Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 126 |
 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Left eye. Upper arcuate nerve fiber layer contains multiple low density slits. These indicate nerve fiber loss. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 127 |
 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Multiple slit defect in the superior arcuate nerve fiber layer in a 13 year old boy. Right eye. Pair with IIB2_7a. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 128 |
 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Multiple slit defect in the superior arcuate nerve fiber layer in a 13 year old boy. Pair with IIB2_7b. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 129 |
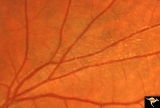 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Need magnification - Left eye - Peculiar punctate dotted surface of internal limiting membrane reflexes. Pairs with IIB2_01a & IIB2_02b. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 130 |
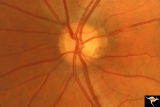 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Need magnification - Left eye - Inferior arcuate nerve fiber slits. Pairs with IIB2_01b & IIB2_01c. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 131 |
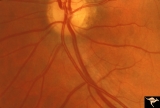 |
Multiple Sclerosis Slits and Thinning in Peripapillary (Retinal) Nerve Riber Layer | Need magnification - Left eye - Inferior arcuate nerve fiber slits. Pairs with IIB2_01a & IIB2_01c. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like atrophy. Disease/Diagnosis: Multiple sclerosis optic neuropathy. Clinical: No symptoms. | Image |
| 132 |
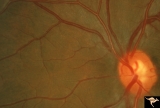 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | Normal nerve fiber layer with Gunn's Dots visible in the upper arcuate fiber zone. This is a normal peripapillary nerve fiber layer in a young woman. Note the way the nerve fiber striations obscure and partially bury the small vessels running across them. Also note the interrupted surface reflex on ... | Image |
| 133 |
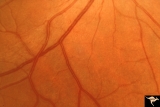 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | Example of 23 year old woman, healthy nerve fiber layer below her optic disc. This is a normal peripapillary nerve fiber layer in a young woman. Note the way the nerve fiber striations obscure and partially bury the small vessels running across them. Also note the interrupted surface reflex on arter... | Image |
| 134 |
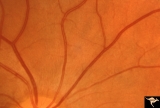 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | Example of 23 year old woman, healthy nerve fiber layer below her optic disc. This is a normal peripapillary nerve fiber layer in a young woman. Note the way the nerve fiber striations obscure and partially bury the small vessels running across them. Also note the interrupted surface reflex on arter... | Image |
| 135 |
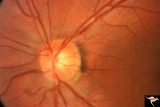 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | This is a normal peripapillary nerve fiber layer in a young woman. Note the way the nerve fiber striations obscure and partially bury the small vessels running across them. Also note the interrupted surface reflex on arteries due to interposed nerve fiber layer tissue. All these vessels are buried i... | Image |
| 136 |
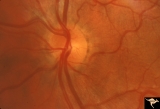 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | This picture is a sample of a normal healthy nerve fiber layer temporal to the optic disc. Note how the nerve fiber layer obscures the small arteriolar branches running within it. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Normal healthy young retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal nerve fiber layer and retina. | Image |
| 137 |
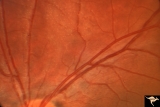 |
Normal Peripapillary Nerve Fiber Layer | Magnification of same disc shown in 1a. Whole fields of Gunn's Dots are visible. Note the way that the reflexes from the internal limiting membrane bend over vertically running arterioles. This is a tent-like effect. Gunn's Dots are footplates of Muller's cells and reflect light from the ophthalmosc... | Image |
| 138 |
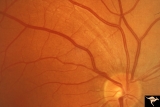 |
