The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1051 |
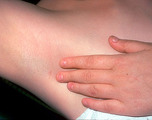 |
Ectodermal dysplasia | Ectodermal dysplasia in the axillae. The patient also had abnormal nail plates and teeth. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1052 |
 |
Undermining with scissors | This demonstrates undermining with scissors. The closed jaws are inserted beneath the dermis, and | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1053 |
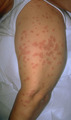 |
Thickness biopsy | When a patient has an eruption and the diagnosis is unknown, it is best to do a full thickness biopsy by doing a punch or small excision of one of the lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1054 |
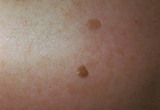 |
Seborrheic keratoses | Seborrheic keratoses. They are a benign thickening and darkening of the epidermis with varying amounts of loose adherent scale. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1055 |
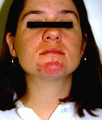 |
Papulopustular eruption | Close-up view of the papulopustular eruption on this pregnant patient. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1056 |
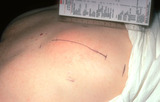 |
Layered closure | Large lesions can be removed using the layered closure. This was a large lipoma on the back of a patient, and I removed this in my office. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1057 |
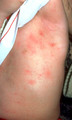 |
Children with scabies | Children who have scabies generally have inflammatory lesions in the axillae. This shows typical axillary lesions. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1058 |
 |
Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris | Pregnant patient with papulopustular flare of acne vulgaris. To our knowledge, oral erythromycin or ampicillin or amoxicillin can be used safely, and topical erythromycin, clindamycin, or benzoyl peroxide also appear to be safe. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1059 |
 |
Skin Tumor | Tumors of various sorts can be produced by anything that grows within the dermis.This demonstrates that the tumor was within the skin, and moves freely with the skin. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1060 |
 |
Treatment of comedonal acne | When a patient has comedos along with less than about 15 red papules and pustules, one can use the regimen shown either on the patient's left or the patient's right. The method I usually use is shown on the patient's right: The patient is to apply benzoyl peroxide 2.5% gel to the face q am, and Reti... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1061 |
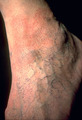 |
Venous pressure | With increased venous pressure induced by incompetent valves within the venous system of the leg, there is extravasation of fluid from the capillaries into the surrounding tissue. This separates the capillaries from the cells to which they supply nutrition, and those cells are damaged or even die. T... | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1062 |
 |
Ingrown nail | Appearance of ingrown nail. The nail plate is dystrophic, and in this case has induced significant foreign body reaction and secondary infection. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1063 |
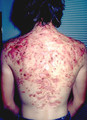 |
Severe nodulocystic acne | This is the back of the same patient shown in Slide 16, and the nodules, cysts, and scarring are evident. This is both painful and disfiguring, and can have a profound detrimental psychological effect on the person who suffers this. Thankfully, we do have effective therapy now for it. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1064 |
 |
Children with scabies | Child with scabies showing pruritic red papules around the ankle. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1065 |
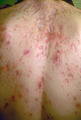 |
Severe acne vulgaris | Severe acne vulgaris involving the back. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1066 |
 |
Exaggerated insect bite reaction | Exaggerated insect bite reaction. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1067 |
 |
Excision: suturing | The second throw is initiated by placing the needle holder on the inside the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1068 |
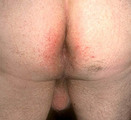 |
Atopic dermatitis involving the perianal area | Atopic dermatitis involving the perianal area. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1069 |
 |
Freezing with liquid nitrogen | Freezing is done to mainly destroy epidermal growths. As long as the indicated freezing times are followed, generally there is no scarring. Occasionally the dermis is injured as shown here, and hypertrophic or keloid scars can be formed, especially on areas of tension, such as the elbow. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1070 |
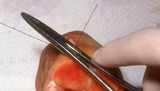 |
Excision: knot tying | The needle holder is placed on the inside the long arm (needle bearing end) of the V as shown. Before beginning to tie the knot, insure that the two ends of the suture come out the same side of the loop, and that the order is: loop, short (non-needle bearing) end, long (needle bearing) end. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1071 |
 |
Recessive epidermolysis bullosa | This child has recessive epidermolysis bullosa. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1072 |
 |
Treatment for rosacea | Typical treatment for rosacea is to take 500 mg of tetracycline in the morning, and . . . | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1073 |
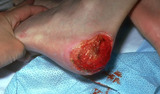 |
Normal fat at the base of a debrided wound of the heel | This shows normal fat, but note is bleeding freely. I found when debriding a wound it is best to give an oral or injected analgesic before debridement, and when the patient is quite relaxed I then infuse the area to be debrided with a mixture of lidocaine and bupivacaine with epinephrine. | Surgical Methods | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
| 1074 |
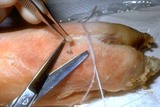 |
Punch biopsy | The plug should be gently lifted with forceps, and the fatty strand at the base should be snipped. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology | |
| 1075 |
 |
Stasis dermatitis | The area should be first cleansed with sterile saline or soap and water. | Knowledge Weavers Dermatology |
