John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
 |
Blepharospasm with Apraxia of the Eye | Image/MovingImage | |
| 202 |
 |
Voluntary Nystagmus | Example of patient with voluntary nystagmus. Discussion of how a lack of uniform, patterned movement of the eyes along with associated lid movements suggests that activity is voluntary. | Image/MovingImage |
| 203 |
 |
Levator Disinsertion | Example of patient with levator disinsertion, a lid disorder. Patient is pregnant and wears poorly fitting contacts. Discussion of characteristics, such as lid ptosis (shown in the left eye of patient), but with full levator function. | Image/MovingImage |
| 204 |
 |
Marcus Gunn Jaw Winking | Example of patient with Marcus Jaw Winking. Patient is led through instructions for movement of jaw (open, close, back and forth), with eyelid seen to be affected. Patient is then led through instructions for direction of gaze and pursuit. | Image/MovingImage |
| 205 |
 |
CPEO | Patient with Chronic Progressive External Ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) | Image/MovingImage |
| 206 |
 |
Duane's Retraction Syndrome Type 1: Lid Retraction | Example of patients with Duane's Retraction Syndrome, Type 1. Description of components of Duane's Syndrome: limitation of abduction, variable limitation of adduction, and palpebral fissure narrowing and globe retraction with attempted adduction. Type 1 includes limited or absent abduction with norm... | Image/MovingImage |
| 207 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Example of a patient with Cogan's lid twitch, with discussion of how to detect it in an exam. | Image/MovingImage |
| 208 |
 |
Rotary Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rotary nystagmus, showing occasional counterclockwise rotary movements of both eyes. Seen more in intrinsic disorders of the brainstem. | Image/MovingImage |
| 209 |
 |
Spasmus Nutans | Example of patient with spasmus nutans. | Image/MovingImage |
| 210 |
 |
Rotary Downbeat | Patient with rotary downbeat nystagmus (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 211 |
 |
Oculopalatal Myoclonus (PPT) | Oculopalatal myoclonus (OPM) Rhythmic oscillations of eyes and palate. Occurred after specific brainstem injury from stroke, following stenting. Related Video: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,128 Disease/Diagnosis: Oculopalatal myoclonus | Image/MovingImage |
| 212 |
 |
Oculopalatal Myoclonus | Oculopalatal myoclonus (OPM) Rhythmic oscillations of eyes and palate. Occurred after specific brainstem injury from stroke, following stenting. Related PowerPoint Presentation: http://content.lib.utah.edu/u?/EHSL-Moran-Neuro-opth,129 Disease/Diagnosis: Oculopalatal myoclonus. | Image/MovingImage |
| 213 |
 |
Ocular Flutter | Two examples of patients, the first with rotary, flutter-like movements, but not ocular flutter, and the second with genuine ocular flutter. Discussion of difference between ocular flutter and nystagmus, and how to elicit ocular flutter. | Image/MovingImage |
| 214 |
 |
Flutter in Downgaze | Examination of patient with flutter in downgaze (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 215 |
 |
Square Wave Jerks | Example of patient with square wave jerks. Discussion of difference between square wave jerks (saccadic oscillations) and horizontal nystagmus. | Image/MovingImage |
| 216 |
 |
Intermittent Square Wave Jerks | Patient with intermittent square wave jerks (no audio) | Image/MovingImage |
| 217 |
 |
Opsoclonus | Example of patients with opsoclonus, a saccadic abnormality. Discussion of characteristics of opsoclonus, such as involuntary, rapid, brief, random, conjugate saccades. Discussion of possible causes, including brain stem encephalitis (as in first patient), a paraneoplastic effect, tumors, and drug t... | Image/MovingImage |
| 218 |
 |
Hemifacial Spasm | Example of patients with hemifacial spasm. First patient has a sequela of Bell's palsy, and is seen to have mainly clonic movements around the eye, with occasional tonic movements around the mouth. Second patient has a cerebellopontine angle epidurmoid tumor, and is seen to have movements around the... | Image/MovingImage |
| 219 |
 |
Binocular Pendular Nystagmus | Example of a patient with binocular pendular nystagmus. Patient has somewhat dissociated nystagmus, with nystagmus seen more prominently in the left eye. Patient shows an occasional jerk nystagmus to the right in the right eye. Left eye oscillations are mostly pendular. | Image/MovingImage |
| 220 |
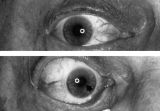 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Right Pupil | Aberrant regeneration of the right pupil in a man with a large intracavernous sinus meningioma causing a pupil-involving, incomplete third cranial nerve palsy. His pupil is round when he gazes straight ahead (top). When he tries to rotate the eye medially, the pupil constricts, but a segment of the ... | Image |
| 221 |
 |
Cyclic Oculomotor Palsy | Example of patient with cyclic oculomotor palsy. | Image/MovingImage |
| 222 |
 |
Superior Oblique Myokymia | Close-up video of a patient with superior oblique myokymia (no audio.) | Image/MovingImage |
| 223 |
 |
Rebound Nystagmus | Example of a patient with rebound nystagmus, where the oscillations alternate direction as the patient shifts gaze in different directions. Discussion of relationship to disease and disorders of the cerebellum, including degenerations of the cerebellum, infarction, and demyelination. | Image/MovingImage |
| 224 |
 |
Brun's Nystagmus | Observation of patient with Brun's Nystagmus. Shows patient gazing to the right and the nystagmus beating in the direction of the gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 225 |
 |
Periodic Alternating Nystagmus | Example of a patient with periodic alternating nystagmus, showing an alternation between left-beats and right-beats as the patient maintains forward gaze. Nystagmus maintain horizontal direction regardless of position of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
