The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1076 |
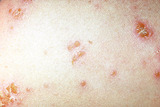 |
Nummular dermatitis | Lesions of acute (red and oozing) nummular dermatitis on the trunk. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1077 |
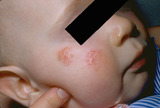 |
Atopic dermatitis in children | Atopic dermatitis often involves the cheeks of children. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1078 |
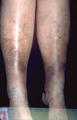 |
Incompetent venous system of the legs | The next step in damage to the skin from an incompetent venous system of the legs is lipo dermatosclerosis. In this condition, there is an increased amount of fibrous tissue both within the dermis and the underlying fat. The extremities appear tense and shiny, and they feel woody and hard to the tou... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1079 |
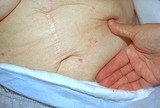 |
Scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution | Same nursing home patient with scabies with inflamed lesions in a paraumbilical distribution. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1080 |
 |
Milium extraction | The appearance after extraction of the milium. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1081 |
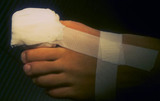 |
Ingrown nail | After cleaning the blood from the toe with hydrogen peroxide and removing the tourniquet, I apply a bulky dressing to absorb the blood, as it may bleed for up to about an hour if the foot is dependent. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1082 |
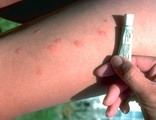 |
Insect Bites | Itchy insect bites can be treated with a topical steroid; I prefer to use an ultra-potent topical steroid, such as Temovate, twice daily to the inflamed lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1083 |
 |
Undermining with scalpel | This demonstrates undermining of the dermis using a scalpel. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1084 |
 |
Scabies with flexural wrist involvement | Same patient with flexural wrist involvement. In this scenario, not only should the patient be treated, but all family members who have had skin-to-skin contact with the patient, as well as nursing personnel and housekeeping personnel who have had contact with the patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1085 |
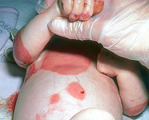 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | A baby with recessive epidermolysis bullosa. This patient links adequate numbers of anchoring fibrils (collagen type 7) to attach epidermis to the underlying dermis. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1086 |
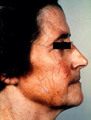 |
Atrophy of facial skin | Atrophy of facial skin induced by overuse of topical steroids to facial skin. The vessels of the deeper dermis and fat can be seen through the thin epidermis/dermis. Upon cessation of use of the steroids, the skin should regain its normal thickness, but it takes months to years for that to occur in ... | Adverse Effects | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1087 |
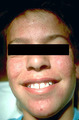 |
Acne surgery | The person appears blotchy immediately after acne surgery, and it takes one to two days for that to resolve. I always ask the patient about upcoming social events or photo sessions over the next several days before initiating acne surgery. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1088 |
 |
Atopic dermatitis involving the neck | Atopic dermatitis involving the neck. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1089 |
 |
Anaphylactic shock | During anaphylactic shock, blood pressure should be monitored regularly. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1090 |
 |
Acute stasis dermatitis | Acute stasis dermatitis, manifested as redness and oozing. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1091 |
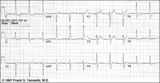 |
LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1092 |
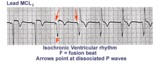 |
Isochronic ventricular rhythm | An isochronic ventricular rhythm is also called an accelerated ventricular rhythm because it represents an active ventricular focus. This arrhythmia is a common reperfusion arrhythmia in acute MI patients. It often begins and ends with fusion beats and there is AV dissociation. Treatment is usuall... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1093 |
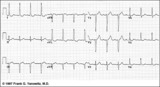 |
LVH: limb lead criteria | In this example of LVH, the precordial leads don't meet the usual voltage criteria or exhibit significant ST segment abnormalities. The frontal plane leads, however, show voltage criteria for LVH and significant ST segment depression in leads with tall R waves. The voltage criteria include 1) R in... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1094 |
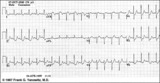 |
ST segment depression | ST segment depression is a nonspecific abnormality that must be evaluated in the clinical context in which it occurs. In a patient with angina pectoris ST depression usually means subendocardial ischemia and, unlike ST elevation, is not localizing to a particular coronary artery lesion. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1095 |
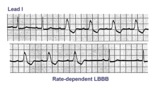 |
Rate-dependent LBBB | In this rhythm strip of sinus arrhythmia, the faster rates have a LBBB morphology. In some patients with a diseased left bundle branch, the onset of LBBB usually occurs initially as a rate-dependent block; i.e., the left bundle fails to conduct at the faster rate because of prolonged refractoriness... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1096 |
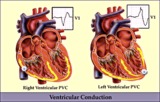 |
RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1097 |
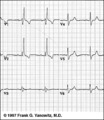 |
RBBB: Precordial leads | RBBB: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1098 |
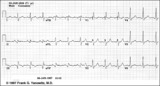 |
Inferior MI and RBBB | Inferior MI and RBBB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1099 |
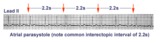 |
Atrial parasystole | Parasystolic rhythms involve an independent ectopic pacemaker resulting in nonfixed coupled premature beats. Parasystole may occur in the atria, as seen in this example, in the AV junction, and in the ventricles. Note the common inter-ectopic interval separating the parasystolic PAC's. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 1100 |
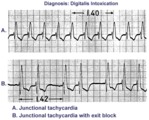 |
Digitalis intoxication: junctional tachycardia with and without exit block | In A the rhythm is junctional tachycardia with RBBB. In B there is 2nd degree exit block with a 3:2 conduction ratio; i.e., every 3rd junctional impulse fails to reach the ventricles... at least for the first two groupings on 1.4sec. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
