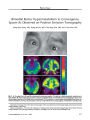
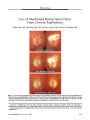
| OCR Text |
Show ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Postganglionic Horner Syndrome in Three Patients With Coincident Middle Ear Infection Robert H. Spector, MD Abstract: Three patients developed a postganglionic Horner syndrome during the course of an ipsilateral uncomplicated middle ear infection. The mechanism may be an effect on the middle ear caroticotympanic sympathetic plexus, for which there is considerable anatomic and physiologic evidence. Why Horner syndrome does not occur more often after middle ear infection is a mystery. (J Neuro-Ophthalmol 2008;28:182-185) The most common causes of an acquired, isolated, non-traumatic, postganglionic Horner syndrome (PGHS) include cluster headache or a structural lesion of the internal carotid artery, such as a carotid artery occlusion, stenosis, dissection, or subcranial aneurysm, or an extrinsic mass that compresses the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion or the sympathetic nerves that exit from it (1). I report three patients who developed a PGHS in association with an ipsilateral uncomplicated middle ear infection. CASE REPORTS Case 1 A 43-year-old woman was reported by her primary care physician to have had a right middle ear infection in March 2006. Findings includes hyperemia of the right tympanic membrane, dulling of the right tympanic light reflex, and a fever of 101F. The syndrome resolved with 6 days of single antibiotic therapy. Eight weeks later, she became febrile and complained of fever and pain in the contralateral left ear. Within 24 hours, her primary care physician found the same ear findings as had been noted on the opposite side, along with a fever of 100.6F. The same antibiotic was prescribed. Within 12 hours after starting the medication, the patient's ear symptoms and fever began to subside. Later that evening, her family noticed that her pupils were unequal. The following morning, an ophthalmologist confirmed anisocoria and reported no other abnormalities on the ophthalmologic examination. I examined the patient the same day (3 days after the onset of left ear pain). She offered no antecedent or recent history of nosebleeds, hemoptysis, dysphagia, anorexia, weight loss, facial pain, or numbness. Left ear pain was minimal. I did not examine the tympanic membrane. In subdued illumination, the right pupil measured 4.0 mm and the left pupil measured 2.5 mm. After direct light stimulation, each pupil constricted to 1.0 mm. Lids and facial moisture were symmetrically normal. The irides were isochromic. Thirty minutes after instillation of 10% cocaine into each conjunctival sac, the right pupil had dilated to 6.5 mm and the left pupil had not dilated. An emergency MRA of the extra- and intracranial vessels and a soft tissue, noncontrast axial MRI of the cervical internal carotid artery showed no abnormalities. Three days later, the anisocoria was unchanged. Lids and facial moisture were still symmetric. Topical instillation of 1% hydroxyamphetamine dilated the right pupil to 7.0 mm and the left pupil only to 3.0 mm. Several old photographs of the patient showed equal-sized pupils. Direct visualization of the nasopharynx by an otolaryn-gologist and a thin-section CT scan of the temporal and mastoid bones, with special attention to the middle ear cavity, gave normal results. One month later, the eye findings were unchanged. Case 2 A 29-year-old man had had frequent middle ear infections during childhood, which, according to his mother, affected the right and left ears with equal frequency. The infections diminished after age 8 and his health was normal until his early 20s, when he had an uncomplicated ear infection that resolved with antibiotics. He could not remember which ear was affected, and medical records were not available. In June 2003, he developed severe left ear pain with a noticeable asymmetry in the size of the pupils. On the second day of symptoms, his primary care physician recorded a temperature of 98.6F and observed hyperemia of Private practice, Atlanta, Georgia. Address correspondence to Robert H. Spector,MD, 980 Johnson Ferry Road, Suite 550, Atlanta, GA 30342; E-mail: fstop007@bellsouth.net 182 J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2008 the left tympanic membrane, obscuration of the left tympanic light reflex, left miosis (not measured), and questionable left upper lid ptosis. Treatment with a single oral antibiotic resolved the ear symptoms and signs, but the anisocoria and questionable ptosis persisted. Examination by an otolaryngologist was otherwise unremarkable. I examined the patient less than a week after he had presented to his primary care physician. By then he was pain-free and afebrile. In subdued illumination, the pupils measured 5.0 mm in the right eye and 3.5 mm in the left eye. After bright light stimulation, both pupils