The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 776 |
 |
Punch biopsy | Punch biopsy is excellent for sampling a skin disease that has multiple essentially identical lesions, or sampling a lesion within the skin. It is designed for full thickness skin biopsy, and is not an effective tool for biopsying the fat. When using it, it should be held as shown, should be spun ve... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 777 |
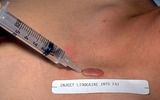 |
Keloid | Before injecting the keloid with the corticosteroid, I recommend injecting local anesthetic into the underlying fat, and waiting about five minutes for the anesthetic to take effect. The anesthetic should not be injected into the keloid as this reduces the amount of space into which one can inject t... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 778 |
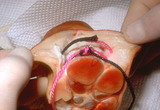 |
Suturing | This demonstrates the deep dermal suture properly placed with the loop, which will be just on the under-surface of the dermis, and the knot will be buried well within the fat. This will prevent the knot from extruding through the dermis and out through the wound. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 779 |
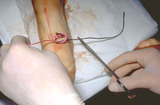 |
Suturing | The loop is then tightened with the hands in their natural position. This is done four times and then the suture is cut leaving suture ends at .5 cm long. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 780 |
 |
Tearing action | They are then opened which creates a tearing action. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 781 |
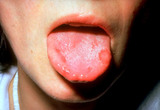 |
Aphthous stomatitis | Aphthous stomatitis (cankers) involving the tongue. Aphthous stomatitis ulcers are painful, and major aphthous stomatitis induces ulcers that last for many weeks, and sometimes induce scarring. | Canker Sore | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 782 |
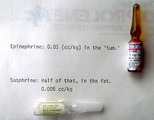 |
Epinephrine | Standard epinephrine (1:1,000) is shown at the top, and the crystalline form (Sus-Phrine) is a concentration of 1:200. Both are administered into the subcutaneous fat, and a dose of epinephrine 1:1,000 is 0.01 cc's per kg, and the dose of Sus-Phrine is half of that (0.005 cc's per kg), and the Sus-P... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 783 |
 |
Excision: suturing | AVis formed as the deep dermal suture exits from the wound, and the suture is pulled so that the short (non-needle bearing end) is about 2 cm long. Both strands of suture should come out on the same side of the loop, and the order must be: loop, short end (non-needle bearing), long end (needle bea... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 784 |
 |
Miliaria | Occlusion of the eccrine sweat glands produces a condition called miliaria; this appears as small red papules and/or vesicles, and associated inflammation. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 785 |
 |
Flea bites | Presumed flea bites. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 786 |
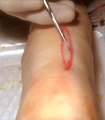 |
Excision procedure | The following slides are a brief review of the excision procedure. The scalpel is angled outward away from the wound edge to ensure that the wound edges are beveled at about 45 o. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 787 |
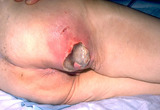 |
Decubitus ulcer | A decubitus ulcer in an older woman in a nursing home. This was induced because the person was lying in one position for too long, and this compromised blood supply to the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 788 |
 |
Forceps | The forceps are held with the non-dominant hand as shown here between the first two or three fingers. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 789 |
 |
Urticaria | Urticaria | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 790 |
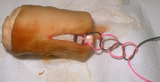 |
Suturing | This demonstrates that a total of four throws should be made when tying the deep dermal suture, and if done properly, square knots are laid down. It is said that square knots provide optimum knot security. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 791 |
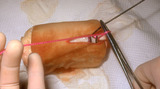 |
Suturing | The short arm of the suture is then grasped with the needle holder, and then the non-dominant (left) hand crosses over the right hand as one tightens the knot pulling along the long axis of the wound. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 792 |
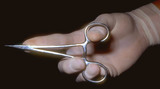 |
Needle holder | The needle holder (sometimes called needle driver) can be held as shown, or | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 793 |
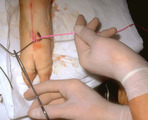 |
Excision procedure | This suture is tightened by crossing the non-dominant (left) and over the dominant (right) hand. This same sequence is continued until four loops have been thrown and then the suture is cut leaving ends approximately .5 cm long. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 794 |
 |
Skin tags | Skin tags. They are rather small, and have a pedunculated base giving them the appearance of a teardrop. | Skin Tags | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 795 |
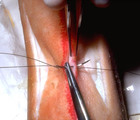 |
Suturing | I exit through the other side of the wound as superficially and closely as possible to the wound edge. Generally, I am about a mm away from the wound edge, and just barely entering the dermis. It is crucial to be as superficial within the dermis and as close to the wound edge on the second pass as i... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 796 |
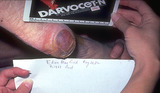 |
Necrosis | The purple/red area on the heel is an area of necrosis of the entire epidermis and dermis that is induced by the person lying in one position for too long. Again, the entire epidermis and dermis are necrotic, and need to be surgically removed. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 797 |
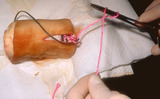 |
Excision: suturing | The needle holder is then placed inside the long arm of the V, and a single loop is thrown around the needle holder. The short arm of the suture is then grasped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 798 |
 |
Excision procedure | The central specimen is then removed ensuring that there is same thickness throughout the specimen. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 799 |
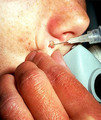 |
Shave technique | This demonstrates the shave technique. Local anesthetic can be injected into the fat beneath the target lesion, or within the lesion itself. One should be extremely careful to inject as little anesthetic as necessary to anesthetize the skin, because the anesthetic will artifactually enlarge and dist... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 800 |
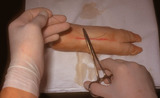 |
Suturing | This demonstrates placing the needle holder on the inside of the long arm of the V using actual suture. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
