The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1176 |
 |
Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) | LAFB is the most common of the intraventricular conduction defects. It is recognized by 1) left axis deviation; 2) rS complexes in II, III, aVF; and 3) small q in I and/or aVL. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1177 |
 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction: lead V1 | The arrows point to two flutter waves for each QRS complex. Atrial rate = 280; ventricular rate = 140. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1178 |
 |
Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1179 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1180 |
 |
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm | Note the small pacemaker spikes before the QRS complexes in many of the leads. In addition, the QRS complex in V1 exhibits ventricular ectopic morphology; i.e., there is a slur or notch at the beginning of the S wave, and>60ms delay from onset to QRS to nadir of S wave. This rules against a suprav... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1181 |
 |
Diffuse anterolateral T wave abnormalities | Diffuse anterolateral T wave abnormalities | T Wave Abnormalities | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 1182 |
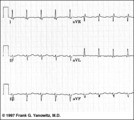 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1183 |
 |
Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1184 |
 |
Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1185 |
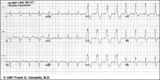 |
RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1186 |
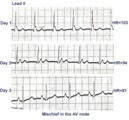 |
ECG of the century: A most unusual 1st degree AV block | On Day 1, at a heart rate of 103 bpm the P waves are not clearly defined suggesting an accelerated junctional rhythm. However, on Day 2, at a slightly slower heart rate the sinus P wave suddenly appears immediately after the QRS complex. In retrospect, the sinus P wave in Day 1 was found burried i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1187 |
 |
RBBB plus mobitz II 2nd degree AV block | The classic rSR' in V1 is RBBB. Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block is present because the PR intervals are constant. Statistically speaking, the location of the 2nd degree AV block is in the left bundle branch rather than in the AV junction. The last QRS in the top strip is a junctional escape, since... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1188 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -60 degrees | Lead aVR is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly negative. The QRS axis, therefore, is -60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1189 |
 |
QRS axis = +30 degrees | Lead III is isoelectric; leads I and II are positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +30 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1190 |
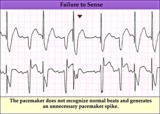 |
Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1191 |
 |
Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1192 |
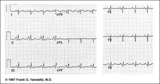 |
RAE & RVH | RAE & RVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1193 |
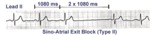 |
Type II, 2nd degree sino-atrial block | Two types of 2nd degree SA block have been described. In type-I, or SA Wenckebach, the P-P interval of the pause is less than 2x the preceding P-P intervals. In type-II SA block the P-P interval of the pause is approximately 2x the normal P-P interval. The distinction between types I and II is no... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1194 |
 |
Bradycardia-dependent LBBB with carotid sinus massage | When carotid sinus massage slows the heart rate in this example, the QRS widens into a LBBB. This form of rate-dependent bundle branch block is thought to be due to latent pacemakers in the bundle undergoing phase 4 depolarization; when the sinus impulse enters the partially depolarized bundle, slow... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1195 |
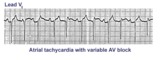 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 AV block | In this rhythm the atrial rate from an ectopic focus is 160 bpm. Atrial activity can be seen on top of T waves, and before QRS's. Careful observation reveals a 3:2 Wenckebach relationship between P waves and QRS's. Atrial tachycardia with block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1196 |
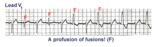 |
Ventricular fusion beats | Fusion beats occur when two or more activation fronts contribute to the electrical event. These may occur in the atria or in the ventricles. In this example the ventricular fusions are the result of simultaneous activation of the ventricles from two foci, the sinus node and a ventricular ectopic... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1197 |
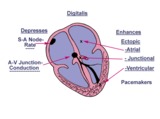 |
Diagram: digitalis effect on rhythm and conduction | Diagram: digitalis effect on rhythm and conduction | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1198 |
 |
Calibration signal - marquette | Calibration signal - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1199 |
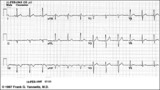 |
Old inferior MI | Old inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1200 |
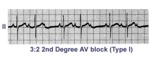 |
Second degree AV block, type I, with 3:2 conduction ratio | There are two types of 2nd degree AV Block. In this example of Type I or Wenckebach AV block there are 3 P waves for every 2 QRSs; the PR interval increases until a P wave fails to conduct. This is an example of group beating. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
