The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
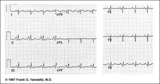 |
RAE & RVH | RAE & RVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 202 |
 |
Oxidation of a polyunsaturated fatty acid -- part I | The cycles of beta-oxidation prior to the one involving the original Delta-12 double bond act to get past the Delta-9 double bond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 203 |
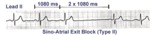 |
Type II, 2nd degree sino-atrial block | Two types of 2nd degree SA block have been described. In type-I, or SA Wenckebach, the P-P interval of the pause is less than 2x the preceding P-P intervals. In type-II SA block the P-P interval of the pause is approximately 2x the normal P-P interval. The distinction between types I and II is no... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 204 |
 |
Bradycardia-dependent LBBB with carotid sinus massage | When carotid sinus massage slows the heart rate in this example, the QRS widens into a LBBB. This form of rate-dependent bundle branch block is thought to be due to latent pacemakers in the bundle undergoing phase 4 depolarization; when the sinus impulse enters the partially depolarized bundle, slow... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 205 |
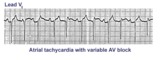 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 AV block | In this rhythm the atrial rate from an ectopic focus is 160 bpm. Atrial activity can be seen on top of T waves, and before QRS's. Careful observation reveals a 3:2 Wenckebach relationship between P waves and QRS's. Atrial tachycardia with block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 206 |
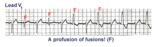 |
Ventricular fusion beats | Fusion beats occur when two or more activation fronts contribute to the electrical event. These may occur in the atria or in the ventricles. In this example the ventricular fusions are the result of simultaneous activation of the ventricles from two foci, the sinus node and a ventricular ectopic... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 207 |
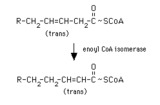 |
enoyl CoA isomerase reaction | Enoyl CoA isomerase converts a trans-3-enoyl CoA to a trans-2-enoyl CoA. Thus a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA or the product of the 2,4-dienoyl CoA reductase reaction can proceed through beta-oxidation. | Enoyl CoA Isomerase Reaction | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 208 |
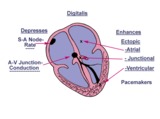 |
Diagram: digitalis effect on rhythm and conduction | Diagram: digitalis effect on rhythm and conduction | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 209 |
 |
Structures of the ketone bodies | These are the structures of the ketone bodies. Acetoacetate and beta-hydroxybutyrate are important physiological substrates. Acetone is a byproduct, and is not metabolized further. It is excreted in the urine and in expired air. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 210 |
 |
Calibration signal - marquette | Calibration signal - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 211 |
 |
Old inferior MI | Old inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 212 |
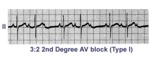 |
Second degree AV block, type I, with 3:2 conduction ratio | There are two types of 2nd degree AV Block. In this example of Type I or Wenckebach AV block there are 3 P waves for every 2 QRSs; the PR interval increases until a P wave fails to conduct. This is an example of group beating. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 213 |
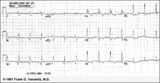 |
Infero-posterior MI with RBBB | This is an unusual RBBB because the initial R wave is taller than the R wave in lead V1. This is the clue for true posterior MI. The tall initial R wave in V1 is a pathologic R wave analagous to the pathologic Q wave of an anterior MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 214 |
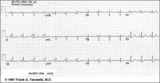 |
Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) & Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) | RAE is recognized by the tall (>2.5mm) P waves in leads II, III, aVF. RVH is likely because of right axis deviation (+100 degrees) and the Qr (or rSR') complexes in V1-2. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 215 |
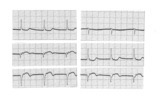 |
Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Frontal plane: accelerated junctional rhythm and inferior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 216 |
 |
QRS axis = -30 degrees | Lead II is isoelectric; I is positive; III is negative. The axis is -30 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 217 |
 |
Voltage criteria for LVH | Voltage criteria for LVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 218 |
 |
Infero-posterior MI | Infero-posterior MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 219 |
 |
RBBB - marquette | RBBB - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 220 |
 |
Triacylglycerol structure | The structure of a typical triacylglycerol (triglyceride). | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 221 |
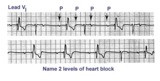 |
Second degree AV block, type I, with bradycardia-dependent RBBB | An interesting and unusual form of rate-dependent bundle branch block. Normal sinus rhythm at 85 bpm is present with a 3:2 and 2:1 2nd degree AV block. The progressive PR prolongation in the 3:2 block makes this a type-I or Wenckebach block.Long cycles end in RBBB; short cycles have normal QRS dur... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 222 |
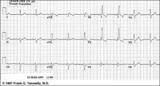 |
Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | This is the most common of the bifascicular blocks. RBBB is most easily recognized in the precordial leads by the rSR' in V1 and the wide S wave in V6 (i.e., terminal QRS forces oriented rightwards and anterior). LAFB is best seen in the frontal plane leads as evidenced by left axis deviation (-50... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
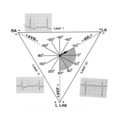
| 223 |
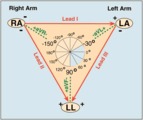 |
Frontal plane lead diagram | The six frontal plane leads are illustrated with their respective positive and negative poles.When forced to intersect at a center point, the six leads inscribe a 360 degree circle. The normal frontal plane axis is from -30 degrees to + 90 degrees, shaded in grey. Left axis deviation is from -30 d... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 224 |
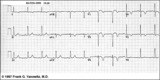 |
Anteroseptal MI: fully evolved | The QS complexes, resolving ST segment elevation and T wave inversions in V1-2 are evidence for a fully evolved anteroseptal MI. The inverted T waves in V3-5, I, aVL are also probably related to the MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 225 |
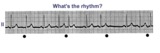 |
Atrial parasystole | The evenly spaced dots indicate ectopic atrial activity from a parasystolic atrial pacemaker. Non-fixed coupled PACs are seen having a common inter-ectopic interval. One of the PACs is nonconducted. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
