The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 201 |
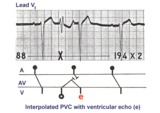 |
PVC with venticular echo | The PVC in this example retrogradely enters the AV junction and returns, usually down a different pathway, to reactivate the ventricles....a ventricular echo. This is unlikely to be an interpolated PVC because the PR interval following the PVC is too short for the sinus impulse to have entered the ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 202 |
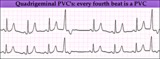 |
PVC's - marquette | PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 203 |
 |
PVCs - marquette | PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 204 |
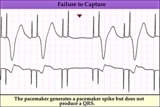 |
Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 205 |
 |
Pacemaker failure to pace - marquette | Pacemaker failure to pace - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 206 |
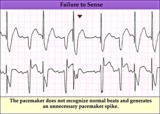 |
Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 207 |
 |
Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 208 |
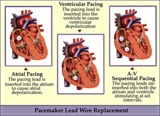 |
Pacemaker lead wire placement diagram - marquette | Pacemaker lead wire placement diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 209 |
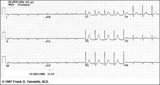 |
Postero-lateral MI: Fully Evolved | The true posterior MI is recognized by pathologic R waves in leads V1-2. These are the posterior equivalent of pathologic Q waves (seen from the perspective of the anterior leads). Tall T waves in these same leads are the posterior equivalent of inverted T waves in this fully evolved MI. The loss o... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 210 |
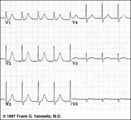 |
Postero-lateral MI: Precordial Leads | Postero-lateral MI: Precordial Leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 211 |
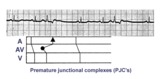 |
Premature junctional complexes with retrograde P waves | The ladder diagram illustrates the PJC with retrograde atrial capture | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 212 |
 |
Propionyl CoA carboxylase reaction | Propionyl CoA is metabolized by a process that first converts it to D-methylmalonyl CoA. The reaction is catalyzed by propionyl CoA carboxylase,and requires energy in the form of ATP. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 213 |
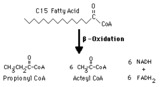 |
Propionyl CoA production from odd-chain fatty acids | Beta-oxidation of fatty acids with an odd number of carbons inthe chain yields the three-carbon propionyl CoA as the final fragment. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 214 |
 |
QRS axis = +30 degrees | Lead III is isoelectric; leads I and II are positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +30 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 215 |
 |
QRS axis = +60 degrees | Lead aVL is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 216 |
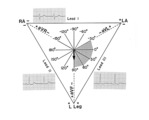 |
QRS axis = +90 degrees | Lead I is isoelectric; II and III are positive; the axis is +90 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 217 |
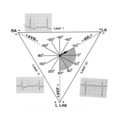 |
QRS axis = -30 degrees | Lead II is isoelectric; I is positive; III is negative. The axis is -30 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 218 |
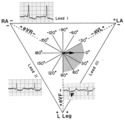 |
QRS axis = 0 degrees | Lead aVF is isoelectric; lead I is positive; therefore, the QRS axis is 0 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 219 |
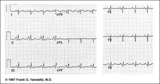 |
RAE & RVH | RAE & RVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 220 |
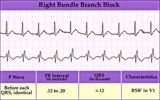 |
RBBB - marquette | RBBB - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 221 |
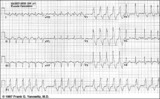 |
RBBB + LAFB = bifascicular block | The RBBB is diagnosed by the wide QRS with prominent anterior (e.g., V1) and late rightward (e.g., I, V6) forces. The LAFB is recognized by the marked left axis deviation (-75 degrees) in the frontal plane, rS complexes in II, III, aVF, and the tiny q-wave in aVL. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 222 |
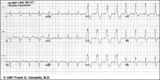 |
RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 223 |
 |
RBBB plus mobitz II 2nd degree AV block | The classic rSR' in V1 is RBBB. Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block is present because the PR intervals are constant. Statistically speaking, the location of the 2nd degree AV block is in the left bundle branch rather than in the AV junction. The last QRS in the top strip is a junctional escape, since... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 224 |
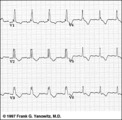 |
RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 225 |
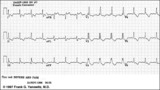 |
RBBB with primary ST-T wave abnormalities | RBBB is recognized by 1) rR' in V1; 2) QRS duration>0.12s; 3) terminal QRS forces oriented rightwards and anterior. In RBBB the ST-T waves should be oriented opposite to the terminal QRS forces. In this example there areprimary ST-T wave abnormalitiesin leads I, II, aVL, V5, V6. In these leads th... | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
