The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_heal"
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
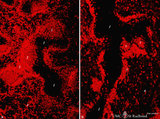 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. A: Normal rat spleen. (1) the dark, unstained area represents the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) filled with T cells. (2) red-stained germinal centre of a B cell follicle that is surrounded by the marginal zone (3... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; immunofluorescence; B lymphocytes | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 102 |
 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on CD3-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section.. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the dark-blue stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thy... | cyclophosphamide; CD3 monoclonal antibody; lymphoid tissue ; immunosuppression | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 103 |
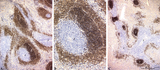 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on splenic B cells (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section of B cells with the antibody Mark-1. The PALS area (1) contains T cells and remains unstained blue. The positively stained B cells (brown) are found in the germinal centres (2) and in the coron... | cyclophosphamide; immunosupression; B lymphocytes; Mark 1 antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 104 |
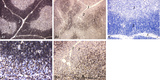 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the CD8-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the darkly stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thymus ... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 105 |
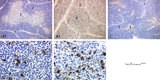 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the resident macrophages in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days. The darkly stained cortex of th normal thymus (A1, A2) decreases its dark stain... | cyclophosphamide; ED1 macrophages ; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 106 |
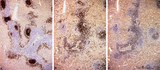 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide treatment on the B and T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with antibodies to B cells (Mark 1), CD3 and CD8 T cells. (A): B cells in the follicles, germinal centres (2) and corona are stained positive brown, while the PALS area (1) is negative (blue)... | CD3 lymphocytes; CD8 lymphocytes; B lymphocytes; cyclophosphamide | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 107 |
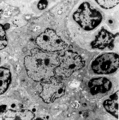 |
Thymic nurse cell (TNC) (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The thymic nurse cell (TNC) consists of an epithelial reticular cell (type II) enclosing thymocytes. The TNC exists as a sealed structure in situ, i.e. the lymphocytes within the TNC are isolated from the general thymic environment. TNC are located in the cortex, where mature ... | epithelioreticular cell type II; thymic nurse cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 108 |
 |
Thymus (human, fetus) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Reticular fibers are demonstrated in the interlobular septa in the thymic cortical area (2) of this lobule. In the medulla (1) the more loosened reticular framework is more distinct. The reticular fibers are produced by the epithelioreticular cells and are particular ... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); reticular fibers; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 109 |
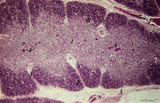 |
Thymus (human, newborn) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The thymus is a bilobed lymphoepithelial organ derived as an outgrowth from the third branchial (pharyngeal) pouch, and situated in the anterior mediastinum. Each lobe is divided into multiple lobules by fibrous septa or trabeculae (3). Each lobule consists of an outer co... | epithelioreticular cells (ERC); thymus hormones; Hassalls corpuscle ; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 110 |
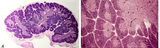 |
Thymus (human, newborn, low and higher magnification) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabeculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a l... | Zhen; thymus cortex; thymus medulla; Hassall's corpuscle ; Lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 111 |
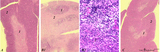 |
Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 4 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation. A: Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2). B1: Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP ... | cyclophosphamide; immunosuppression; involution; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 112 |
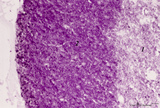 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Stain: Hematoxylin. Autoradiography after pulse labeling with tritiated thymidin. Most of the (black) radioactive labeling is found in the outer thymic cortex (3) where pre-T cells divide and subsequently migrate to the lighter stained medulla (1) that consists of a more loosened framework of epith... | thymus cortex; thymus medulla; thymidin labeling; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 113 |
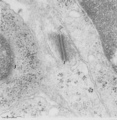 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. (1) A well developed desmosome (1) of an epithelioreticular cells type II (TEC2). Apart from few free ribosomes, glycogen granules (2) are present in the electron-light cytoplasm. (3) part of an electron-grey thymocyte with many ribosomes. | epithelioreticular cell type II ; desmosome; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 114 |
