John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Basal Encephaloceles | Text | |
| 52 |
 |
Basic Eye Alignment Exam | Demonstration of basic eye alignment examination. Includes: a. Tools b. Cover-Uncover and SPCT c. Alternate Cover and APCT d. Maddox Rod Testing | Image/MovingImage |
| 53 |
 |
Basic Headache | Presentation covering an overview of headache and migraine. | Text |
| 54 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam | Demonstration of a basic neurologic examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 55 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Coordination | Demonstration of a coordination examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 56 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Cranial Nerves | Demonstration of a cranial nerve examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 57 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Mental Status | Demonstration of a mental status examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 58 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Motor Examination | Demonstration of a motor examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 59 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Sensory | Demonstration of a sensory examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 60 |
 |
Basic Neurologic Exam: Station and Gait | Demonstration of a station and gait examination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 61 |
 |
Before Tensilon | Example of patient with myasthenia gravis. Demonstration of baseline examination, followed by administration of 2mg of tensilon, which is a test dose. Procedure for administration of tensilon test is described, including variations. Patient is then shown after being given 4mg of tensilon, with very ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 62 |
 |
Benign Episodic Unilateral Mydriasis | Presentation covering benign episodic mydriasis. | Text |
| 63 |
 |
Bilateral Asynchronous Blepharospasm with Facial and Cervical Dystonia | Bilateral Asynchronous Blepharospasm with Facial and Cervical Dystonia. | Image/MovingImage |
| 64 |
 |
Bilateral Facial Myokymia | Example of a patient with a brain stem glioma. Shows bilateral facial myokymia. | Image/MovingImage |
| 65 |
 |
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia | Example of patient with bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient is led through instructions for direction and distance of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 66 |
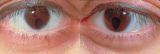 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas | Coloboma literally means a "gap"-and can be used to describe any fissure, hole, or gap in the eye. The term most often is used to refer to a congenital gap in the disc, retina, the choroid, and the iris. Colobomas occur because the embryonic fissure fails to fuse. Since the fissure closure begins in... | Image |
| 67 |
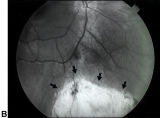 |
Bilateral Iris Colobomas (B) | Bilateral iris colobomas. B. Bilateral colobomatous defects of the inferonasal retina (black arrows) are also present, as shown in the right eye. | Image |
| 68 |
 |
Bilateral Ptosis | Video of patient with bilateral ptosis. | Image/MovingImage |
| 69 |
 |
Binocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with binocular pendular nystagmus. Patient has somewhat dissociated nystagmus, with nystagmus seen more prominently in the left eye. Patient shows an occasional jerk nystagmus to the right in the right eye. Left eye oscillations are mostly pendular. | Image/MovingImage |
| 70 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 71 |
 |
Blepharospasm with Apraxia of the Eye | Image/MovingImage | |
| 72 |
 |
Brainstem Trauma | Image/MovingImage | |
| 73 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 74 |
 |
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion | Video of central retinal artery occlusion. | Image/MovingImage |
| 75 |
 |
Clover-leaf Visual Field Defects | Description of clover-leaf visual field defects. | Text |
