The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 151 |
 |
Scheme survey uvula - soft palate, human, adult | 1. nasal side - pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium (respiratory epithelium); 2. oral side - non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; 3. mixed glands (pharyngeal glands); 4. uvular muscle; 5. mucous palatine glands | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 152 |
 |
Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue - human, adult | 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform papillae; 6. fungiform papillae; 7. epiglottis; 11. lingual tonsils | oral cavity | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 153 |
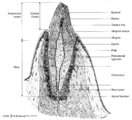 |
Scheme survey tooth (longitudinal section; human; canine) | Canine tooth in osseous alveolus. | oral cavity; pulp canal | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 154 |
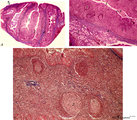 |
Survey and details of palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The survey in (A) shows that the palatine tonsil (localized in the lateral wall of the oropharynx) consists of crypts (1) and folds of the surface epithelium (stratified squamous) surrounded by accumulations of lymphoid cells organized in follicles (2). (B): the lining epithelium (5) i... | stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 155 |
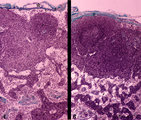 |
T cell depletion in lymph nodes (dog) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Left and right: survey of lymph nodes. A: lymph node after treatment with anti-thymocyte-antiserum (ATS); B: normal, untreated lymph node ATS treatment results in a considerable depletion of the T cells in the paracortical area (2), while also the germinal centre (1) i... | T cell depletion; follicle; medulla; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 156 |
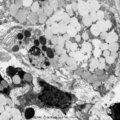 |
Submandibular gland (gerbil) | Electronmicroscopy. Upper two mucous cells of a seromucous acinus contain secretion droplets of different densities (light grey). Note partly fused mucous droplets. In the middle a serous cell cell with darkly stained granules. At the bottom a dense stained intercalated cell without granules. The ba... | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 157 |
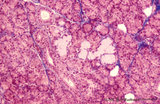 |
Submandibular gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The submandibular gland consists of mixed glands, i.e., the serous cells outnumber the mucous cells (seromucous acini). Locally crescent-shaped groups of serous cells (demi-lunes of Giannuzzi) are localized close to mucous cells to form an acinus.Intralobular ducts (left half) and thin ... | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 158 |
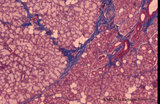 |
Sublingual gland (human) | Stain: Azan. The sublingual gland is a mixed gland and characteristic in human is the presence of large areas of serous cells neighboring areas with mucous cells. Inter- and intra-lobular ducts are present. Note inter- and intra-lobular septa (blue) and scattered fat cells (white). | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 159 |
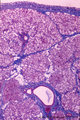 |
Submandibular gland (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey: on top capsule of dense connective tissue (blue) with septa dividing parenchyma of serous cells into lobules. At the bottom a large interlobular duct. Note white fat cells (adipocytes). | oral cavity; seromucous gland | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 160 |
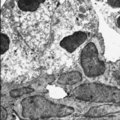 |
Submandibular gland (rat) | Electronmicroscopy. Darkly stained cells around the lumen of an intercalated duct and close to the lightly stained (partly degranulated) serous cells. | oral cavity; seromucous gland; intercalated duct | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 161 |
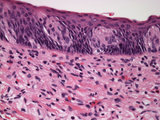 |
Taste bud | Human taste bud with underlying neural tissue. | HEAL Reviewed Collection | |
| 162 |
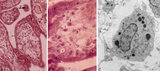 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, midpregnancy) | (A) Lower and (B) higher magnification. Stain: Hematoxylin - azophloxine. (C) electron microscopy of Hofbauer cell. (A, B) show tertiary villi and intervillous spaces. Squeezed between villi fibrinoid clots (1). The large arrow (2) points to either a detached, free circulating large STC (syncyt... | placenta; chorionic villi; Hofbauer cell; fibrinoid; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 163 |
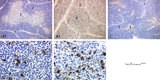 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the resident macrophages in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days. The darkly stained cortex of th normal thymus (A1, A2) decreases its dark stain... | cyclophosphamide; ED1 macrophages ; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 164 |
