The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
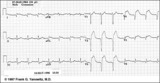 |
Extensive anterior/anterolateral MI: recent | Significant pathologic Q-waves (V2-6, I, aVL) plus marked ST segment elevation are evidence for this large anterior/anterolateral MI. The exact age of the infarction cannot be determined without clinical correlation and previous ECGs, but this is likely a recent MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 152 |
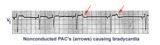 |
Nonconducted PAC's slowing the heart rate | Consecutive nonconducted PAC's, indicated by arrows, can significantly slow the heart rate. Note the distortion of the ST-T waves caused by the PAC. A hint in recognizing nonconducted PAC's is to find conducted PAC's in the same rhythm strip. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 153 |
 |
three fates of PAC's: 1. normal conduction; 2. aberrant conduction; 3. non-conduction | three fates of PAC's: 1. normal conduction; 2. aberrant conduction; 3. non-conduction | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 154 |
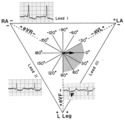 |
QRS axis = 0 degrees | Lead aVF is isoelectric; lead I is positive; therefore, the QRS axis is 0 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 155 |
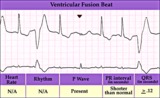 |
Ventricular fusion beat - marquette | Ventricular fusion beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 156 |
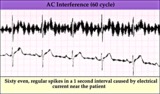 |
60 cycle artifact - marquette | 60 cycle artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 157 |
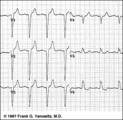 |
LBBB: precordial leads | LBBB: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 158 |
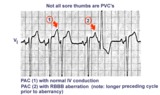 |
Not all sore thumbs are ventricular in origin | PACs have three fates: normal conduction into ventricles, aberrant conduction in ventricles due to bundle branch or fascicular block, and non-conduction due to block in AV junction. In this example PAC 1 is normally conducted and PAC 2 is conducted with RBBB aberration. The longer preceding cycle ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 159 |
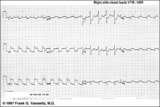 |
Acute infero-postero-lateral MI | Hyperacute ST segment elevation is seen in leads II, III, aVF (inferior location) and in leads V4-6 (apical lateral wall location). Hyperacute ST depression is seen in leads V1-2 (an expression of posterior wall injury). in addition there are reciprocal ST segment depression changes in leads I an... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 160 |
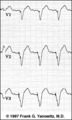 |
Ventricular Pacemaker Rhythm: V1-3 | Note the small pacemaker spikes before the QRS complexes. In addition, the QRS complex in V1-3 exhibits ventricular ectopic morphology; i.e., there is a slur or notch at the beginning of the S wave, and >60ms delay from onset to QRS to nadir of S wave. This rules against a supraventricular rhythm wi... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 161 |
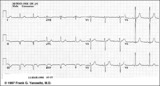 |
Inferior MI: fully evolved | Significant pathologic Q-waves are seen in leads II, III, aVF along with resolving ST segment elevation and symmetrical T wave inversion. This is a classic inferior MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 162 |
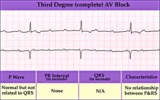 |
Complete AV block (3rd degree) with junctional rhythm | Complete AV block (3rd degree) with junctional rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 163 |
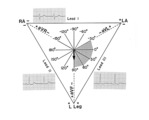 |
QRS axis = +90 degrees | Lead I is isoelectric; II and III are positive; the axis is +90 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 164 |
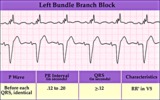 |
Left bundle branch block - marquette | Left bundle branch block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 165 |
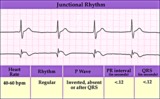 |
Junctional escape rhythm | Junctional escape rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 166 |
 |
Acetyl CoA structure | Acetyl CoA Structure. The thioester bond linking the acetyl group to CoA is ahigh energybond. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 167 |
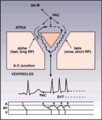 |
Diagram: AV nodal reentrant tachycardia | The AV node often has dual pathways; in this diagram the alpha pathway is fast, but has a long refractory period; the beta pathway is conducts more slowly, but recovers faster.In sinus rhythm the faster alpha pathway is used and accounts for the normal PR interval. When a PAC occurs, however, the i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 168 |
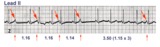 |
Atrial parasystole | In atrial parasystole non-fixed coupled PACs, shown by arrows, occur at a common inter-ectopic interval or at multiples of this interval. Atrial fusions, not shown here, may also occur when the PAC occurs in close temporal proximity to the sinus impulse. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 169 |
 |
Use of greek letters to designate carbons in fatty acids | The carbon next to the -COOH group is the alpha carbon; the next one is the beta carbon, and so forth. The carbon most distant from the -COOH group is designated omega. Carbons close to the omega carbon may be designated in relation to it. E.g., the third carbon from the end is omega - 3, and the... | Nomenclature | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 170 |
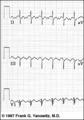 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction: leads II, III, V1 | Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction: leads II, III, V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 171 |
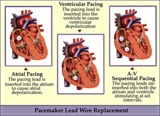 |
Pacemaker lead wire placement diagram - marquette | Pacemaker lead wire placement diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 172 |
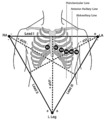 |
Frontal and horizontal plane lead diagram | Frontal and horizontal plane lead diagram | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 173 |
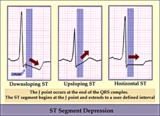 |
ST segment diagram - marquette | ST segment diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 174 |
 |
Atrial bigeminy - marquette | Atrial bigeminy - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
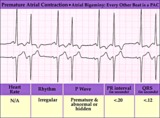
| 175 |
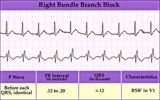 |
Right Bundle Branch Block | Right Bundle Branch Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
