The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA lyase reaction | In this mitochondrial process hydroxymethylglutaryl CoA is converted to acetoacetate, a ketone body. Acetyl CoA is another product. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 102 |
 |
An interpolated PAC | Although most PACs reset the sinus node producing an incomplete compensatory pause, this PAC, indicated by the black arrow, is interpolated, i.e., sandwiched between two sinus beats. Note that the subsequent sinus P wave conducts with prolonged PR interval due to the relative refractoriness of the... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 103 |
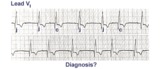 |
Incomplete AV dissociation due To 2nd degree AV block | 2nd degree AV block is evident from the nonconducted P waves. Junctional escapes, labled J, terminate the long pauses because that's the purpose of escape pacemakers....to protect us from too slow heart rates. All QRSs with shorter RR intervals are capture beats, labeled c. Atypical RBBB with a q... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 104 |
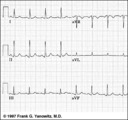 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +50 degrees | 1) lead aVL is the smallest QRS and closest to being the isoelectric lead; 2) perpendiculars to aVL are +60 and -120 degrees; 3) lead I is positive; 4) therefore, the axis is closest to being +60 degrees. Because aVL is actually slightly positive, the axis is only about +50 degrees (i.e., slightly ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 105 |
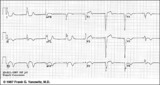 |
Atypical LBBB with primary T wave abnormalities | Primary T wave abnormalities in LBBB refer to T waves in the same direction as the major deflection of the QRS. These are seen in leads I, III, aVL, V2-4. Most likely diagnosis is myocardial infarction. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 106 |
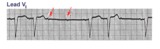 |
Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block with LBBB | The QRS morphology in lead V1 shows LBBB. The arrows point to two consecutive nonconducted P waves, most likely hung up in the diseased right bundle branch. This is classic Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 107 |
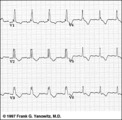 |
RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 108 |
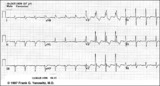 |
Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 109 |
 |
PVC with R-on-T - marquette | PVC with R-on-T - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 110 |
 |
PVCs - marquette | PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 111 |
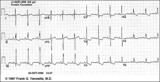 |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) & Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) | In this case of severe pulmonary hypertension, RVH is recognized by the prominent anterior forces (tall R waves in V1-2), right axis deviation (+110 degrees), and P pulmonale (i.e., right atrial enlargement). RAE is best seen in the frontal plane leads; the P waves in lead II are >2.5mm in amplitud... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 112 |
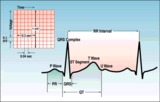 |
ECG intervals and waves | The P wave represents atrial activation; the PR interval is the time from onset of atrial activation to onset of ventricular activation. The QRS complex represents ventricular activation; the QRS duration is the duration of ventricular activation. The ST-T wave represents ventricular repolarizatio... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 113 |
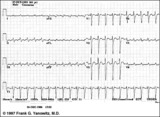 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | Flutter waves are best seen in lead V1; one immediately follows the QRS and the other precedes the next QRS. The regular ventricular rate of 150 bpm should always prompt us to condider this diagnosis. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 114 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -45 degrees | There is no isoelectric, but leads aVR and II are the closest to being isoelectric, placing the axis between -30 and -60 degrees. The axis, therefore, is about -45 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 115 |
 |
Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 116 |
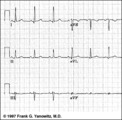 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 117 |
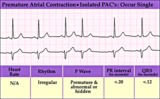 |
Isolated PAC - marquette | Isolated PAC - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 118 |
 |
Acetyl CoA metabolism -- overview | Major metabolic sources of acetyl CoA and some of the processes in which it serves as a substrate. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 119 |
 |
Oleic acid structure | Oleic acid is a typical monounsaturated fatty acid. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 120 |
 |
Inferolateral ST segment elevation | ST Segment elevation with a straight or convex upwards configuration usually means transmural ischemia (or injury) and is seen in the setting of acute myocardial infarction. This ECG finding may also be seen transiently during coronary artery spasm. Unlike ST depression, ST elevation is often loca... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 121 |
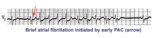 |
A PAC initiates paroxysmal atrial fibrillation | The arrow indicates slight alteration of the ST-T wave by a PAC. The PAC, in turn, falls during the vulnerable period of atrial repolarization and initiates atrial fibrillation. Similar but more catastrophic events happen in the ventricles when PVC's occur during the vulnerable period, i.e. R-on-T... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 122 |
 |
Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block | The P-wave is notched, wider than 0.12s, and has a prominent negative (posterior) component in V1 - all criteria for left atrial abnormality or enlargement (LAE). The PR interval >0.20s. Minor ST-T wave abnormalities are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 123 |
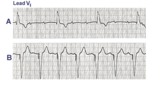 |
3rd degree AV block rx'ed with a ventricular pacemaker | In A the ECG shows complete or 3rd degree AV block with a left ventricular escape rhythm, as evidenced by the upright QRS morphology. In B the artificial right ventricular pacemaker rhythm is shown. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 124 |
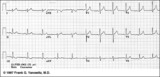 |
Lead Error: V1 & V3 are Transposed | In this normal 12-lead ECG the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this lead placement error. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 125 |
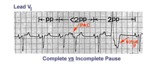 |
PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