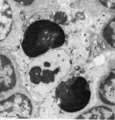 |
Thymus cortex (mouse, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (2) a cortical macrophage (starry-sky macrophage) is seen and shows an electron-light nucleus (N) and a distinct nucleolus. The cell has engulfed two apoptotic thymocytes (1). The cytoplasm also contains small electron-dense lysosomes and myelin figures ... | cortical macrophage; epithelioreticular cell type II ; apoptotic thymocyte; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 115 |
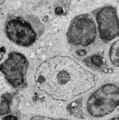 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Within the thymic cortex a type II epithelioreticular cell or so-called (sometimes multinucleated) thymic nurse cell (TNC) shows a characteristic electron-light nucleus and nucleolus (1). The branches are squeezed between the thymocytes (2). In the cytoplasm a variety of empty a... | MHC class I and II expression; epithelioreticular cell type I and II; thymic nurse cell TNC; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 116 |
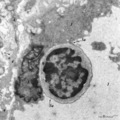 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells (4) separate connective tissue compartment (capsule, trabeculae, blood vessels) from the thymic parenchyma. At the left the capsule is bordered by a basal lamina (4a) of two projections (4) of type I epithelioreticular cells. Close to them, part o... | lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell type I; diapedesis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 117 |
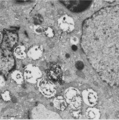 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Two epithelioreticular cells type II or TEC2 (1) show the characteristic vacuoles (*) partly filled with granules (thymulin, lymphokines). At (--><--) small desmosomes. Apart from the mitochondria electron-dense lysosomal structures are present as well as tonofilaments (1, kera... | epithelioreticular cell II ; desmosome; MHC-II expression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 118 |
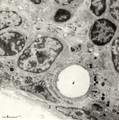 |
Thymus cortex (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Type I epithelioreticular cells separate connective tissue compartment from the thymic parenchyma. With occludens junctions and desmosomes as barriers they form wide-mesh networks creating specific microenvironments for developing T cells. The extensions of type I cells (5) are... | thymus cortex; epithelioreticular cell type I; epithelioreticular cell type II; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 119 |
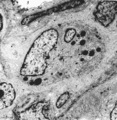 |
Thymus medulla (rat, neonate) | Electron microscopy. An interdigitating cell in the thymic corticomedullary region shows a large electron-light cytoplasm with a complex branching (7) at the periphery. The nucleus is sectioned twice (1). There is abundance of organelles as well as of quite uniform electron-dense lysosomal structure... | medullar epithelioreticular cell; interdigitating cell; corticomedullar region; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 120 |
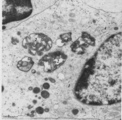 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Epithelioreticular cells of the medulla (1) close to each other. The electron-light cytoplasm contains many small vesicles (1, Golgi area) as well as cross-sections of vacuoles (2) with small finger-like cytoplasmic extrusions in the lumen. Electron-dense lysosomal structures (3... | medullar epithelioreticular cell ; thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 121 |
 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Surrounded by thymocytes (3) a medullary macrophage with an electron-light nucleus (1). The cytoplasm contains many electron-dense lysosomes of varying sizes and forms (2). | medullar macrophage; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 122 |
 |
Thymus medulla (rat, young adult) | Electron microscopy. Epithelioreticular cell of the medulla with an electron-light cytoplasm contains cross-sections of vacuoles with small finger-like cytoplasmic extrusions in the lumen (1). Electron-dense lysosomal structures (2) are also present as well as bundles of intermediate filaments (kera... | medullar epithelioreticular cell ; keratin filaments; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 123 |
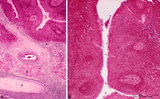 |
Tubal tonsil (human) | Stain: Azan. The tubal tonsil consists of a collection of lymphoid nodules near the auditory tube opening and forms part of the Waldeyers ring of defense in the nasopharyngeal cavity. This tonsil has fewer crypts (1), and the surface is covered by one to more layered ciliated epithelium (2). The la... | tubal tonsil; nasopharynx | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 124 |
 |
Venous circulation pattern in perfused spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The composed picture shows part of the splenic circulation system at several enlargements (inset, A, B). The open venous sinusoids (1) drain via short pulp veins into thin-walled trabecular veins (2), subsequently into thick-walled trabecular veins (4). The trabeculae originate from the... | splenic circulation; trabecular veins; sinusoid ; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 125 |
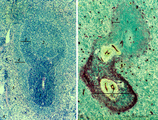 |
White pulp of spleen (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin in A and alkaline phosphatase in B (with substrate Naphtol Fast Blue RR). The general structure of the white pulp of the spleen and its specific microenvironment for T and B cells is well illustrated using alkaline phosphatase that strongly stains the capillaries around th... | alkaline phosphatase; PALS; T lymphocytes; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
