The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
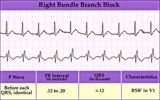 |
Right Bundle Branch Block | Right Bundle Branch Block | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 152 |
 |
2nd degree AV block, type I, with accelerated junctional escapes and a ladder diagram | The ladder diagram illustrates a Wenckebach type AV block by the increasing PR intervals before the blocked P wave. After the blocked P wave, however, a rev-ed up junctional pacemaker terminates the pause. Note that the junctional beats have a slightly different QRS morphology from the sinus beats... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 153 |
 |
Atrial tachycardia with exit block and AV block | The ectopic P waves, easily seen in this example,occur in groups, separated by short pauses. This is likely due to an exit block just distal to the atrial pacemaker. Because not all of the P waves make it to the ventricles, there is also 2nd degree AV block. Therefore, two levels of block are pre... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 154 |
 |
LVH | In this example of LVH, the precordial leads don't meet the usual voltage criteria or exhibit significant ST segment abnormalities. The frontal plane leads, however, show voltage criteria for LVH and significant ST segment depression in leads with tall R waves. The voltage criteria include 1) R in a... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 155 |
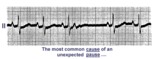 |
A nonconducted PAC causes an unexpected pause | Unexpected pauses in rhythm have several causes, the most frequent being a nonconducted PAC. In this example the nonconducted PAC is seen in the ST segment of the pause. Note the change in the ST-T compared to the other ST-T waves. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 156 |
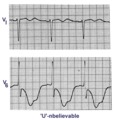 |
Giant TU fusion waves | TU fusion waves are often seen in long QT syndromes. The differential diagnosis of this ECG abnormality includes electrolyte abnormalities -hypokalemia, CNS disease, e.g., subarachnoid hemorrhage; hereditary long QT syndromes, and drugs such as quinidine. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 157 |
 |
Left anterior fascicular block (LAFB) | LAFB is the most common of the intraventricular conduction defects. It is recognized by 1) left axis deviation; 2) rS complexes in II, III, aVF; and 3) small q in I and/or aVL. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 158 |
 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction: lead V1 | The arrows point to two flutter waves for each QRS complex. Atrial rate = 280; ventricular rate = 140. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 159 |
 |
Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Long QT Interval and Giant Negative T Waves | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 160 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -15 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 161 |
 |
Ventricular pacemaker rhythm | Note the small pacemaker spikes before the QRS complexes in many of the leads. In addition, the QRS complex in V1 exhibits ventricular ectopic morphology; i.e., there is a slur or notch at the beginning of the S wave, and>60ms delay from onset to QRS to nadir of S wave. This rules against a suprav... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 162 |
 |
Diffuse anterolateral T wave abnormalities | Diffuse anterolateral T wave abnormalities | T Wave Abnormalities | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
| 163 |
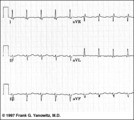 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -45 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 164 |
 |
Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Marked sinus arrhythmia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 165 |
 |
Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Muscle tremor artifact - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 166 |
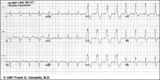 |
RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | RBBB + LAFB: bifascicular block | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 167 |
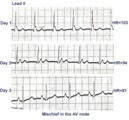 |
ECG of the century: A most unusual 1st degree AV block | On Day 1, at a heart rate of 103 bpm the P waves are not clearly defined suggesting an accelerated junctional rhythm. However, on Day 2, at a slightly slower heart rate the sinus P wave suddenly appears immediately after the QRS complex. In retrospect, the sinus P wave in Day 1 was found burried i... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 168 |
 |
RBBB plus mobitz II 2nd degree AV block | The classic rSR' in V1 is RBBB. Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block is present because the PR intervals are constant. Statistically speaking, the location of the 2nd degree AV block is in the left bundle branch rather than in the AV junction. The last QRS in the top strip is a junctional escape, since... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 169 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -60 degrees | Lead aVR is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly negative. The QRS axis, therefore, is -60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 170 |
 |
QRS axis = +30 degrees | Lead III is isoelectric; leads I and II are positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +30 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 171 |
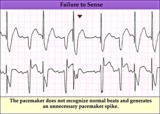 |
Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Pacemaker failure to sense - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 172 |
 |
Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Pacemaker fusion beat - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 173 |
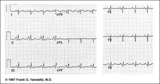 |
RAE & RVH | RAE & RVH | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 174 |
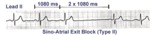 |
Type II, 2nd degree sino-atrial block | Two types of 2nd degree SA block have been described. In type-I, or SA Wenckebach, the P-P interval of the pause is less than 2x the preceding P-P intervals. In type-II SA block the P-P interval of the pause is approximately 2x the normal P-P interval. The distinction between types I and II is no... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 175 |
 |
Bradycardia-dependent LBBB with carotid sinus massage | When carotid sinus massage slows the heart rate in this example, the QRS widens into a LBBB. This form of rate-dependent bundle branch block is thought to be due to latent pacemakers in the bundle undergoing phase 4 depolarization; when the sinus impulse enters the partially depolarized bundle, slow... | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