Ocular Hypertension | There is an argument about whether this is a pseudo nerve fiber layer defect, because defect does not reach the disc. The vessels transversing the defect are not exposed and there is no change in the visual field and no other slit like defects. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Sl... | Image |
| 139 |
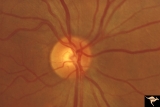 |
Ocular Hypertension | Need color work to show superior slit 1972. Right eye. Ocular hypertension. No field defect recognized. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Ocular hypertension. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
| 140 |
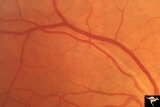 |
Ocular Hypertension | 1972. Right eye. Ocular hypertension. No field defect recognized. Pair with IIB1b & c. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
| 141 |
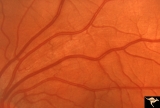 |
Ocular Hypertension | Multiple slit like defects in the upper arcuate nerve bundles. 1971. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
| 142 |
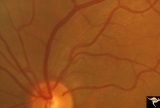 |
Ocular Hypertension | Multiple slit defects in the upper arcuate bundles. 1972. Anatomy: Peripapillary nerve fiber layer. Pathology: Slit-like defects in the arcuate nerve fiber bundles. Disease/Diagnosis: Elevated intraocular pressure. Clinical: Elevated intraocular pressure. | Image |
| 143 |
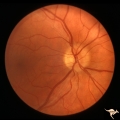 |
P43a Asymmetrical Papilledema due to Brain Tumor | Right eye. Early papilledema. Incipient papilledema barely recognizable. Early papilledema due to posterior fossa meningioma in a boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Papilledema. Disease/ Diagnosis: Asymmetrical papilledema due to posterior fossa meningioma. | Image |
| 144 |
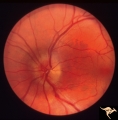 |
P43b Asymmetrical Papilledema due to Brain Tumor | Left eye. Early papilledema. Clearly has papilledema. Early papilledema to posterior fossa meningioma in a boy. | Image |
| 145 |
 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome with extreme retino-arteriolar narrowing. CAR Syndrome. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Disease/Diagnosis: Cancer associated retinopathy. Clinical: Progressive visual loss, progressive night blindness,... | Image |
| 146 |
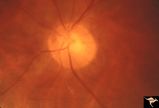 |
Paraneoplastic Retinopathy | Cancer associated retinopathy syndrome with extreme retino-arteriolar narrowing. CAR Syndrome. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Oat cell carcinoma of the lung with paraneoplastic retinopathy. Disease/Diagnosis: Cancer associated retinopathy. Clinical: Progressive visual loss, progressive night blindness,... | Image |
| 147 |
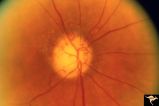 |
R3C9 Nettleship Collaterals: a Result of Calcific Embolization of the Central Retinal Artery | Result of calcific embolization of the central retinal artery. The embolus itself can not be seen within the tissue of the optic disc. Numerous chorio-retino collaterals are filling the branches of a central retinal artery. Such an eye is always blind. These collaterals indicate that the patient pro... | Image |
| 148 |
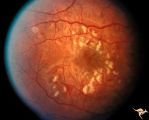 |
Retinal (Macular) Involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy | Retinal (macular) involvement in Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Note interesting microvascular changes associated with the retinal disease. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Cerebral and retinal degeneration. Disease/Diagnosis: Subacute Sclerosing Pan Encephalopathy (SSPE). Clinical: Progr... | Image |
| 149 |
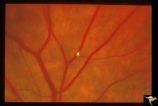 |
Retinal Signs of Atheromatous Embolization | Retinal signs of atheromatous embolization. Note the way the cholesterol emboli stick at arteriole bifurcation. Note second plaque hidden at the juncture below. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Intraluminal cholesterol crystals. Disease/Diagnosis: Carotid atheromatous vascular disease. Clinical: No visua... | Image |
| 150 |
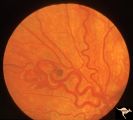 |
Retinocerebral Arteriovenous Malformation (Wyburn Mason Syndrome) | Retinocerebral arteriovenous malformation showing one major arteriovenous loop. (Cross reference with V12-28 this section). Cross reference with V12-28 this section, Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Arteriovenous malformation. Disease/Diagnosis: Wyburn Mason Syndrome. Clinical: Single arteriovenous l... | Image |
