The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
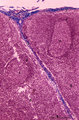 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. From the blue-stained dense capsule a long trabecula (3) flanked by paratrabecular (intermediate) sinuses penetrates between the paracortical areas (6). Paratrabecula... | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset | |
| 52 |
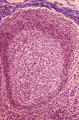 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the cortex of a lymph node with the capsule (1) and subcapsular (or marginal) sinus (2) filled with lymphocytes. Below the subcapsular sinus a darkly stained rim or corona (3) of small lymphocytes (B cells) surrounds the lucid stained germinal centre (4). The white spaces repre... | follicle; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 53 |
 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left and right: survey of lymph nodes, compare the individual differences between the nodes. The pictures display the cortex (1) with capsule (3), and the medulla (2). The cortex consists of (secondary) follicles displaying a clear germinal centre (4). The paracortex (T cell area) is ... | follicle; paracortex; cortex; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 54 |
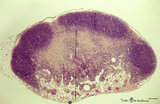 |
Lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin. For comparison with the human lymph node a survey of a small rodent lymph node is demonstrated. Basically the same divisions are found: (1) a cortex (outer cortex zone, nodular cortex or superficial cortex) covered with a (2) thin capsule and subcapsular sinus; a paracor... | follicle; hilum; medulla; cortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 55 |
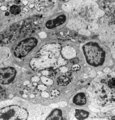 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. In the paracortical area (inner cortex) of a lymph node interdigitating cells (1) are found (so-called IDC, antigen-presenting cell or APC). They show branched extensions (3) in between the closely apposed surrounding T lymphocytes (2). In the cytoplasm of the IDC lysosomal inc... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 56 |
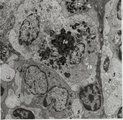 |
Lymph node (rat) | Electron microscopy. Within the reticular framework of lymph nodes a variety of active reticular cells are present, some of them (1) have phagocytised foreign material (1a) and contain numerous lysosomal structures (1a) and large Golgi areas (1b)). Others are less active (2). (3) wandering interdig... | electron microscopy; interdigitating cell; antigen-presenting cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 57 |
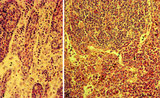 |
Lymph nodes (rat) | Stain: Hematoxylin & pyronin. Pyronin was formerly used to demonstrate young blast cell types rich in polysomes and packed rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) resulting in a reddish stain of the cytoplasm. A: Part of the medulla with medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum o... | infection; medullar cord; plasma cells ; macrophages | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 58 |
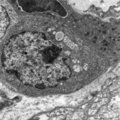 |
Lymphoblast in splenic cord of red pulp (rat) | Electron microscopy. A free circulating more matured lymphoblast with a conspicuous nucleus and nucleolus (1) still contains many polysomes (2), the swollen mitochondria (3) are obvious. A single fat droplet (4) and Golgi vesicles (5) are present. The cell is partly surrounded by reticular cell exte... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 59 |
 |
Lymphoblast in splenic white pulp (rat, human) | Electron microscopy (A, rat) and Methyl green (B, human). Upon antigenic stimulation the lymphocytes in the germinal centre proliferate and generate activated B cells or lymphoblasts which seed towards marginal zone and red pulp while differentiating. Due to the increased number of lymphoblasts, ret... | electron microscopy; lymphoblast | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 60 |
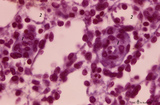 |
Macrophage-sheathed capillaries in spleen (human) | Azan. The branching of each penicillar arteriole gives rise to capillaries and a slow-down of the blood stream. In certain regions monocyte-derived macrophages leave the capillary and enter its wall where they develop into macrophages. Together with the present reticular cells these cell accumulatio... | macrophage-sheathed capillaries; penicillar arterioles; sinusoid | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 61 |
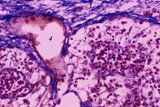 |
Medulla of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla showing medullary cords (1) and medullary sinuses (2) close to the hilum and capsule (3). The medullary cords consist of a meshwork of reticular fibers and reticular cells (blue-stained). The cords (1) are more stuffed with lymphocytes and other blood cells. The sinu... | medullar cords; medullar sinus; hilum | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 62 |
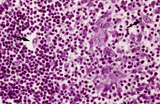 |
Medulla of thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. The light-stained medulla consists of a loosened framework of epithelial reticular cells, macrophages, thymocytes and capillaries. Accumulations of a specialized type of epithelial reticular cells (1) are localized between the thymocytes. These clusters represent precursors of fu... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); thymus medulla; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 63 |
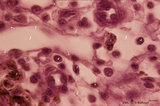 |
Medullary cords and sinus in lymph node (mouse) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Detail of medullary sinus (1) flanked by part of medullar cords (2). The sinus space (1) is lined by flattened littoral cells (foamed cytoplasm) (?) and dispersedly filled with lymphocytes (4) and macrophages (brown hemo-pigment) (3). Within the medullary cords one finds ... | medullar cords; medullar sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 64 |
