The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
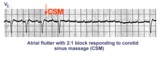 |
Massage parlor games | When unsure of the mechanism of a supraventricular tachycardia, carotid sinus massage may help make the diagnosis. In this example, carotid sinus massage causes marked AV block which permits easy recognition of the rapid, regular atrial flutter waves. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 152 |
 |
Wandering baseline artifact - marquette | Wandering baseline artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 153 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = +15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 154 |
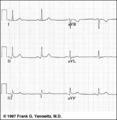 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = +30 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 155 |
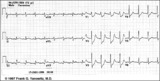 |
Acute inferoposterior MI | Acute inferoposterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 156 |
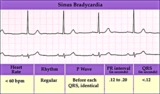 |
Sinus bradycardia | Sinus bradycardia | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 157 |
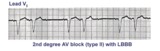 |
2nd degree AV block, mobitz type II, with LBBB | The wide QRS complexes in lead V1 indicates LBBB. 2nd degree AV block, Mobitz II is suggested by the two fixed PR intervals prior to the nonconducted P wave. The location of the block is most likely in the right bundle, because Mobitz II is usually a sign of bilateral bundle branch disease. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 158 |
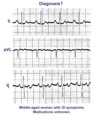 |
A very subtle atrial tachycardia with 2:1 block | Although at first glance this looks like normal sinus rhythm at 95 bpm. On closer look, there are 2 P waves for every QRS; the atrial rate is 190 bpm. Note the hidden P in the T waves. This rhythm is likely due to digitalis intoxication, as are the GI symptoms. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 159 |
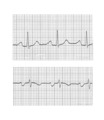 |
Left atrial enlargement | Left atrial enlargement is illustrated by increased P wave duration in lead II, top ECG, and by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1, bottom tracing. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 160 |
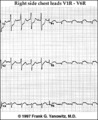 |
Acute postero-lateral MI: precordial leads | Acute postero-lateral MI: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 161 |
 |
Pacemaker failure to pace - marquette | Pacemaker failure to pace - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 162 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 90 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 163 |
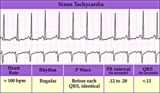 |
Junctional tachycardia - marquette | Junctional tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 164 |
 |
Diagram: frontal plane leads | Diagram: frontal plane leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 165 |
 |
Inferoposterior MI | Inferoposterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 166 |
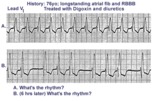 |
Digitalis intoxication: Junctional tachycardia with and without AV block | In a patient with longstanding atrial fibrillation being treated with digoxin, a regular tachycardia, as seen in A, with a RBBB suggests a junctional or supraventricular tachycardia. Group beating, in B, is likely due to a 2nd degree, Type 1, exit block below the ectopic junctional focus. This is h... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 167 |
 |
Nonconducted PACs and junctional escapes | Although at first glance this looks like 2nd degree AV block, the P waves indicated by the arrows are premature and not sinus P waves. The pause is long enough to encourage a junctional escape focus to take over. Note the sinus P waves just before the escape beats. Had the escapes not occurred, t... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 168 |
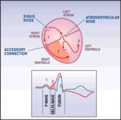 |
WPW diagram | The short PR interval is due to a bypass track, also known as the Kent pathway. By bypassing the AV node the PR shortens. The delta wave represents early activation of the ventricles from the bypass tract. The fusion QRS is the result of two activation sequences, one from the bypass tract and one... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 169 |
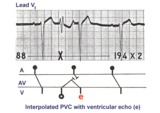 |
PVC with venticular echo | The PVC in this example retrogradely enters the AV junction and returns, usually down a different pathway, to reactivate the ventricles....a ventricular echo. This is unlikely to be an interpolated PVC because the PR interval following the PVC is too short for the sinus impulse to have entered the ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 170 |
 |
Left bundle branch block (LBBB) | LBBB is recognized by 1) QRS duration>0.12s; 2) monophasic R waves in I and V6; and 3) terminal QRS forces oriented leftwards and posterior. The ST-T waves should be oriented opposite to the terminal QRS forces. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 171 |
 |
PAC with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC with RBBB aberrant conduction | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 172 |
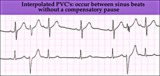 |
Interpolated PVCs - marquette | Interpolated PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 173 |
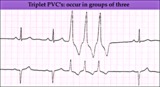 |
PVC triplet - marquette | PVC triplet - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 174 |
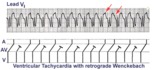 |
Ventricular tachycardia with retrograde wenckebach | Approximately 50 percent of ventricular tachycardias are associated with AV dissociation. The other 50 percent have retrograde atrial capture. This example shows ventricular tachycardia with retrograde Wenckebach. The retrograde P waves are hard to find, but the arrows are of some help. | Wenckebach AV Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 175 |
 |
Nonconducted and aberrantly conducted PAC's | In A the slow sinus rhythm is actually caused by nonconducted PACs hidden in the ST segment. This is confirmed in B where some of the PACs are aberrantly conducted with LBBB, and some PACs are nonconducted. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
