The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 101 |
 |
Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Long QT: an ECG marker for sudden cardiac death | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 102 |
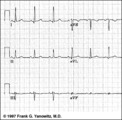 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = 0 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 103 |
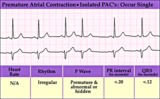 |
Isolated PAC - marquette | Isolated PAC - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 104 |
 |
Inferolateral ST segment elevation | ST Segment elevation with a straight or convex upwards configuration usually means transmural ischemia (or injury) and is seen in the setting of acute myocardial infarction. This ECG finding may also be seen transiently during coronary artery spasm. Unlike ST depression, ST elevation is often loca... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 105 |
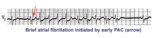 |
A PAC initiates paroxysmal atrial fibrillation | The arrow indicates slight alteration of the ST-T wave by a PAC. The PAC, in turn, falls during the vulnerable period of atrial repolarization and initiates atrial fibrillation. Similar but more catastrophic events happen in the ventricles when PVC's occur during the vulnerable period, i.e. R-on-T... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 106 |
 |
Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block | The P-wave is notched, wider than 0.12s, and has a prominent negative (posterior) component in V1 - all criteria for left atrial abnormality or enlargement (LAE). The PR interval >0.20s. Minor ST-T wave abnormalities are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 107 |
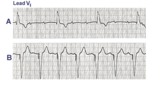 |
3rd degree AV block rx'ed with a ventricular pacemaker | In A the ECG shows complete or 3rd degree AV block with a left ventricular escape rhythm, as evidenced by the upright QRS morphology. In B the artificial right ventricular pacemaker rhythm is shown. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 108 |
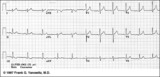 |
Lead Error: V1 & V3 are Transposed | In this normal 12-lead ECG the V1 and V3 chest electrodes are interchanged. Experienced ECG interpreters should be able to spot this lead placement error. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 109 |
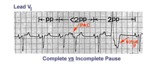 |
PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | PAC and PVC: complete vs. incomplete pause | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 110 |
 |
Electronic atrial pacing - marquette | Electronic atrial pacing - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 111 |
 |
Normal sinus rhythm - marquette | Normal sinus rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 112 |
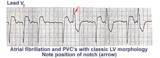 |
Left ventricular PVC's | In lead V1, these PVC's are positive or anterior in direction indicating probable LV origin with late activation of the right ventricle. The arrow points to the notch on the downstroke of the PVC making its morphology highly unlikely to be an aberrantly conducted supraventricular beat. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 113 |
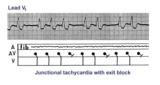 |
Junctional tachycardia with exit block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Theladder diagramsays it all: the atria are fibrillating; there is complete heart block in the AV junction; a junctional tachycardia focus is firing at about 130 bpm, but not all junctional impulses reach the ventricles due to 2nd degree exit block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 114 |
 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +90 degrees | 1) Lead I is isoelectric; 2) perpendiculars to lead I are +90 and -90 degrees; 3) leads II, III, aVF are positive; 4) therefore, the axis must be +90 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 115 |
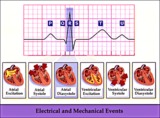 |
Electrical and mechanical events diagram - marquette | Electrical and mechanical events diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 116 |
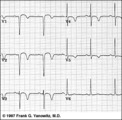 |
Anteroseptal MI, fully evolved: precordial leads | Anteroseptal MI, fully evolved: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 117 |
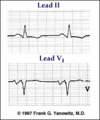 |
Left atrial enlargement: leads II and V1 | Left atrial enlargement: leads II and V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 118 |
 |
Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Fully evolved inferior MI: frontal plane | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 119 |
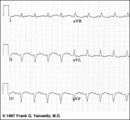 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Frontal plane QRS axis = -75 degrees | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 120 |
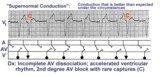 |
Supernormal conduction: 2nd degree AV block with rare captures; accelerated ventricular rhythm | This complicated rhythm strip illustrates 'supernormal' conduction... a situation where conduction is better than expected. The ladder diagram shows that the accelerated ventricular rhythm prevents most of the sinus impulses from reaching the ventricles. Only appropriately timed sinus impulses rea... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 121 |
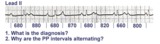 |
Complete AV block, junctional escape rhythm, and ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia | Complete AV block is seen as evidenced by the AV dissociation. A junctional escape rhythm sets the ventricular rate at 45 bpm. The PP intervals vary because of ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia; this is defined when the PP interval that includes a QRS is shorter than a PP interval that excludes a ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 122 |
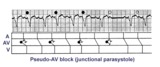 |
Junctional parasystole and pseudo-AV block | This complicated rhythm strip shows normal sinus rhythm and a competing junctional parasystolic focus. Solid circles indicate junctional premature beats from the parasystolic focus. Open circles indicate non-conducted junctional prematures; the first open circle is a nonconducted junctional prematur... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 123 |
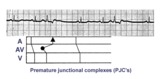 |
Premature junctional complexes with retrograde P waves | The ladder diagram illustrates the PJC with retrograde atrial capture | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 124 |
 |
Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block: Leads II and V1 | Left Atrial Abnormality & 1st Degree AV Block: Leads II and V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
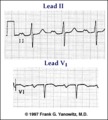
| 125 |
 |
Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Right Axis Deviation & RAE (P pulmonale): Leads I, II, III | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
