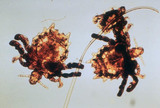 |
Pubic lice | Pubic lice. They are 1-2 mm diameter and are visible with the naked eye. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 808 |
 |
Head lice | On close inspection one could often see the adult lice as shown here. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 809 |
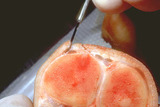 |
Excision procedure | This demonstrates the 45 degree angle in cross-section. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 810 |
 |
Pemphigus | This patient has pemphigus. In this disease, there are antibodies produced against components of the materials that hold the epidermal cells together, and the epidermis breaks apart within the mid-epidermal level. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 811 |
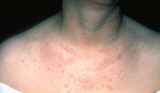 |
Seborrheic keratoses | One month after freezing seborrheic keratoses showing slight residual inflammation and postinflammatory hyperpigmentation. This generally resolves within several months after the procedure. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 812 |
 |
Micrograph of the base of hair follicle | An electron micrograph of the base of hair follicle. The epidermal papilla, shown at the bottom center, controls the growth rate of the hair follicle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 813 |
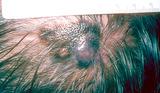 |
Melanoma | Melanoma in the scalp of a patient approximately 65-years-old. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 814 |
 |
Ingrown nail | This demonstrates local infiltration of the skin around the nail. It is crucial to inject slowly and to advance the needle slowly. I found local infiltration to be superior to a digital block. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 815 |
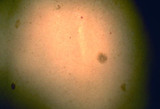 |
Capillary hemangiomas | The red papules are benign vascular growths called capillary hemangiomas. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 816 |
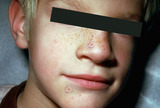 |
Spider telangiectasia | The red lesion on the nose is a spider telangiectasia. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 817 |
 |
Fleas | The flea. These have been shown to live up to 40 days without a blood meal. The major disease we see in the Intermountain West that is carried by fleas is plague, and this is actually seen very rarely. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 818 |
 |
Scalpel | This shows the scalpel, handle and blade. Note that the angle at the base of the blade, as well as the ankle at the attachment base of the scalpel handle should be the same. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 819 |
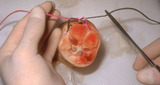 |
Suturing | The short and (non-needle bearing end) of the suture is then grasped with the needle holder, and the suture is pulled taut forming a double loop as shown here in cross-section. One cannot tighten the suture by pulling across the wound, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 820 |
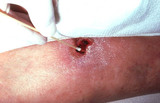 |
Wound culturing | If the tissue around the wound is red and tender suggesting infection, then the wound should be cultured. The best mode of culture of a long-standing wound is to actually biopsy tissue at the base of the wound and culture that tissue. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 821 |
 |
Body louse | Body louse. They are several mm long and therefore visible with the naked eye. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 822 |
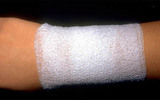 |
Cotton gauze | The topical antibiotic and non-adherent dressing are secured in place with tape or a cotton gauze wrap. The third principle of wound care is to ensure good nutrition, and the most important element of that would be to keep pressure off the wound, particularly if the patient is immobilized and can't ... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 823 |
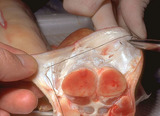 |
Suturing | This demonstrates in cross-sectional view the placement of the deep dermal suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 824 |
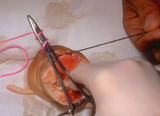 |
Suturing | The needle holder is placed on the inside of the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V, and the suture is wrapped twice around the needle holder. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 825 |
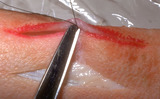 |
Suturing | This demonstrates cutting the deep dermal suture just above the knot. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
