The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
1 - 25 of 7
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
 |
Bone | At a later stage of the developing skull, note the differences in cell density and organization between the immature or woven bone and the mature or lamellar bone. Often a cementing line separates the two types of bone. UCLA Histology Collection. | bone; lamellar bone; Skull | UCLA Histology |
| 2 |
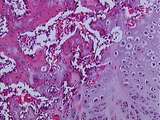 |
Bone / Cartilage | At a higher magnification of this fracture, we can identify cartilage cells undergoing hypertrophy, calcified cartilage, and woven bone. UCLA Histology Collection. | bone; cartilage | UCLA Histology |
| 3 |
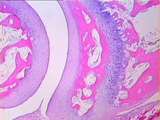 |
Bone / Cartilage | There is articular cartilage on each side of the joint space. Bone is stained pink. Find the synovial fold that generates the synovial fluid which lubricates the joint. Also find bone marrow spaces and the epiphyseal growth plate. UCLA Histology Collection. | articular cartilage; bone; epiphyseal growth plate | UCLA Histology |
| 4 |
 |
Bone | Identify the following: cartilage cell hypertrophy, calcified cartilage, bone spicules, and bone marrow space. UCLA Histology Collection. | bone; cartilage | UCLA Histology |
| 5 |
 |
Bone | Here we can identify dead bone, since there are no cells in the lacunae (osteocytes die once deprived of a blood supply). Woven bone and calcified cartilage are also present. UCLA Histology Collection. | bone | UCLA Histology |
| 6 |
 |
Bone | Intramembranous bone formation. In the fetal skull, plates of bone are laid down in the mesenchymal field. This image shows woven or immature bone, which tends to be more cellular than lamellar or adult bone. Osteoprogenitor cells differentiate into osteoblasts, which produce the osteoid or uncalcif... | bone; Intramembranous bone formation; Skull | UCLA Histology |
| 7 |
 |
Bone / Cartilage | A healing fracture recapitulates the events of fetal endochondral ossification. A hyaline cartilage fracture callus forms to hold together the two ends of bone. Woven bone develops around (and eventually replaces) the cartilage, connecting the broken bone. Fracture healing occurs within the perioste... | bone; cartilage; periosteum | UCLA Histology |
1 - 25 of 7
