| Title |
Reexaminatuon of Fuel-NO Reduction in a Gas-Fired Furnace |
| Creator |
Ma, H. K.; Pan, K. C.; Lee, W. B. |
| Publisher |
Digitized by J. Willard Marriott Library, University of Utah |
| Date |
1993 |
| Spatial Coverage |
presented at Tulsa, Oklahoma |
| Abstract |
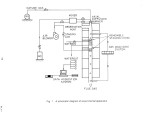
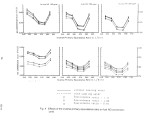
This study tries to examine the effects of temperature and air flow on the conversion yield of fuel NO in a gas-fired furnace. In the experiment, NO was add in natural gas. The added NO can be considered as the nitrogen bearing component in the fuel. Tests, included changing air flow rate, adding cooling water, and adding staged air were performed to characterize and optimize the fuel-rich burning zone and the fuel-lean burnout zone independently. Detailed measurements of O2, CO2, CO, NO, and NOx were made at the fuel-rich burning zone and furnace exit. The effects of operation conditions on fuel NO conversion yield were detailed examined. Results indicated that adding staged air in the fuel-rich burning zone (L / D = 5) will decrease the NO conversion yield. Adding cooling water in a right position may further decrease the NO conversion yield and lower the NO emissions. And, the conversion yield of NO will drop as increasing the initial NO concentration. In addition, the least conversion yield of nitrogen oxides in the fuel rich first stage burning zone will occur at the stoichiometric ratio's inverse value, (O1)^-1,0.66 to 0.76. |
| Type |
Text |
| Format |
application/pdf |
| Language |
eng |
| Rights |
This material may be protected by copyright. Permission required for use in any form. For further information please contact the American Flame Research Committee. |
| Conversion Specifications |
Original scanned with Canon EOS-1Ds Mark II, 16.7 megapixel digital camera and saved as 400 ppi uncompressed TIFF, 16 bit depth. |
| Scanning Technician |
Cliodhna Davis |
| ARK |
ark:/87278/s6fb55j4 |
| Setname |
uu_afrc |
| ID |
10057 |
| Reference URL |
https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6fb55j4 |