The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 251 |
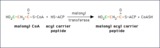 |
Transfer of a malonyl group to the acyl carrier peptide | During fatty acid synthesis the incoming two carbon fragment is introduced as the three-carbon malonyl group. It is added to the -SH group of the acyl carier peptide domain of fatty acid synthase. In a subsequent reaction the carbon shown in green will be lost as bicarbonate ion. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 252 |
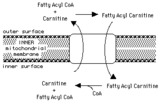 |
Transport of fatty acyl CoA into mitochondria by the carnitine shuttle | Fatty acyl CoA cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane, so it is carried in the form of fatty acyl carnitine. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 253 |
 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA lyase reaction | In this mitochondrial process hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA is converted to acetoacetate, a ketone body. Acetyl CoA is another product. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 254 |
 |
Acetyl CoA metabolism -- overview | Major metabolic sources of acetyl CoA and some of the processes in which it serves as a substrate. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 255 |
 |
Oleic acid structure | Oleic acid is a typical monounsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 256 |
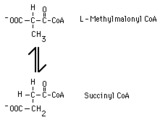 |
methylmalonyl CoA mutase reaction | In the metabolism of propionyl CoA L-methylmalonyl CoA is converted to succinate by methylmalonyl CoA mutase. Succinate can then be metabolized throgh the tricarboxylic acid cycle. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 257 |
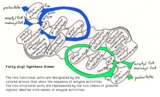 |
Mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer | This schematic diagram is intended to show the sequence of enzyme activities in the two subunits of a mammalian fatty acyl synthase dimer. It is not intended to imply anything about the detailed spatial relationships of the activities. | Coenzyme A Synthetases | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 258 |
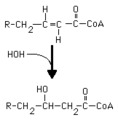 |
Hydration of an enoyl CoA | Hydration of the double bond is catalyzed by enoyl CoA hydratase. The product is an L-3-hydroxyacyl CoA. This reaction is a step in the beta-oxidation of fatty acids. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 259 |
 |
Acetyl CoA structure | Acetyl CoA Structure. The thioester bond linking the acetyl group to CoA is ahigh energybond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 260 |
 |
Use of greek letters to designate carbons in fatty acids | The carbon next to the -COOH group is the alpha carbon; the next one is the beta carbon, and so forth. The carbon most distant from the -COOH group is designated omega. Carbons close to the omega carbon may be designated in relation to it. E.g., the third carbon from the end is omega - 3, and the... | Nomenclature | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 261 |
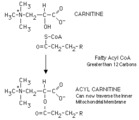 |
Acylation of carnitine by a long chain fatty acyl CoA | Long chain fatty acyl CoA cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane to participate in beta-oxidation. The fatty acyl group is therefore transferred to a carrier, carnitine, in a reversible reaction catalyzed by carnitine acyl transferase I. The resulting fatty acyl carnitine crosses the membra... | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 262 |
 |
Four systems for denoting fatty acids | There are four commonly used ways of designating fatty acids. The first two columns show samples of names, and the last two columns show systems of abbreviating these names. | Nomenclature | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 263 |
 |
Reduction of 2-enoyl acyl carrier peptide | A 2-enoyl acyl group on the acyl carrier peptide is reduced by NADPH in a reaction catalyzed by enoyl acyl carrier peptide reductase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 264 |
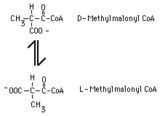 |
methylmalonyl CoA racemase reaction | In the metabolism of propionyl CoA, D-methylmalonyl CoA is produced by a carboxylase reaction. This product must be converted to L-methylmalonyl CoA in order to be metabolized further. The conversion is catalyzed by methylmalonyl CoA racemase. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 265 |
 |
Oxidation of a polyunsaturated fatty acid -- part I | The cycles of beta-oxidation prior to the one involving the original Delta-12 double bond act to get past the Delta-9 double bond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 266 |
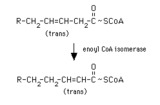 |
enoyl CoA isomerase reaction | Enoyl CoA isomerase converts a trans-3-enoyl CoA to a trans-2-enoyl CoA. Thus a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA or the product of the 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase reaction can proceed through beta-oxidation. | Enoyl CoA Isomerase Reaction | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 267 |
 |
Structures of the ketone bodies | These are the structures of the ketone bodies. Acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are important physiological substrates. Acetone is a byproduct, and is not metabolized further. It is excreted in the urine and in expired air. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 268 |
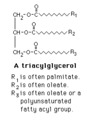 |
Triacylglycerol structure | The structure of a typical triacylglycerol (triglyceride). | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 269 |
 |
Dehydrogenation of fatty acyl CoA | Fatty acyl CoA is dehydrogenated by FAD in a reaction catalyzed by one of the acyl CoA dehydrogenases. Note that the dehydrogenation occurs between the alpha- and beta-carbons. | FAD | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 270 |
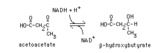 |
Reduction of acetoacetate | Acetoacetate is reduced by NADH in a reversible reaction catalyzed by beta-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. This reaction is the source of beta-hydroxybutyrate in the blood of individuals with ketosis. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 271 |
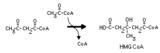 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA synthase reaction | This irreversible reaction occurs in the mitochondria, where it is the first step in ketone body synthesis. It also occurs in the cytoplasm, where it leads to isoprenoid and steroid synthesis. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 272 |
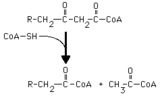 |
Thiolase reaction | Thiolase (3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase) cleaves a long chain fatty acyl CoA, forming acetyl CoA and a long chain fatty acyl CoA that is two carbons shorter. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 273 |
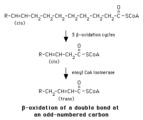 |
Beta-oxidation of a delta-9 fatty acyl CoA | Enoyl CoA isomerase is required to move the double bond in a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA to a position where it can continue in beta-oxidation. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 274 |
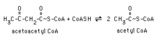 |
Thiolase reaction with acetoacetyl CoA | Thiolase (3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase) cleaves acetoacetyl CoA, forming two molecules of acetyl CoA. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 275 |
 |
Stearic acid structure | Stearic acid is a typical long chain saturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
