Best known for his world-renowned neuro-ophthalmology unit based at the University of California, San Francisco, William Hoyt, MD collected here more than 850 of his best images covering a wide range of disorders.
William F. Hoyt, MD, Professor Emeritus of Ophthalmology, Neurology and Neurosurgery, Department of Ophthalmology, University of California, San Francisco.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 76 |
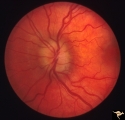 |
Buried Drusen | Buried drusen. Left eye. Note lumpy disc margin, especially temporally. Also note absence of optic cup. Excellent example of pseudo papilledema with buried drusen. Pair with PP_13a. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical notes... | Image |
| 77 |
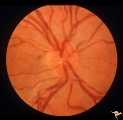 |
Crowded Disc (Family) | Right eye. PP3 a & b: sister; PP4 a & b brother; Congenital disc margin blurring with crowded discs. Excellent example of pseudo papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variant of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variant of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clinical: Appearance is ... | Image |
| 78 |
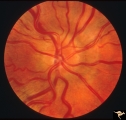 |
Crowded Disc (Family) | Right eye. PP3 a & b: sister; PP4 a & b brother; Congenital disc margin blurring with crowded discs. Excellent example of pseudo papilledema that caused serious diagnostic confusion which led to a pneumoencephalogram (PEG) and arteriogram. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the opt... | Image |
| 79 |
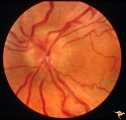 |
Crowded Disc (Family) | Left eye. PP3 a & a: sister; PP4 a & b brother; Congenital disc margin blurring with crowded discs. Excellent example of pseudo papilledema that caused serious diagnostic confusion which led to a pneumoencephalogram (PEG) and arteriogram. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the opti... | Image |
| 80 |
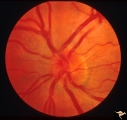 |
Crowded Disc (Family) | Left eye. PP3 a & b: sister; PP4 a & b brother; Congenital disc margin blurring with crowded discs. Excellent example of pseudo papilledema. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Crowded disc. Clinical: Appearance ... | Image |
| 81 |
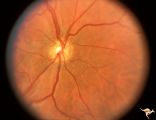 |
H01 Panhypoplasia | Extreme hypoplasia. Very small disc. Peri-papillary halo (choroidal). Right eye. Note: normal vessels. Same patient as H_2. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. Clinical: Blind child. | Image |
| 82 |
 |
H02 Panhypoplasia | Extreme hypoplasia. Very small disc. Peri-papillary halo (choroidal). Left eye. Note: normal vessels. Same patient as H_1. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. Clinical: Blind child. | Image |
| 83 |
 |
H03 Panhypoplasia | Extreme hypoplasia. Note absence of retinal nerve fiber layer. Left eye. Girl. Same patient as H_4. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Hypoplasia of the optic nerve. Disease/ Diagnosis: Hypoplasia. Clinical: Left eye. Girl. | Image |
| 84 |
 |
Hemorrhagic Complication of Drusen | PP31a, left and PP31, right taken in April. PP31c: left taken after an interval of 2 months. Hemorrhage. Hemorrhagic complications of drusen. 15 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Patient complained of blurre... | Image |
| 85 |
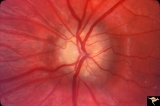 |
Hemorrhagic Complication of Drusen | PP31a, left and PP31, right taken in April. PP31c: left taken after an interval of 2 months. Hemorrhage. Hemorrhagic complications of drusen. 15 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Hemorrhage in drusen disc. | Image |
| 86 |
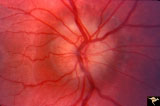 |
Hemorrhagic Complication of Drusen | PP31a, left and PP31, right taken in April. PP31c: left taken after an interval of 2 months. Hemorrhage. Hemorrhagic complications of drusen. 15 year old boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Drusen. | Image |
| 87 |
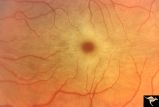 |
Macular Cherry Red Spots in Niemann-Pick disease | Close up view of macular cherry red spots in Niemann-Pick disease. Same patient as R2A2a. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal ganglion cell accumulation of lipid. Disease/Diagnosis: Niemann-Pick disease. Clinical: Severe mental retardation and blindness. Fatal. | Image |
| 88 |
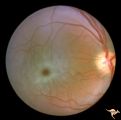 |
Macular Cherry Red Spots in Niemann-Pick disease | Macular cherry red spots in Niemann-Pick disease. Same patient as R2A2b. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Retinal ganglion cell accumulation of lipid. Disease/Diagnosis: Niemann-Pick disease. Clinical: Severe mental retardation and blindness. Fatal. | Image |
