Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_novel_wfh
| Identifier | Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
 |
C_33 | C33 Anomalous Pale Disc | Woman. Multiple cilioretinal arteries. Veins all empty into eye. Anomalous venous exit from nasal edge of optic disc. Visual function normal. Pair with C_36. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc; Congenital |
| 177 |
 |
C_34 | C34 Anomalous Pale Disc | Multiple cilioretinal arteries. Anomalous venous exit from nasal edge of optic disc (Vein of Kraupa). Visual function normal. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc |
| 178 |
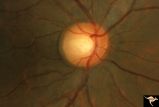 |
C_35 | C35 Anomalous Pale Disc | Macro disc appears pale because of large diameter. Woman. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc |
| 179 |
 |
C_36 | C36 Anomalous Pale Disc | Multiple cilioretinal arteries. Pale appearance. Normal optic nerve function. Good example of "empty disc". Pair with C_33. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc; Congenital |
| 180 |
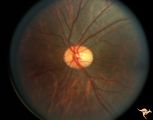 |
C_37 | C37 Anomalous Pale Disc | "Watermelon" disc. Woman. Normal function. Left eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc |
| 181 |
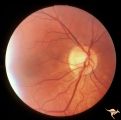 |
C_38 | C38 Anomalous Pale Disc | Megalopapilla in -8 myopic eye. Right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Clinical: High myope. | Cavitary Anomalies; Anomalous Pale Disc; Macro Disc |
| 182 |
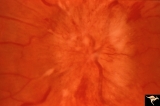 |
C4_01 | C401 Luetic Papillopathy (Gumma of the Optic Disc) | Diffuse optic disc swelling with tortuous capillary dilations indicating inflammatory cellular infiltration. October 2001. Same eye as C4_02. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to syphillitic infection. Luetic papillopathy (Syphyllis). Clinical: Visual loss. | Disc Swelling; Inflammatory Papillopathies; Luetic Papillopathy; Gumma of the Optic Disc); Syphilis |
| 183 |
 |
C4_02 | C402 Luetic Papillopathy (Gumma of the Optic Disc) | November 2001. Same eye as C4_01 after treatment with penicillin. Disc swelling went away and good visual function returned. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to syphillitic infection. Disease/ Diagnosis: Luetic papillopathy (Syphillis). Clinical: Improving visual loss. | Disc Swelling; Inflammatory Papillopathies; Luetic Papillopathy (Gumma of the Optic Disc); Syphilis |
| 184 |
 |
C4_03 | C403 Luetic Papillopathy (Gumma of the Optic Disc) | 40 year old man with AIDS and neurosyphillis with severe visual field defect. The disc is pale and swollen and its arteries are strikingly narrowed (syphillitic vasculitis). Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to syphillitic infection. Disease/ Diagnosis: Luetic papillopathy (Syphy... | Disc Swelling; Inflammatory Papillopathies; Luetic Papillopathy; Gumma of the Optic Disc |
| 185 |
 |
R2B1_2 | Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar macular degeneration in a 7 year old boy with blindness. Rectal biopsy positive for storage material. Nature of cerebral degeneration was not defined in era when picture was taken. Sister also had similar findings. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital r... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degeneration; Congenital Retinal Cerebellar Degeneration |
| 186 |
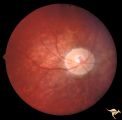 |
R2B1_3a | Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degenerative disease in a 12 year old boy who was blind and demented. His siblings were also blind. Was referred to as Voght-Spielmeyer Disease (Pair with R2_B1_3b shows granular retinal degeneration.) Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retina... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degeneration; Congenital Retinal Cerebellar Degeneration |
| 187 |
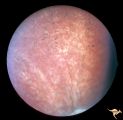 |
R2B1_3b | Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degenerative disease in a 12 year old boy who was blind and demented. His siblings were also blind. Was referred to as Vogt-Spielmeyer Disease. Pair with R2_B1_3a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retinal cerebral degeneration. Clinical: Sev... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degeneration; Congenital Retinal Cerebellar Degeneration |
| 188 |
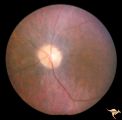 |
R2B1_4 | Cerebellar Macular Degeneration | Cerebellar retinal degeneration with narrowed arterioles. Disc pallor. Granular retinal degeneration. 10 year old boy with mental degenerations and seizures. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Optic atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Congenital retinal cerebellar degeneration. Clinical: Severe mental retardation ... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degeneration; Congenital Retinal Cerebellar Degeneration |
| 189 |
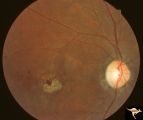 |
R2B2_1a | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Ocular fundus shows prominent retinal degeneration in the region of the maculae, bilateral optic disc pallor with narrowed retinal arterioles. Interesting peripapillary halo of retinal pigment degeneration. Most consistent with Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Anatomy: Retina. Patholog... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease; Olivopontocerebellar Degeneration; Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 7 |
