John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
 |
Introduction to the Basic Neurologic Exam | Introduction to the neurological examinations section of NExT. | Image/MovingImage |
| 127 |
 |
Latent Nystagmus | Example of a patient with latent nystagmus. Demonstrates a lack of oscillations in forward gaze, followed by the occlusion of each eye, showing how this generates a jerking oscillation in the non-occluded eye away from the occluded eye. | Image/MovingImage |
| 128 |
 |
Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy | Images and visual fields from a boy with acute visual loss. | Text |
| 129 |
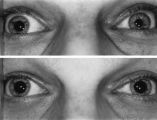 |
Left-sided Dilation Lag in a Man with Horner's Syndrome | Left-sided dilation lag in a 29-year-old man with Horner's syndrome caused by a posterior mediastinal ganglioneuroma. Note that the degree of anisocoria is greater after 5 seconds in darkness (top) compared with findings after 15 seconds in darkness (bottom). | Image |
| 130 |
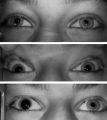 |
Left-sided Horner's Syndrome with an Acquired Preganglionic Localization | Left-sided Horner's syndrome in a 12-year-old girl with an acquired preganglionic localization based on clinical and pharmacologic testing. The cause remained undetermined after extensive radiologic investigations. Left-sided ptosis and miosis are evident in room light (top), and the degree of aniso... | Image |
| 131 |
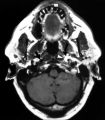 |
Left-sided Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Left-sided internal carotid artery dissection identified on T-1 weighted magnetic resonance image from a 52-year-old man who suddenly developed left-sided neck and orbital pain along with a droopy left upper eyelid while dragging a deer out of the woods during hunting season. The normal dark flow vo... | Image |
| 132 |
 |
Levator Disinsertion | Example of patient with levator disinsertion, a lid disorder. Patient is pregnant and wears poorly fitting contacts. Discussion of characteristics, such as lid ptosis (shown in the left eye of patient), but with full levator function. | Image/MovingImage |
| 133 |
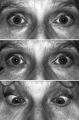 |
Light-near Dissociation | Light-near dissociation in a 51-year-old woman with multiple sclerosis who experienced double vision for 1 week. Her pupils are 5 mm in diameter in room light (top), react poorly in response to direct light reaction (middle), but constrict promptly in response to near stimulation (bottom). She also ... | Image |
| 134 |
 |
Light-near Dissociation | Example of patient with Argyll Robertson pupil with neurosyphilis. Shows a lack of pupillary response to light and some pupillary response to nearness of finger. | Image/MovingImage |
| 135 |
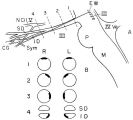 |
Location of Pupillomotor Fibers | Location of pupillomotor fibers are depicted as dark regions on cross-sections of the right (R) and left (L) oculomotor nerve at various locations along its course, including its emergence from the brain stem in the interpeduncular fossa (1), the midsubarachnoid segment (2), the level of the dorsum ... | Image |
| 136 |
 |
Macula | Overview of the structure and viewing of the macula. | Text |
| 137 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Example of patient with Marcus Jaw Winking. Patient is led through instructions for movement of jaw (open, close, back and forth), with eyelid seen to be affected. Patient is then led through instructions for direction of gaze and pursuit. | Image/MovingImage |
| 138 |
 |
Measuring Visual Acuity | Demonstration on self of visual acuity exam, using a standard card. | Image/MovingImage |
| 139 |
 |
MELAS and RP | MELAS; Mitochondrial Encephalopathy with Lactic Acidosis, Stroke and Pigmentary Changes in retina-associated with a retinal dystrophy. This 53 year old man had seizures, encephalopathy and lactic acidosis typical of MELAS. His fundus examination showed granularity and some slight pigmentary changes ... | Text |
| 140 |
 |
Migraine and Cluster Pathophysiology and Treatment | Video lecture covering pathophysiology and treatment of migraine and cluster headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | Image/MovingImage |
| 141 |
 |
Mimics of Atrophy | Text | |
| 142 |
 |
Monocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with monocular pendular nystagmus, with discussion of situations in which this condition is seen: acquired disorder of the visual-sensory pathway, and acquired disorder of the brain stem (e.g. multiple sclerosis). | Image/MovingImage |
| 143 |
 |
The Multifocal Electroretinogram: Clinical Applications | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | Text |
| 144 |
 |
Multifocal Electroretinograms | The most important development in ERGs is the multifocal ERG (mfERG). Erich Sutter adapted the mathematical sequences called binary m-sequences creating a program that can extract hundreds of focal ERGs from a single electrical signal. This system allows assessment of ERG activity in small areas of ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 145 |
 |
Near Reflex and Accomodation | Description of testing the near reflex and accomodation. | Text |
| 146 |
 |
Normal Eye Movements | This is an examination of a person with normal eye movements. Notice the patient has normal excursions. He has normal pursuit and saccades (horizontally and vertically). | Text |
| 147 |
 |
Normal Light Reflex without RAPD | This clip demonstrates the examination of the Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD.) Demonstration of gauging the size of the pupil in light, testing light reflexes, swinging flashlight test for optic nerve abnormality. | Image/MovingImage |
| 148 |
 |
Normal Optic Disc | Overview of the structure and function of the normal optic disc. | Text |
| 149 |
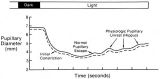 |
The Normal Pupillary Light Reflex | The normal pupillary light reflex is initiated following exposure to light. After a brief latency, both the right (solid line) and left (broken line) pupil constrict, then undergo a small amount of redilation (escape), followed by oscillations (hippus) if the light is sustained. Hippus is not a path... | Image |
| 150 |
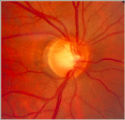 |
Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Image |