| 89 |
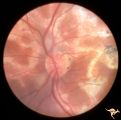 |
Multifocal Choroidopathy | Multifocal choroidopathy in a patient with uveitis. Anatomy: Retina. Disease/Diagnosis: Uveitis, Multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy. Clinical: Visual loss. | Image |
| 90 |
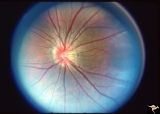 |
PP8b Crowded Disc with Significant Nasal Disc Blurring | Congenital nasal disc blurring. Myopic eyes. Thai girl patient. One wonders about vitreal adherence to the disc. PP 8b left eye. Pair with PP 8a right eye. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Normal variation of the optic disc. Disease/ Diagnosis: Normal variation of the optic disc. Congenital blurred d... | Image |
| 91 |
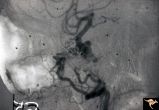 |
Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum (PXE) | Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) Lateral view of right internal carotid angiogram showing complete occlusion of the subcranial internal carotid artery with collateral formation (so called 'rete mirabile"") filling the supraclinoid carotid artery. Also shows evidence of the carotid cavernous fistula e... | Image |
| 92 |
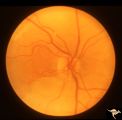 |
R3C4 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. This fundus shows two calcific emboli in the retinal arteriole tree. The embolus at the end of the disc has caused a retinal infarction and the embolus above the optic disc has also caused a retinal infarction. Note that these white emboli stick in the retinal vessel in mids... | Image |
| 93 |
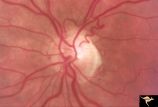 |
R3C5 Calcific Retinal Emboli | Calcific retinal emboli. There is a round gray embolus occluding the superior temporal branch of the retinal artery. Note that the blood column is absent in the superior temporal retinal artery for a short distance off of the disc margin. Note that two collateral branches now fill the distal tempora... | Image |
| 94 |
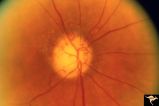 |
R3C9 Nettleship Collaterals: a Result of Calcific Embolization of the Central Retinal Artery | Result of calcific embolization of the central retinal artery. The embolus itself can not be seen within the tissue of the optic disc. Numerous chorio-retino collaterals are filling the branches of a central retinal artery. Such an eye is always blind. These collaterals indicate that the patient pro... | Image |
| 95 |
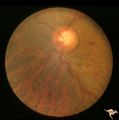 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy showing produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in the black and white photo (R3B2b). Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Car... | Image |
| 96 |
 |
Slow Flow (Chronic Hypoxic) Retinopathy | Examples of Slow flow (chronic hypoxic) retinopathy produced by a carotid-cavernous sinus fistula. Arteriole pressure was low in the retina and venous pressure was elevated. Note the characteristic dot and blot hemorrhages in this black and white photo. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: carotid-cavernous ... | Image |
| 97 |
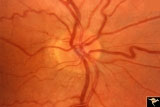 |
Unilateral Buried Drusen | PP20a: Right eye. Normal disc without optic cup.PP20b: Left eye. Buried drusen nasally and exposed drusen at the temporal margin. Boy. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Normally functioning eye with drusen. Right eye nor... | Image |
| 98 |
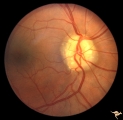 |
Vascular Complications of Drusen: Drusen Causing Loss of Superior Retinal Arterial Supply | PP32a: right; PP32b: left eye. Right eye is an obvious drusen disc. Patient had marked field defects. Left eye has occlusion of superior branch of the central retinal artery at 11:30 with the inferior retinal artery supplying collateral to the superior retina. Notice the branch of the inferior ret... | Image |
| 99 |
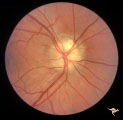 |
Visible Drusen | PP24a. Right eye. Exposed drusen. There are inferior nerve fiber layer defects in the upper arcuate bundles. Optic disc is also hypoplastic. Anatomy: Optic disc. Pathology: Drusen of the optic disc. Disease/Diagnosis: Drusen of the optic disc. Clinical: Hypoplastic optic disc with drusen. | Image |
| 100 |
 |
Von Hippel Lindau Disease with Photocoagulation Effect | Von Hippel Lindau Disease with appearance of Xenon photocoagulation on a mini hemangioblastoma. Anatomy: Retina. Pathology: Hemangioblastoma. Disease/Diagnosis: Von Hippel Lindau disease. Clinical: No visual symptoms. | Image |