| 190 |
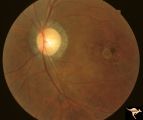 |
R2B2_1b | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Ocular fundus shows prominent retinal degeneration in the region of the maculae, bilateral optic disc pallor with narrowed retinal arterioles. Interesting peripapillary halo of retinal pigment degeneration. Most consistent with Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Anatomy: Retina. Patholog... | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease; Olivopontocerebellar Degeneration; Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 7 |
| 191 |
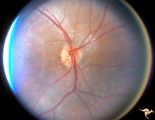 |
R2B2_2a | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Cerebellar degeneration with granular maculae changes and bone spicules. Right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar macular degenerative disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Clinical notes: Blindness and cerebellar degeneration. | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease |
| 192 |
 |
R2B2_2b | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Cerebellar degeneration with granular maculae changes and bone spicules. Right eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar macular degenerative disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Clinical notes: Blindness and cerebellar degeneration. | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease |
| 193 |
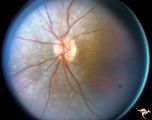 |
R2B2_2c | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Cerebellar degeneration with granular maculae changes and bone spicules. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar macular degenerative disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Clinical: Blindness and cerebellar degeneration. | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease |
| 194 |
 |
R2B2_2d | Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease | Cerebellar degeneration with granular maculae changes and bone spicules. Left eye. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebellar macular degenerative disease. Disease/Diagnosis: Spinal Cerebellar Degeneration Type 7 (SCA-7). Clinical notes: Blindness and cerebellar degeneration. | Pigmentary Retinopathy; Cerebellar Macular Degenerative Disease |
| 195 |
 |
R3D1 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Retinal signs of Susac's Syndrome in acute phase consist of areas of retinal artery infarction from branch retinal artery occlusions. These patients are usually women, many of whom are demented and have hearing loss. Refs: 1) Susac, Hardiman, Sellhorst. Neurology. 1979. 29:313-316 2) Susac ""Susa... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy |
| 196 |
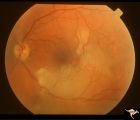 |
R3D2 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Retinal signs of Susac's Syndrome in acute phase consist of areas of retinal artery infarction from branch retinal artery occlusions. This fundus shows two area of retinal infarction from occlusion of both superior and inferior branch retinal arterioles. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Microangiopathy... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy; Retinal Disorders; Inflammatory; Infectious |
| 197 |
 |
R3D3 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Retinal signs of Susac's Syndrome in acute phase consist of areas of retinal artery infarction from branch retinal artery occlusions. Branch artery occlusion beginning to clear. Note the occluded arteriole lying on top of the infarcted zone. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Microangiopathy involving br... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy |
| 198 |
 |
R3D4 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Retinal signs of Susac's Syndrome in acute phase consist of areas of retinal artery infarction from branch retinal artery occlusions. Shows clearing retinal branch artery occlusion. Pathology: Retina. Pathology: Microangiopathy involving brain, auditory nerve and retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Cerebro... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy |
| 199 |
 |
R3D5 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | This fundus picture from a patient with Susac Syndrome shows a focal shiny plaque in the inferior retinal arteriole. This plaque is not the result of embolism, but is the result of the microangioplastic process underlying the syndrome. (NANOS 2001 by Egan, RA). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Microangi... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy |
| 200 |
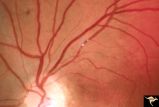 |
R3D6 | Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy (Susac Syndrome) | Two plaques which have been called Psuedo-emboli. This plaque is not the result of embolism, but is the result of the microangioplastic process underlying the syndrome. (NANOS 2001 by Egan, RA). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Microangiopathy involving brain, auditory nerve and retina. Disease/Diagnosi... | Occlusive Vascular Disease; Cerebroretinal Microangiopathy; Susac Syndrome; Retinocochleocerebral Vasculopathy |
