John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Measuring Visual Acuity | Demonstration on self of visual acuity exam, using a standard card. | Image/MovingImage |
| 152 |
 |
Spiral and Stellate Visual Fields Non-physiologic Variants | Description of testing the spiral and stellate visual fields. | |
| 153 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of Third Nerve, Bilaterally (1 degree OD, 2 Digrees OS) | Example of patient with bilateral aberrancy of the third nerve. Shows lids popping up (synkinetic) with adduction. Patient had bilateral internal carotid artery aneurisms with third nerve compression. | Image/MovingImage |
| 154 |
 |
Introduction to Headache, Migraine and Secondary Headaches | Video lecture covering an introduction to headache, migraine, and secondary headaches by Kathleen Digre, MD. | |
| 155 |
 |
Transillumination - Lisch Nodules | Demonstration of transillumination of the Lisch nodules on a patient with neurofibromatosis. Shows how Lisch nodules that were not very visible in slit-lamp examination are better seen with transillumination, which may therefore be useful in detecting Lisch nodules earlier in children where they are... | Image/MovingImage |
| 156 |
 |
Introduction to the Basic Neurologic Exam | Introduction to the neurological examinations section of NExT. | |
| 157 |
 |
Nutritional Amblyopia | Example of patient with amblyopia with nutritional causes. | Text |
| 158 |
 |
Blepharospasm | Example of patient with blepharospasm. Patient is led through instructions for direction of gaze and opening and closing of eyes. Patient is led through same exercises again after receiving indomethacin treatment. | Image/MovingImage |
| 159 |
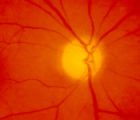 |
4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 160 |
 |
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | PPT describing Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION). Covers clinical signs, such as monocular vision loss, swollen nerve, and visual field defects, as well as risk factors. | Text |
| 161 |
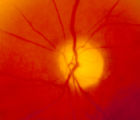 |
4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 162 |
 |
Optic Disc: Anatomy, Variants, Unusual discs | Discussion of viewing the optic disc. Includes development of direct ophthalmoscope. Covers normal optic disc and nerve fiber; nerve fiber loss and defects; cilioretinal arteries; venous anomolies; papilledema; pseudopapilledema; myopic disc; hyperoptic disc; little red discs; megallopapilla; myelin... | Text |
| 163 |
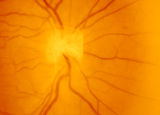 |
3-3 - Bergmeister Papilla | Image | |
| 164 |
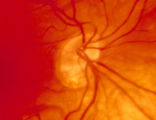 |
3-4 - Tilted Disc | Tilted discs are normal variants caused by oblique insertion of the optic nerve to the globe. They can be and frequently are mistaken for papilledema. In this case the superior edge of the disc is tilted and appears elevated. This disc exhibits a nasal inferior tilt. | Image |
| 165 |
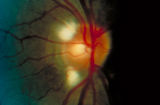 |
3-5b - Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Myelinated nerve fibers are frequently confused with papilledema. The feathery edge of the myelinated fibers that conceal the disc and vessel should provide the clue. These myelinated nerve fibers make the disc look blurred. | Image |
| 166 |
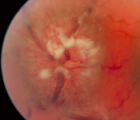 |
3-35a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 4 Stage 4 = Complete obliteration of the cup and complete obscuration of at least some vessels on the surface of the disc. There may be small dilated capillaries on the disc that resemble telangiectasia. It is not the NFL infarcts or hemorrhages but the obscuration of the ... | Image |
| 167 |
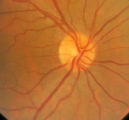 |
3-31b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 0 GRADING PAPILLEDEMA GRADING PAPILLEDEMA We grade papilledema in order to tell us how severe it is. The most sensible grading scheme has been provided by Lars Frisén. STAGE 0: This woman had documented increased intracranial pressure of 340 mm water. Very little if any ... | Image |
| 168 |
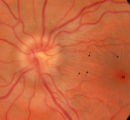 |
3-32b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 1 Stage 1 = C shaped blurring of the nasal, superior and inferior borders. Usually the temporal margin is normal. Also notice the chorio-retinal folds (arrows) that eminate toward the macula (m) | Image |
| 169 |
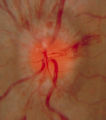 |
3-34c Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 3 Stage 3 = Elevation of the entire disc with partial obscuration of the retinal vessels at the disc margin. Here the vessels are partly obscured and make the development into stage 3 easier to call. | Image |
| 170 |
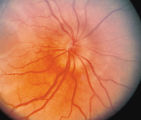 |
3-33b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 2 = Elevation of the disc margin 360 degrees. Since the blood vessels at the disc margin are not swollen or obscured, this disc could be mistaken for pseudo-papilledema. | Image |
| 171 |
 |
Papilledema 2013 | Discussion of papilledema, the swelling due to increased pressure. | Text |
| 172 |
 |
Stages of Papilledema | Text | |
| 173 |
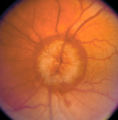 |
3-36a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 5 Stage 5 = Dome-shaped appearance with all vessels being obscured. (Sometimes called "champagne cork" swelling--because of its dome shape.) | Image |
| 174 |
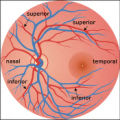 |
2-37a - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 175 |
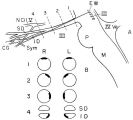 |
Location of Pupillomotor Fibers | Location of pupillomotor fibers are depicted as dark regions on cross-sections of the right (R) and left (L) oculomotor nerve at various locations along its course, including its emergence from the brain stem in the interpeduncular fossa (1), the midsubarachnoid segment (2), the level of the dorsum ... | Image |