constricted to 2.0 mm. The left upper lid was slightly ptotic. Facial moisture and facial sensation were symmetric. Corneal reflexes were equal. There was no palpable cervical lymphadenopathy. Topical instillation of 10% cocaine caused the right pupil to dilate to 7.5 mm but no dilation of the left pupil. MRA of the extracranial and intracranial vessels and a soft tissue axial MRI of the cervical internal carotid artery gave normal results. Three days later, the pupils were unchanged. After the topical instillation of 1% hydroxyamphetamine, the right pupil dilated to 7.5 mm and the left pupil dilated to 4.0 mm. Several childhood photographs of the patient showed equal-sized pupils. A thin-section CT of the temporal and mastoid bones, with special attention to the middle ear cavity, gave normal results. The patient subsequently had no ear sym-ptoms, but the eye findings remained unchanged. Case 3 A 7-year-old boy had the diagnosis of a left middle ear infection on January 21, 2006. A single antibiotic was prescribed. On the second day of treatment, he had noticeable left upper lid ptosis and unequal pupils. One day later, a pediatrician confirmed the findings and referred the patient to a pediatric otolaryngologist, who diagnosed a left Horner syndrome. No additional studies were recommen-ded. An antibiotic was prescribed. The ear symptoms and signs readily resolved, but the eye signs persisted. I examined the patient 2.5 weeks after the onset of symptoms. Left upper lid ptosis and miosis were present. In subdued illumination, the right pupil measured 6.0 mm and the left pupil 3.5 mm. After light stimulation, both pupils constricted to 2.5 mm. Left upper lid ptosis did not fatigue during prolonged upgaze. The topical instillation of a 1% hydroxyamphetamine ophthalmic solution caused the right pupil to dilate to 7.5 mm but the left pupil only to 4.0mm. Facial moisture, facial sensation, and facial movement were symmetrically normal. DISCUSSION I have described one child and two adults who developed a PGHS during an ipsilateral and otherwise uncomplicated middle ear infection. All three patients showed miosis and preserved facial sweating; ptosis ranged from being not present to obvious. A sympathetically denervated iris dilator was supported by relatively sluggish dilation of the affected pupil in darkness and reduced dilation of that pupil after topical instillation of 10% cocaine. The postganglionic origin of this denervation was proven by lack of dilation after instillation of 1% hydroxyamphetamine. Despite timely and appropriate medical therapy of the ear infection, the eye findings persisted. Preserved facial sweating with a PGHS can be explained simply by understanding the gross anatomy of the cervical sympathetic pathway. The ascending sudomo-tor sympathetic fibers, after synapsing in the superior cervical ganglion, course along the external carotid artery plexus and eventually join the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve. A cervical sympathetic lesion distal to the carotid bifurcation, which would only involve the ascend-ing pericarotid sympathetic fibers, would spare the sudomotor fibers that effect facial moisture. The sympathetic postganglionic fibers destined for the eye originate in cell bodies located in the superior cervical ganglion. Postganglionic sympathetic nerves ascend in the pericarotid plexus to join with the ophthalmic division of the fifth cranial nerve that carries them to the eye. Controversy exists regarding the presence, course, and function of branches of the ascending oculosympathetic nerves that branch off the pericarotid plexus and enter the middle ear. Their presence is indisputable in the rabbit, cat, dog (2,3), and human (4). Such fibers branch off the pericarotid plexus in the carotid sheath and pierce the posterior wall of the carotid canal, which also forms the anterior wall of the tympanic or middle ear cavity (Fig. 1). According to Kobrak (5), the posterior wall of the carotid canal or anterior wall of the middle ear varies in thickness from dense bone to a membranous septum in which mul-tiple dehiscences are present. Exactly what percentages of septa are thick, thin, or filled with dehiscences have never been quantified. But direct observations clearly show an array of nerve filaments penetrating the septum that merge into a plexus atop the promontory (or promontorium) of the middle ear, a prominent swelling on the floor of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. This plexus of nerve fibers atop the promontorium is made up of ‘‘caroticotympanic nerves.'' De Kleijn and Socin (6) found ‘‘entire aggregates'' of caroticotympanic nerves crossing the tympanic cavity in cats., Other investigators (4) have made the same observations in humans. Frenckner (4) performed detailed surgical dissections of the exposed middle ear in living humans, believing that extirpation of the caroticotympanic