John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Exophthalmometry | Demonstration of exophthalmometry examination. | Text |
| 52 |
 |
Facial Myokymia Unilateral | Example of patient with facial myokymia, a disorder of the seventh nerve, probably due to brain stem involvement. Patient has multiple sclerosis. Discussion of characteristics, such as continuous, undulating, contractions in the distribution of the seventh nerve, and a spreading of these movements t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Facial Nerve Exam | Explanation of a facial nerve exam. | Image/MovingImage |
| 54 |
 |
Flutter in Downgaze | Examination of patient with flutter in downgaze (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 55 |
 |
Fourth Nerve Palsy | Demonstration of examination of patient who experienced blurry vision and pain in the left eye. Demonstrates checking of eye movements, focusing on object while each eye is covered and uncovered, turning head both ways and repeating. Shows limitation of depression in adduction of left eye, left hype... | Image/MovingImage |
| 56 |
 |
Fusional Vergence Amplitudes | Demonstration of fusional vergence amplitudes examination. Incluudes: a. Convergence Amplitudes b. Divergence Amplitudes c. Vertical Ampitudes | Text |
| 57 |
 |
Gaze Palsy with Facial Weakness from Pontine AVM | Example of a patient with torsional nystagmus in both eyes and pendular nystagmus in the left eye. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 58 |
 |
Hemifacial Spasm | Example of patients with hemifacial spasm. First patient has a sequela of Bell's palsy, and is seen to have mainly clonic movements around the eye, with occasional tonic movements around the mouth. Second patient has a cerebellopontine angle epidurmoid tumor, and is seen to have movements around the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
 |
How to Measure the RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination technique for measuring the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD). Demonstration of balancing an afferent papillary defect using filters in a patient with a resolving optic neuritis and an afferent papillary defect on the left. | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
 |
How to Use the Direct Ophthalmoscope in an Exam | Demonstration of using the direct ophthalmoscope to examine the optic disc. Covers hand placement , which eye to use, and distance from patient. | Image/MovingImage |
| 61 |
 |
Intermittent Square Wave Jerks | Patient with intermittent square wave jerks (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 62 |
 |
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia (2 Examples) | Two examples of patients with internuclear ophthalmoplegia. First patient has a right internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient had subacute bacterial endocarditis with a bacterial abscess in the brain stem. Ductions and gaze to the right look good, but when gazing to the left, the right eye does not ad... | Image/MovingImage |
| 63 |
 |
Introduction to Fogging Refraction | An introduction to fogging refraction. | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Introduction to Headache, Migraine and Secondary Headaches | Video lecture covering an introduction to headache, migraine, and secondary headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
 |
Introduction to the Basic Neurologic Exam | Introduction to the neurological examinations section of NExT. | Image/MovingImage |
| 66 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus | Example of a patient with latent nystagmus. Demonstrates a lack of oscillations in forward gaze, followed by the occlusion of each eye, showing how this generates a jerking oscillation in the non-occluded eye away from the occluded eye. | Image/MovingImage |
| 67 |
 |
Levator Disinsertion | Example of patient with levator disinsertion, a lid disorder. Patient is pregnant and wears poorly fitting contacts. Discussion of characteristics, such as lid ptosis (shown in the left eye of patient), but with full levator function. | Image/MovingImage |
| 68 |
 |
Light-near Dissociation | Example of patient with Argyll Robertson pupil with neurosyphilis. Shows a lack of pupillary response to light and some pupillary response to nearness of finger. | Image/MovingImage |
| 69 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Example of patient with Marcus Jaw Winking. Patient is led through instructions for movement of jaw (open, close, back and forth), with eyelid seen to be affected. Patient is then led through instructions for direction of gaze and pursuit. | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Measuring Visual Acuity | Demonstration on self of visual acuity exam, using a standard card. | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
Migraine and Cluster Pathophysiology and Treatment | Video lecture covering pathophysiology and treatment of migraine and cluster headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | Image/MovingImage |
| 72 |
 |
Monocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with monocular pendular nystagmus, with discussion of situations in which this condition is seen: acquired disorder of the visual-sensory pathway, and acquired disorder of the brain stem (e.g. multiple sclerosis). | Image/MovingImage |
| 73 |
 |
Multifocal Electroretinograms | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
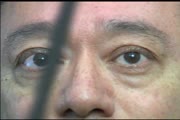 |
Normal Eye Movements | This is an examination of a person with normal eye movements. Notice the patient has normal excursions. He has normal pursuit and saccades (horizontally and vertically). | Text |
| 75 |
 |
Normal Light Reflex without RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination of the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD.) Demonstration of gauging the size of the pupil in light, testing light reflexes, swinging flashlight test for optic nerve abnormality. | Image/MovingImage |
