The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
The Accommodation Reflex | This three minute video describes and animates the events taking place in the eye during accommodation. Narration describes the events. Three dimensional animation shows convergence of the eyes. The view changes to a cut-away view of the eye interior to show pupillary constriction and changes in the... | Near Triad; Pupillary Constriction; Ciliary Muscle | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 2 |
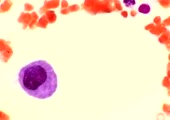 |
Thrombogenesis | Megakarocyte morphogenesis and platelet formation. | Thrombogenesis | HEAL Reviewed Collection |
| 3 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 4 |
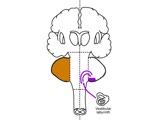 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 5 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction (x2) | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 6 |
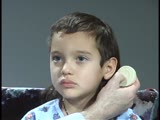 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 8 - Auditory Acuity, Weber & Rinne Tests | This patient has decreased hearing acuity of the right ear. The Weber test lateralizes to the right ear and bone conduction is greater than air conduction on the right. He has a conductive hearing loss. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the Univ... | Cranial Nerve Examination; Weber Test; Rinne Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 7 |
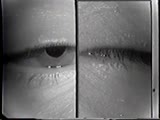 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 3, 4 & 6 - Inspection & Ocular Alignment | This patient with ocular myasthenia gravis has bilateral ptosis, left greater then right. There is also ocular misalignment because of weakness of the eye muscles especially of the left eye. Note the reflection of the light source doesn't fall on the same location of each eyeball. NeuroLogic Exam ha... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 8 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields (x2) | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 9 |
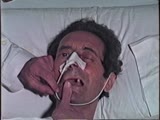 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Motor (x2) | The first patient shown has weakness of the pterygoids and the jaw deviates towards the side of the weakness. The second patient shown has a positive jaw jerk which indicates an upper motor lesion affecting the 5th cranial nerve. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. NeuroLogic Exam h... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 10 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 11 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Anatomy: Cranial Nerve 1 | Olfaction is the only sensory modality with direct access to cerebral cortex without going through the thalamus. The olfactory tracts project mainly to the uncus of the temporal lobes. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 12 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Sensory, Taste (x2) | The patient has difficulty correctly identifying taste on the right side of the tongue indicating a lesion of the sensory limb of the 7th nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Offic... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 13 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 14 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 15 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing of agonist and antagonist muscle action. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medi... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements; Adiadochokinesis | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 16 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Foot - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient taps her foot on the examiner's hand or on the floor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 17 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 18 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Normal Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient should be observed walking as she normally would. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing the video requ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 19 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Natural Gait | The patient should be able to walk with a smooth, coordinated gait. There should be normal associated movement of the upper extremities. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Edu... | Gait Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 20 |
 |
Gait Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait | Have the patient walk heel-to-toe. The patient should be able to balance without falling or stepping to the side. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Universit... | Gait Examination; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 21 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Vergence (x2) | Light-near dissociation occurs when the pupils don't react to light but constrict with convergence as part of the near reflex. This is what happens in the Argyll-Robertson pupil (usually seen with neurosyphilis) where there is a pretectal lesion affecting the retinomesencephalic afferents controllin... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 22 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Check Reflex (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is unable to stop flexion of the arm on sudden release so the arm may strike the chest and doesn't recoil to the initial position. This is most likely due to failure of timely triceps contraction. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at th... | Coordination Examination; Check Reflex | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 23 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 24 |
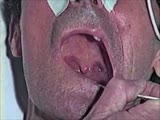 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor (x2) | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 25 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity (x2) | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
