The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
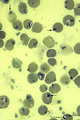 |
Reticulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: Brilliant cresyl blue. The blue stained reticulum strands and aggregates (1) are ribosomal residues in the young red blood cells that just have expelled their nuclei. The reticulocytes are not to be confused with large Heinz bodies. Heinz bodies (↓, arrows) are red cell inclusions composed ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 177 |
 |
Reticulocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: Brilliant cresyl blue. After expulsion of the erythroblastic nucleus the remaining cell is called reticulocyte. This staining visualizes the remained aggregated strands of polysomes as a fine network. The expulsed nucleus will be phagocytosed by macrophages and reticular cells in the bone mar... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 178 |
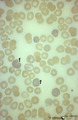 |
Reticulocytosis in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The slightly pale blue stained cells (1) represent the reticulocytes. These young red blood cells are stained bluish because of the presence of ribosomal RNA. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 179 |
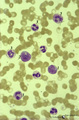 |
Shift to the left response of granulocytes in blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). During infection a shift towards a relative increase of the number of neutrophilic granulocytes (3) with reduced lobulation of the nuclei and immature white cells, occurs in blood. (1) promonocyte. (2) (pro)myelocyte. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 180 |
 |
Small, medium and large lymphocytes in blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The picture shows three activation stages of lymphocytes as (1) small, (2) medium and (3) large lymphocytes. In that range the nucleus becomes less condensed and more transparent, while the amount of cytoplasm increases. The large lymphocyte also contains some granul... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 181 |
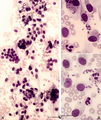 |
Survey and detail of a peripheral blood smear contaminated with endothelial cells (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Survey (A) and details (B) show aggregates of elongated cells with a large nucleus, mostly situated at the end of a smear between the erythrocytes and granulocytes. These endothelial cells are contaminants derived from blood vessels during puncture. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 182 |
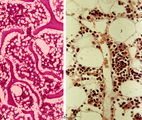 |
Survey and detail of bone marrow section (human) | Stain: modified hematoxylin and eosin (A, B). The bone marrow consists of bone trabecles or crests (1) covered with osteoclasts and osteoblasts. Between the trabecles bone marrow parenchym (2) consisting of progenitor cells, reticular cells and fat cells (3). Numerous capillaries (B, 4) and enlarged... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 183 |
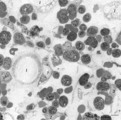 |
Survey of bone marrow (bone marrow, rabbit) | Electron microscopy. Within the loose reticular tissue a great variety of different stages of young erythrocytes (3, 4) as well as of young granulocytes (5) is present. (2) indicates reticular cells and (2b) phagocytizing reticular cells. (1) fat cells (adipocytes); (6) myeloid cell; (7) capillary. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 184 |
 |
Survey of bone marrow section (human) | Stain: modified hematoxylin and eosin. In this survey the white spots (1) are fat cells. The marrow is well filled with cells of erythropoietic and myelopoietic series. The very large cells are usually megakaryocytes. Cells with very dark condensed nuclei belong mostly to the erythropoietic series. | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 185 |
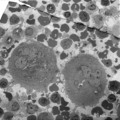 |
Survey of megakaryocytes (peripheral blood, human) | Electron microscopy. In a section of a so-called buffy coat collected from peripheral blood two huge polyploid megakaryocytes (1) (diameter up to 160 μm) are present. Note the dark granules in the future platelets. (2) erythroblasts; (3) reticulocytes and erythrocytes; (4, 5) monocytes. The arrows ... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 186 |
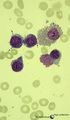 |
Three basophilic erythroblasts in bone marrow smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Three basophilic erythroblasts (1) with intense blue stained cytoplasm, and some so called ears or cytoplasmic projections (arrows). Chromatin strands are thicker than in the proerythroblast. Generally no nucleoli are seen. (2) Damaged or smudged eosinophilic myelocy... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 187 |
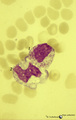 |
Toxic granulation and vacuolation in neutrophilic myelocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myelocyte (1) and the metamyelocyte (2) show toxic granulation and vacuolation and cytoplasmic swelling. Vacuoles may represent the terminal stage of autophagocytosis. Granules may burst and their contents undergo autophagocytosis in a number of pathologic condit... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 188 |
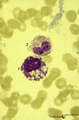 |
Toxic granulation and vacuolization in neutrophilic myelocytes in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). The myelocyte (1) and the metamyelocyte (2) show toxic granulation, vacuolisation and cytoplasmic swelling. Toxic granulation is characterized by violet-purple granules of varying size in the cytoplasm; generally admixed with normal pink granules. The phenomenon occu... | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset | |
| 189 |
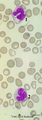 |
Vacuolar degeneration of neutrophils in peripheral blood smear (human) | Stain: May-Grnwald-Giemsa (MGG). Toxic degeneration of neutrophil resulting in vacuolization of cytoplasm (1); cell with beginning vacuolization (2). | Poja Histology Collection - Blood & Bone Marrow Subset |
