Contents | 103 Total
The development of a self contained device for monitoring cardiac output including a survey of related physiology and bioinstrumentation
| Publication Type | honors thesis |
| School or College | College of Science |
| Department | Biological Sciences |
| Thesis Supervisor | Richard A. Normann |
| Honors Advisor/Mentor | B. Gale Dick |
| Creator | Erickson, Evelyn Jo |
| Title | The development of a self contained device for monitoring cardiac output including a survey of related physiology and bioinstrumentation |
| Date | 1982-06 |
| Year graduated | 1982 |
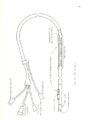
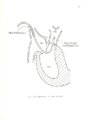
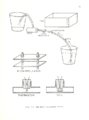
| Description | A thermodilution method for measuring cardiac output has been proposed. The new experimental technique is described with emphasis on the early research and development. A positive change in blood heat content is induced when a .OSF capacitor is discharged through a coil of nichrome or chrome I resistance wire. This technique guarantees high reproducibility. The coil, located in the vena cava, is not expected to dangerously heat. Measurements of the coil temperature in still water show a maximum temperature change of 6T = 2.829°C. The proposed technique gives results which correlate well with actual flow (correlation coefficient r = .990). It promises to be accurate, reproducible, practical, and economical. |
| Type | Text |
| Publisher | University of Utah |
| Subject | Cardiac output - Measurement; Medical instruments and apparatus |
| Language | eng |
| Rights Management | (c) Evelyn Jo Erickson |
| Format Medium | application/pdf |
| ARK | ark:/87278/s6fz19dp |
| Setname | ir_htca |
| ID | 1308578 |
| Reference URL | https://collections.lib.utah.edu/ark:/87278/s6fz19dp |