The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal" Subject: "Kidney"
1 - 25 of 12
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Kidney, normal, unfixed | Kidney, normal, unfixed. External surface. Photograph. Multimedia. | Kidney; Urogenital system; Anatomy | Slice of Life |
| 2 |
 |
Diabetes, kimmelstiel-wilson glomerulosclerosis | Diabetes, kimmelstiel-wilson glomerulosclerosis | Kidney; Diabetic Nephropathies | Slice of Life |
| 3 |
 |
Kidney | In this section through the renal papilla, identify the terminal collecting tubules (lined by columnar epithelium). Also note a straight segment of the loop of Henle, many thin loops of Henle, and cross-sections of the vasa recta. UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; renal papilla; terminal collecting tubules | UCLA Histology |
| 4 |
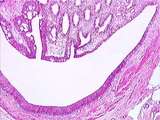 |
Kidney | The renal papilla is the site where terminal collecting ducts empty urine into the U-shaped minor calyx. The lumen of the minor calyx is lined by transitional epithelium. Strands of circular smooth muscle are found in the wall of the minor calyx. UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; minor calyx; renal papilla; terminal collecting ducts | UCLA Histology |
| 5 |
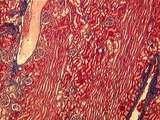 |
Kidney | In this trichrome stained section of the renal cortex there are sections of an interlobular artery and interlobular vein. Also identify the long medullary rays and several renal corpuscles. UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; medullary rays; trichrome | UCLA Histology |
| 6 |
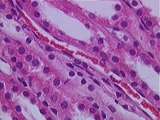 |
Kidney | Present here in the kidney medulla are sections of straight distal tubules (low cuboidal walls), straight proximal tubules (tall cuboidal walls), and vasa recta (lined by endothelium). UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; medulla; straight distal tubules; straight proximal tubules; vasa recta | UCLA Histology |
| 7 |
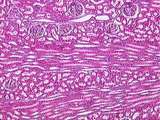 |
Kidney | This section can be identified as renal cortex because of the presence of renal corpuscles and medullary rays. Sections of an interlobular artery are also present. UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; renal corpuscles; renal cortex | UCLA Histology |
| 8 |
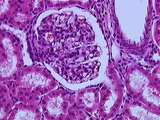 |
Kidney | A number of features of the renal corpuscle can be seen here. The parietal and visceral layers of Bowman's capsule, which consist of two types of simple squamous epithelium, line the capsular space. The filtrate leaves the glomerulus via the urinary pole, which leads to a proximal convoluted tubule ... | Bowman's capsule; Kidney; renal corpuscle; renal cortex | UCLA Histology |
| 9 |
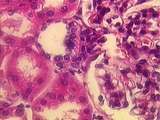 |
Kidney | At the vascular pole of this renal corpuscle can be seen cross-sections of the afferent and efferent arterioles. A well-defined macula densa is present in the wall of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT), adjacent to the afferent arteriole. There are also a number of cross-sections of proximal convolu... | Kidney; Renal Corpuscle | UCLA Histology |
| 10 |
 |
Kidney | In this image we see the glomerulus of a renal corpuscle, surrounded by dark red proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) and lighter stained distal convoluted tubules (DCT). The basement membranes of the parietal wall of Bowman's capsule and surrounding tubules are stained blue. UCLA Histology Collection. | glomerulus; Kidney; trichrome | UCLA Histology |
| 11 |
 |
Kidney | In this higher power view of the above image, the wall of the minor calyx can be seen to consist of transitional epithelium. The bands of smooth muscle and connective tissue of the wall of the calyx can be seen clearly. UCLA Histology Collection. | Kidney; Minor Calyces; Minor Calyx | UCLA Histology |
| 12 |
 |
Kidney | A number of features are seen in this glomerulus. Identify the simple squamous epithelium of the parietal layer of the renal corpuscle. Also note the dark podocyte nuclei of the visceral layer which wrap around the many glomerular capillaries. UCLA Histology Collection. | glomerulus; Kidney; renal corpuscle | UCLA Histology |
1 - 25 of 12