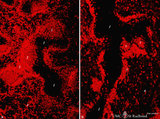 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. A: Normal rat spleen. (1) the dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) filled with T cells. (2) red-stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; immunofluorescence; B lymphocytes | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 165 |
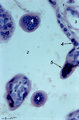 |
Tertiary villi (human placenta, full-term, cross-section) | Stain: Hematoxylin ? azophloxine. A few tertiary villi (1) within the intervillous space (2) contains capillary (3) and embryonic connective tissue (*). It remains covered by the postmitotic multinucleated syncytiotrophoblast cell (STC, 4). Distinct nuclear accumulation in the STC indicates the so-c... | placenta; tertiary villi; syncytiotrophoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Placenta |
| 166 |
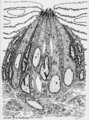 |
Taste bud of the tongue | Scheme electronmicroscopy. Generally a taste bud is composed of about 20 to 70 spindle-shaped epithelial cells. Slender type I cell ('Dark' cell) and oval shaped type II cell ('Light' cell) with a pale, round nucleus with their apices end in microvilli in the taste pore. The number of type I cells i... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore; electronmicroscopy | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 167 |
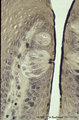 |
Taste buds of foliate papillae of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit) | Stain: Heidenhain's iron hematein. Taste buds within the lining (non-keratinized) epithelium of the groove. Note the pore in the left taste bud, with darkly stained fluffy apical microvilli. The lightly stained gustatory nerve fibers (nuclei of Schwann cells) approach the left taste buds. The taste ... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 168 |
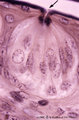 |
Taste bud of a foliate papil of the tongue (dorsal side, rabbit; high magnification) | Stain: Heidenhain's iron hematein. Taste bud with slender cells and darker stained spiky nuclei (type I cell), and cells with light stained round nuclei (type II cells). Below axons of the gustatory nerve fibers and nuclei of Schwann cells. Arrow points to narrow pore where dark stained fluffy struc... | oral cavity; foliate papillae; taste pore | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 169 |
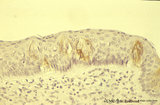 |
Taste bud of a foliate papilla of the tongue (dorsal side, human) | Stain: antikeratin-7 / immunoperoxidase and hematoxylin counterstained. Type I cells with small slender nuclei are identified by positive staining with cytokeratin 7 (monoclonal antibody OVTL12/30). | cytokeratin; oral cavity; foliate papilla; von Ebner | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 170 |
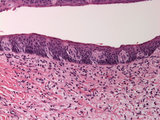 |
Taste bud | Human taste bud with underlying neural tissue. | HEAL Reviewed Collection | |
| 171 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. Oral side (left) with stratified squamous epithelium, at the right side part of a tooth (dentin), at the bottom side part of the alveolar bone. The epithelium shows slight parakeratosis with many narrow deep papillae of the lamina propria (oral side). On the tooth-relat... | oral cavity; junctional epithelium; alveolar bone; gingival sulcus | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 172 |
 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top part of the gingival sulcus, at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Top left shows foci of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, left side faint stained bundle of fibers (p... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 173 |
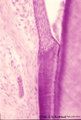 |
Tooth ('free' gingiva of decalcified tooth, human, adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin and eosin. On top the gingival sulcus; at the left stratified junctional epithelium normally attached to the surface of the enamel (dissolved due to decalcification). Below the epithelium a focus of chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, followed by a bundle of fibers of the per... | oral cavity; acellular cementum; junctional epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 174 |
 |
Tongue (macroscopy, dorsal side, human) | At the bottom (apex) of the picture the dorsal side is covered with numerous closed packed, small, conical filiform papillae. Interspersed among them are the larger fungiform papillae. Posteriorily the circumvallatae papillae are arranged in a V-shape row. Behind the V-row the area is covered with l... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
| 175 |
 |
Tongue Papillae Scheme - tongue, human, adult | A. Scheme survey dorsal surface of tongue (human, adult). Magnification 35x. B. Scheme of filiform and fungiform papillae (tongue, human, adult). Magnification 35x. 1. foliate papillae (rudimentary in human); 2. circumvallate papillae; 3. foramen cecum; 4. palatine tonsils; 5. filiform ... | oral cavity; papillae | Poja Histology Collection - Oral Cavity Subset |
