John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
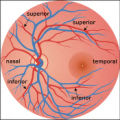 |
2-37a - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 2 |
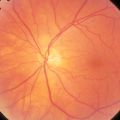 |
2-37b - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 3 |
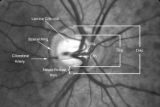 |
2-4a - Disc Anatomy | The optic disc appearance is determined by: the size of the eye, the size of the scleral canal, how the nerve is inserted into the globe, the appearance of the lamina cribrosa, where myelination stops, and what is left behind in normal development. Even though this is a disc with a very large cup, i... | Image |
| 4 |
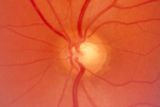 |
2-53a - Venous Pulsations | On the disc, look for spontaneous venous pulsations. Spontaneous venous pulsations can be seen in the large trunks of veins at the level of the disc margin. They are normally present and seen in 37-90% of normals -- depending on the experience of the examiner and the shape of the disc. The spontaneo... | Image |
| 5 |
 |
3 Step Test | Demonstration of patient examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 6 |
 |
Abducting (Dissociated) Nystagmus | Example of a patient with abducting (dissociated) nystagmus. Patient has a subtle internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Right eye has right-beating jerk nystagmus, with smaller oscillations in the left eye. Disease/Diagnosis: Abducting Nystagmus | Image/MovingImage |
| 7 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Lid | Patient with left third nerve palsy demonstrates anisocoria and mild vertical gaze limitation and aberrant movement of the left upper lid. Patient is instructed through all gaze positions. Left upper lid does not descend during downgaze but retracts instead. | Image/MovingImage |
| 8 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Seventh Nerve | Examples of patients with aberrant regeneration of the seventh nerve. First example is a patient with contractions around the mouth and dimpling, demonstrated with slow and rapid eye blinking. Second example shows contraction around nose with eye blink. | Image/MovingImage |
| 9 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Third | Patient with a right third nerve palsy demonstrates ptosis, anisocoria and ophthalmoplegia. During attempted downgaze, the right upper lid flutters back up (aberrant movement) and remains retracted. | Image/MovingImage |
| 10 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Third and Sixth Nerves | Image/MovingImage | |
| 11 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of Third Nerve, Bilaterally (1 degree OD, 2 Digrees OS) | Example of patient with bilateral aberrancy of the third nerve. Shows lids popping up (synkinetic) with adduction. Patient had bilateral internal carotid artery aneurisms with third nerve compression. | Image/MovingImage |
| 12 |
 |
Before Tensilon | Example of patient with myasthenia gravis. Demonstration of baseline examination, followed by administration of 2mg of tensilon, which is a test dose. Procedure for administration of tensilon test is described, including variations. Patient is then shown after being given 4mg of tensilon, with very ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 13 |
 |
Bilateral Facial Myokymia | Example of a patient with a brain stem glioma. Shows bilateral facial myokymia. | Image/MovingImage |
| 14 |
 |
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia | Example of patient with bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient is led through instructions for direction and distance of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 15 |
 |
Bilateral Ptosis | Video of patient with bilateral ptosis. | Image/MovingImage |
| 16 |
 |
Binocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with binocular pendular nystagmus. Patient has somewhat dissociated nystagmus, with nystagmus seen more prominently in the left eye. Patient shows an occasional jerk nystagmus to the right in the right eye. Left eye oscillations are mostly pendular. | Image/MovingImage |
| 17 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 18 |
 |
Blepharospasm with Apraxia of the Eye | Image/MovingImage | |
| 19 |
 |
Brainstem Trauma | Image/MovingImage | |
| 20 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 21 |
 |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion | Video of central retinal artery occlusion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 22 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Example of a patient with Cogan's lid twitch, with discussion of how to detect it in an exam. | Image/MovingImage |
| 23 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Image/MovingImage | |
| 24 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Example of patients with congenital nystagmus. First patient's nystagmus are mostly jerk and not pendular. Second patient's nystagmus are mostly pendular. Both patients show a uniform horizontal oscillation. Second patient also shows differences in frequency of oscillations depending on gaze, includ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 25 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | Patient with congenital nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
