Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_wfh"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 176 |
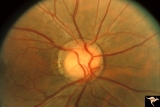 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | All venous systems drain through single vein. ""Where do they go?"" Disc edge veins of Kraupa. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 177 |
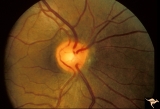 |
Venous Anomalies - Exit Anomalies | Inferior edge veins of Kraupa. Arterial branches appear to be cilioretinal. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Congenital anomaly, exit anomaly. Disease/Diagnosis: Exit anomaly, edge veins. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 178 |
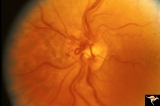 |
Venous Anomalies - Prepapillary Venous Convolutions (Acquired) | Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Acquired after central retinal vein occlusion. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Disease/Diagnosis: Prepapillary venous convolutions - acquired. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 179 |
 |
C31 Empty Disc | Right eye. Papillorenal Syndrome (PRS). Same patient as C_32. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 180 |
 |
C32 Empty Disc | Left eye. Papillorenal Syndrome (PRS). Same patient as C_31. Anatomy: Optic disc. | Image |
| 181 |
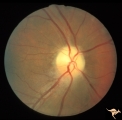 |
IB109 Post Ischemic (AION) Cupless Atrophy | Right eye, 1983 Top half of disc is pale. Striking focal arteriole narrowing. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 182 |
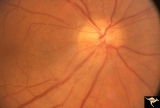 |
IB114a Post Ischemic (AION) Cupless Atrophy | 1991, acute AION in a disc with a cup, pair with IB1_14b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 183 |
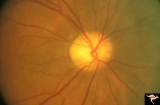 |
IB114b Post Ischemic (AION) Atrophy in a Disc with a Cup | 1996, same as IB1_14a five years later reveals pallor, arteriole narrowing and optic cup. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Disease/ Diagnosis: Post ischemic (AION) cupless atrophy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 184 |
 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation showing multiple arteriovenous shunts, both small and large. (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Arteriovenous loop in the inferior temporal r... | Image |
| 185 |
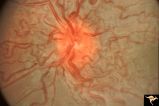 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Florid arteriovenous malformation of the optic disc and surrounding retina, Caput medusa (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. | Image |
| 186 |
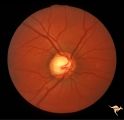 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis); Color of the retina is deep red (sometimes called tomato catsup) due to a four fold thickening of the choroidal vascular bed. Optic disc is cupped due to elevated intraocular pressure. (Secondary glaucoma) Patient had a major ""port wine"" m... | Image |
| 187 |
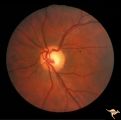 |
Sturge Weber Syndrome (Encephalotrigeminal Angiomatosis) | Left eye is normal, without the deep red from thickened Choroid. Pair with R1_B1a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Diffuse choroidal hemangioma; Glaucoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Sturge Weber Syndrome. Clinical: Port wine hemangioma of the face. | Image |
| 188 |
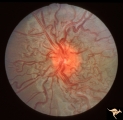 |
Vascular Disc Anomalies - Retinal Arteriovenous Malformations | Retinal arteriovenous malformations. No corresponding malformation of brain. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Retinal arteriovenous malformation. Clinical: Asymptomatic. | Image |
| 189 |
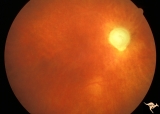 |
IC103c Central Retinal Artery Occlusion with Choroidal Arteriole Occlusion | 1988, Central retinal artery occlusion and choroidal vascular occlusion, 70 year old woman with history of central retinal artery occlusion 30 years prior. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Combined central retinal and choroidal arteriolar occlusion. Disease/ Diagnosis: Combined central retinal and ch... | Image |
| 190 |
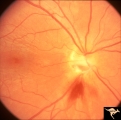 |
G103 Evulsion | Partial evulsion of the right optic nerve. Notice what is left of superior optic nerve. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic disc has been evulsed. Disease/ Diagnosis: Evulsion of the optic disc. | Image |
| 191 |
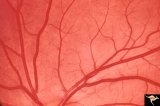 |
Ocular Hypertension | Chronic simple glaucoma. 1976. Magnified of IIB3_3a. Note slits in upper arcuate nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIB3_3a. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intra... | Image |
| 192 |
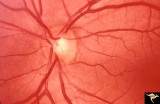 |
Ocular Hypertension | Chronic simple glaucoma. 1976. Note slits in upper arcuate nerve fiber layer. Pair with IIB3_3b. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
| 193 |
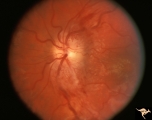 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with ""Twin Peaks"" papilledema. Central band of the optic disc is completely atrophic and does not swell. ""Axons that are not there can not swell."" Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Optic tract injury. Disease/Diagnosis: Twin peaks papilledema. Clinical: Left homony... | Image |
| 194 |
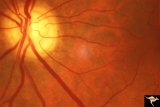 |
Diffuse Atrophy | Bilateral primary or retrograde optic atrophy from bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Pair with IIA1_2a. Left eye. 1984. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Disease/Diagnosis: Retrograde optic atrophy. Clinical: Bilateral visual loss. | Image |
| 195 |
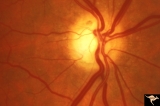 |
IIA102a Diffuse Atrophy | Bilateral primary or retrograde optic atrophy from bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Pair with IIA1_2b. Right eye. 1984. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Bilateral optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Disease/ Diagnosis: Retrograde optic atrophy. Clinical: Bilateral visual loss. | Image |
| 196 |
 |
Segmental Atrophy - Hemianopic (Band) Atrophy | Segmental Atrophy - Band atrophy with temporal hemianopia. 1983. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Atrophy of the chiasm or left optic tract. Disease/Diagnosis: Segmental band atrophy. Clinical: Right temporal field defect. | Image |
| 197 |
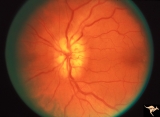 |
G208 Traumatic AION | Traumatic vitreopapillary evulsion (traumatic AION). Traumatic AION from evulsion of the vitreopapillary adhesion. Leakage on disc surface where vitreous was adherent. Pair with G2_9b. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: AION. Disease/ Diagnosis: Traumatic AION. | Image |
| 198 |
 |
G209 Traumatic AION | Traumatic vitreopapillary evulsion (traumatic AION). Fluorescein angiogram shows petal shaped avascular zones on the surface of the disc. Pair with G2_8a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: AION. Disease/ Diagnosis: Traumatic AION. Imaging: Flourescein angiogram. | Image |
| 199 |
 |
C403 Luetic Papillopathy (Gumma of the Optic Disc) | 40 year old man with AIDS and neurosyphillis with severe visual field defect. The disc is pale and swollen and its arteries are strikingly narrowed (syphillitic vasculitis). Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Axoplasmic stasis due to syphillitic infection. Disease/ Diagnosis: Luetic papillopathy (Syphy... | Image |
| 200 |
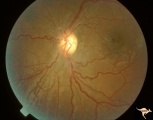 |
ID05a Post Papilledema Optic Atrophy from Pseudotumor Cerebri | Left eye, October 1999, Post papilledema optic atrophy from pseudotumor cerebri. Note optociliary veins in both discs. Gliosis and partial pallor following long standing papilledema and intracranial pressure. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Post papilledema atrophy and gliosis from long standing el... | Image |
