The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Format: "image/png" Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
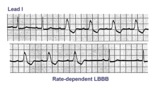 |
Rate-dependent LBBB | In this rhythm strip of sinus arrhythmia, the faster rates have a LBBB morphology. In some patients with a diseased left bundle branch, the onset of LBBB usually occurs initially as a rate-dependent block; i.e., the left bundle fails to conduct at the faster rate because of prolonged refractoriness... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 77 |
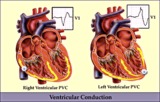 |
RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | RV vs LV PVC's - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 78 |
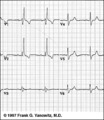 |
RBBB: Precordial leads | RBBB: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 79 |
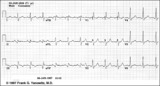 |
Inferior MI and RBBB | Inferior MI and RBBB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 80 |
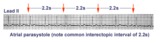 |
Atrial parasystole | Parasystolic rhythms involve an independent ectopic pacemaker resulting in nonfixed coupled premature beats. Parasystole may occur in the atria, as seen in this example, in the AV junction, and in the ventricles. Note the common inter-ectopic interval separating the parasystolic PAC's. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 81 |
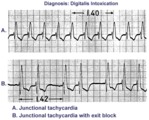 |
Digitalis intoxication: junctional tachycardia with and without exit block | In A the rhythm is junctional tachycardia with RBBB. In B there is 2nd degree exit block with a 3:2 conduction ratio; i.e., every 3rd junctional impulse fails to reach the ventricles... at least for the first two groupings on 1.4sec. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 82 |
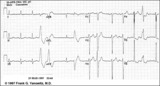 |
LVH and many PVCs | The combination of voltage criteria (SV2 + RV6>35mm) and ST-T abnormalities in V5-6 are definitive for LVH. There may also be LAE as evidenced by the prominent negative P terminal force in lead V1. Isolated PVCs and a PVC couplet are also present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 83 |
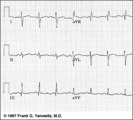 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +150 degrees (RAD) | This is an unusual right axis deviation (RAD). Lead I is negative, which usually means RAD. Lead II is the isoelectric lead, which almost always means -30 degrees; but in this example the axis is 180 degrees away from -30, or +150 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 84 |
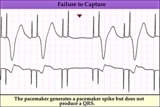 |
Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Pacemaker failure to capture - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 85 |
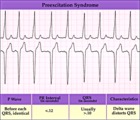 |
WPW type preexcitation - marquette | WPW type preexcitation - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 86 |
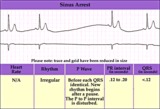 |
Sinus pause or arrest - marquette | Sinus pause or arrest - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 87 |
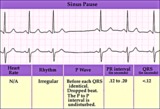 |
SA exit block - marquette | SA exit block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 88 |
 |
An interpolated PAC | Although most PACs reset the sinus node producing an incomplete compensatory pause, this PAC, indicated by the black arrow, is interpolated, i.e., sandwiched between two sinus beats. Note that the subsequent sinus P wave conducts with prolonged PR interval due to the relative refractoriness of the... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 89 |
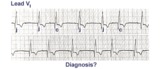 |
Incomplete AV dissociation due To 2nd degree AV block | 2nd degree AV block is evident from the nonconducted P waves. Junctional escapes, labled J, terminate the long pauses because that's the purpose of escape pacemakers....to protect us from too slow heart rates. All QRSs with shorter RR intervals are capture beats, labeled c. Atypical RBBB with a q... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 90 |
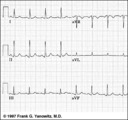 |
Frontal plane QRS axis = +50 degrees | 1) lead aVL is the smallest QRS and closest to being the isoelectric lead; 2) perpendiculars to aVL are +60 and -120 degrees; 3) lead I is positive; 4) therefore, the axis is closest to being +60 degrees. Because aVL is actually slightly positive, the axis is only about +50 degrees (i.e., slightly ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 91 |
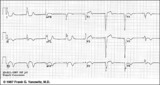 |
Atypical LBBB with primary T wave abnormalities | Primary T wave abnormalities in LBBB refer to T waves in the same direction as the major deflection of the QRS. These are seen in leads I, III, aVL, V2-4. Most likely diagnosis is myocardial infarction. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 92 |
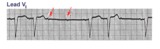 |
Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block with LBBB | The QRS morphology in lead V1 shows LBBB. The arrows point to two consecutive nonconducted P waves, most likely hung up in the diseased right bundle branch. This is classic Mobitz II 2nd degree AV block. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 93 |
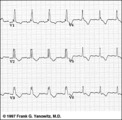 |
RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | RBBB with primary ST-T abnormalities: Precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 94 |
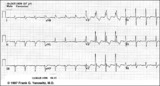 |
Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 95 |
 |
PVC with R-on-T - marquette | PVC with R-on-T - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 96 |
 |
PVCs - marquette | PVCs - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 97 |
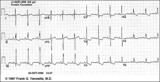 |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy (RVH) & Right Atrial Enlargement (RAE) | In this case of severe pulmonary hypertension, RVH is recognized by the prominent anterior forces (tall R waves in V1-2), right axis deviation (+110 degrees), and P pulmonale (i.e., right atrial enlargement). RAE is best seen in the frontal plane leads; the P waves in lead II are >2.5mm in amplitud... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 98 |
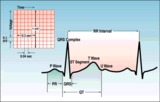 |
ECG intervals and waves | The P wave represents atrial activation; the PR interval is the time from onset of atrial activation to onset of ventricular activation. The QRS complex represents ventricular activation; the QRS duration is the duration of ventricular activation. The ST-T wave represents ventricular repolarizatio... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 99 |
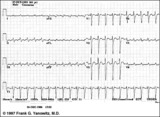 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | Flutter waves are best seen in lead V1; one immediately follows the QRS and the other precedes the next QRS. The regular ventricular rate of 150 bpm should always prompt us to condider this diagnosis. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 100 |
 |
Left axis deviation: QRS axis = -45 degrees | There is no isoelectric, but leads aVR and II are the closest to being isoelectric, placing the axis between -30 and -60 degrees. The axis, therefore, is about -45 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
