| OCR Text |
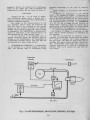
Show THE "COMBURIMETRE" AND ITS USE IN COMBUSTION CONTROL Jean-Claude Benisti Gaz de France Research & Development Division Paris, France C. Vabre Arelco Co Paris, France A. Chapus Recomat Co Paris, France ABSTRACT In any gas-fiped industPial installation, imppovement of ppoduction quality and ovepall efficiency pequipes adequate combustion contpol. Any combustion pequipes a well defined combustion agent/fuel feed patio. Contpol of this patio is genepally done thpough analysis of the combustion ppoducts. If the combustion ppoducts ape polluted op not accessible it is necessapy to know the fuel chapactepistics in opdep to maintain unchanged, by upstpeam action, the ideal conditions fop combustion when those chaPactepistics vapy. The fact that a specific sensop is not corrunepcially available has led Gaz de Fpance to develop a metep called "COMBURIMETRE" in coopepation with a manufactupep. The "COMBURIMETRE" is a combustion simulatop which enables the continuous measupement of an impoptant chapactepistic of distpibuted natupal gas : the combustion aip pequipement index (B) which is defined as B = Va/Id whepe "Va" is theor»etical aip pequipement (unit m3 (n)of aip/m3 (n)of gas) and "d" pelative density with pespect to aip. Mapketed as of thpee yeaps ago, the "COMBURIMETRE" has ppoven its peliability, accupacy and speed of pesponse, and thepefope its capacity to contpol combustion in the most sensitive industpial ppocesses. Fupthepmope, the tight analogy which exists between the combustion aip pequipement index (B=Va/Ia) and the r-lobbe numbep (W = gcv/.f(1) of natupal gases allows using the "COMBURIMETRE" to pegulate a constant thepmal input undep the same conditions. This papep consists of two papts : aftep ppesenting the chapactepistics of the unit, we shall emphasize the vaPious pegulation schemes using the "COMBURIMETRE", and give some application examples. 205 THE GAS INDUSTRY has from its beginnings spurred the development of numerous instruments adapted to its specific needs. Control of the values assumed by certain physical or chemical characteristics of gas is one problem the industry confronts in the fields of both production and utilization. The instrument described in this paper is a new design. It is especially relevant to users concerned by the effects of random variations in the characteristics of gaseous fuels. FUEL GAS IDENTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS PROBLEMS RELATED TO THE UTILIZATION OF A GAS WITH VARIABLE CHARACTERISTICS - Manufacturers today are increasingly keen about the quality of their products and the energy savings they can achieve. It is therefore incumbent on them to improve, if not to modernize, their production plant. In the case of gas-fired industrial furnaces, there is an obvious need for effective control systems. A furnace can be roughly represented as a device (Figure 1) with which one whishes to obtain and maintain at well-specified values certain control variables, such as temperatures at various points or the composition of exhaust gases. Both product quality and furnace efficiency are closely related to the control system's capability (whether manual or automatic) to maintain, by acting upon the controlling variables, the controlled variables at their set points, in spite of the various disturbances to which the furnace may be subjected. Among these disturbances, are those caused by variations in the fuel's characteristics, which can result in modifications to the heat output and the composition of the combustion products. |