nerves might resolve tinnitus or Me´nie`re's disease. Supplementing his operative observations are extensive anatomic studies in cadaver 183 PGHS With Coincident Middle Ear Infection J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2008 specimens. Using osmium-stained preparations and an operating magnifying microscope, he was able to visualize, describe, and illustrate the smallest nerve twigs within the tympanic cavity-their course, branching, and anastomo-ses. Observing wide variation, he noted that ‘‘they were never the same in two cases; some were fully exposed in an open sulcus, others were partially enclosed and a few were fully encased by a thick bony shell'' (4). Although the presence of a caroticotympanic plexus has been well established in several species, the autonomic function of this plexus is less certain. In cats, Barlow and Root (2) proved that these fibers carry autonomic nerve signals. These investigators isolated the superior cervical ganglion in eight cats and traced the ascending sympathetic fibers superiorly to the point where they entered the skull at the medial margin of the auditory bulla. The promontorium and overlying caroticotympanic nerves were identified and isolated. Electrical stimulation of the caroticotympanic nerves was followed by an immediate and striking dilatation of the ipsilateral pupil, whereas interruption of these fibers FIG. 1. The caroticotympanic sympathetic plexus. Filaments of the ascending postganglionic sympathetic nerves branch off the pericarotid plexus and pierce the posterior wall of the carotid canal. This wall also forms the anterior wall of the middle ear cavity. Lying atop the middle ear promontorium is an array of nerves called the caroticotympanic plexus. Note also that the vidian nerve in the vidian canal is formed by the confluence of the sympathetic nerve filaments from the middle ear and the greater superficial petrosal nerve, which branches off the facial nerve distal to the nerve to the stapedius muscle. (Modified from Reference 7.) 184 q 2008 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2008 Spector resulted in an absence of ocular changes upon subsequent stimulation of the cervical sympathetic trunk (2). In the five cats in which the caroticotympanic nerve fibers were surgically interrupted, the characteristic signs of a feline Horner syndrome developed: miosis, protrusion of the nictitating membrane, and, in some cases, narrowing of the palpebral fissure. Although oculosympathetic paralysis and ptosis have not been described in patients who have had their caroticotympanic nerves manipulated, oculosympathetic paralysis has been reported, on rare occasions, in otitis media (7). Given the anatomy, it is surprising that this phenomenon is not encountered more often. The patho-physiology of Horner syndrome with middle ear infection could be attributed either to a change in the pressure dynamics or toxic inflammation of the septum that separates the carotid canal and tympanic cavity or to direct damage and scarring of the caroticosympathetic fibers in the middle ear. Although the number of patients reported here is too small to allow firm conclusions, it is interesting that all had miosis, none had anhidrosis, and ptosis was either absent or obvious. Perhaps the branches off the carotid plexus that form the caroticotympanic plexus in the middle ear carry more signals to the pupillodilator muscles than to the eyelids. This report may raise more questions than it answers; however, it offers the opportunity to revisit the issue and consider whether middle ear disease should be included in the differential diagnosis of an acute-onset PGHS. REFERENCES 1. Grimson BS Thompson HS. Postganglionic Horner syndrome. In: Glaser JS, ed. Neuro-Ophthalmology: Symposium of the University of Miami and the Bascom Palmer Eye Institute. St. Louis: CV Mosby; 1977:190-8. 2. Barlow CM, Root WS. The ocular sympathetic path between the superior cervical ganglion and the orbit in the cat. J Comp Neurol 1949;91:195-207. 3. Francois-Franck C. Cited by de Kleijn A, Socin C. Zur na¨heren Kenntnis des Verlaufs der postgangliona¨ren Sympathieusbahnen fu¨r Pupillenerweiterung, Lidspalteno¨ ffnung und Nickhautretraktion bei der Katze. Arch Ges Physiol 1915;160:407-15. 4. Frenckner P. Observations on anatomy of tympanic plexus and technique of tympanosympathectomy. AMA Arch Otolaryngol 1951; 54:347-55. 5. Kobrak HG. The Middle Ear Chicago. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1959:254 6. de Kleijn A, Socin C. Zur na¨heren Kenntnis des Verlaufs der postgangliona¨ren Sympathieusbahnen fu¨ r Pupillenerweiterung, Lid-spalteno ¨ ffnung und Nickhautretraktion bei der Katze. Arch Gesamte Physiol 1915;160:407-15. 7. Hoefnagel D, Joseph JB. Oculosympathetic paralysis in otitis media. N Engl J Med 1961;265:475-7. 185 PGHS With Coincident Middle Ear Infection J Neuro-Ophthalmol, Vol. 28, No. 3, 2008 |