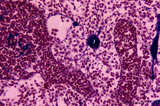 |
Medullary part of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Part of the medulla with darkly stained medullary cords (1) and lightly stained medullary sinuses (2). The cords are stuffed with densely packed lymphocytes and reticular cells. Their blue-stained structures indicate massive bundles of reticular fibres. The sinuses are lined by flattene... | medulla; medullar cords; sinus | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 65 |
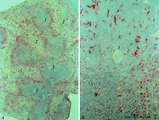 |
MHC-class II dendritic cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red staining of MHC-class II with ER13 antibody. The survey in (A) shows that MHC-class II expressing cells are conspicuously concentrated in dendritic cell types (B) in the transition zone between red pulp (2) and white pulp (1). These dendritic or antigen-pres... | MHC class II; dendritic cells; immunofluorescence | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 66 |
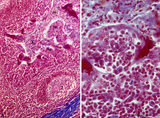 |
Palatine tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A low magnification in A shows the thick blue connective septum (1) with a secondary lymphatic nodule (2). (3) is a cross-section of a crypt filled with detached squamous epithelium (3a) mixed up with keratinized material (red) and a huge amount of lymphocytes (3b). A higher magnificati... | follicle; germinal center; mantle layer; stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 67 |
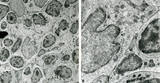 |
Part of lymphatic nodule in spleen (rat) | Electron microscopy. The left image (A) reveals part of a white pulp area stuffed with a dendritic cell (1) between a majority of different types of lymphocytes (2, 3). The right image shows a larger magnification of the same area with the dendritic cell (1) sandwiched in between the enclosing lymp... | dendritic cell; electron microscopy; white pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 68 |
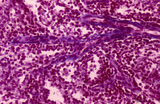 |
Penicillar arterioles in spleen (human) | Stain: Azan. The central or follicular artery in the follicle of the spleen splits into many arterioles. These arterioles spread as so-called penicillar arterioles (1) shown here. They are still surrounded by a very thin perilymphatic sheath (PALS) that disappears as the arteries in a brush-like pat... | penicillar arterioles; red pulp | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 69 |
 |
Phagocytosis in small splenic blood vessel (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells is black-stained due to the staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin. Circulating lymphocytes (2) in the lumen (*) remain unstained. An oblong monocyte (1) developing into a macrophage h... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 70 |
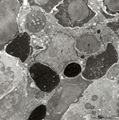 |
Phagocytosis in splenic red pulp (mouse) | Electron microscopy. Stain: Peroxidase reaction with diaminobenzidin staining. A diversity of red blood cells in the red pulp can be discerned due to the DAB staining of hemoglobin by oxidized benzidin (dark and light staining). The macrophage (1) shows peroxidase activity along the nuclear membran... | electron microscopy; phagocytosis | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 71 |
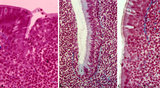 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. The combination demonstrates stages of infiltration (=diapedesis) of lymphocytes in the epithelium of the pharyngeal tonsil. The pharyngeal tonsil or adenoid is located in the nasopharyngeal roof. The agglomerations of lymphocytes (4) are covered by (1) pseudostratified ciliated epithel... | pharyngeal tonsil ; GALT; diapedesis; pseudostratified ciliated epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 72 |
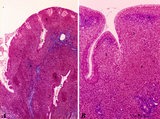 |
Pharyngeal tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissues', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain Azan. The solitary pharyngeal tonsil is localized in the pharyngeal fornix and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. A: The roof of the nasopharynx is covered by a columnar epithelium with faintly light-stained goblet cells (1) and part of a fold shows cle... | pharyngeal tonsil; GALT; pseudostratified columnar epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 73 |
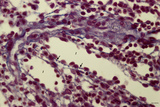 |
Red pulp of spleen with perfused venous sinusoids (human) | Stain: Azan. Cross-sectioned venous sinusoids with splenic cord (1). The wall of a sinusoid is composed of elongated rod-like endothelial cells that are orientated parallel to each other in the long axis of the sinusoid. There is a discontinuous pale-stained basement membrane (difficult to observe i... | sinusoid ; red pulp; splenic cord; central arteriole | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 74 |
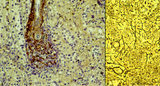 |
Red pulp of spleen with venous sinusoids (monkey, human) | Stain: A: Silver stain (Movat) (monkey); B: Silver stain (Gomori) (human). (A): The darkly stained fibres are conspicuous in the PALS (1) area arranged in parallel rows. The blood vessels continue in the surrounding splenic sinusoids (4). The wall of the sinusoid is built as a grid, the space is su... | sinusoid; reticular fibres | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 75 |
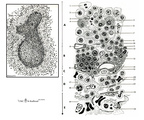 |
Scheme electron microscopy of the border of secondary nodule/red pulp in spleen | The left figure POJA-L974 shows a scheme of histological impression of a survey of a secondary splenic follicle or nodule. The rectangle is enlarged in the right figure POJA-L976B and shows the following elements: A. germinal centre; B. mantle zone; C. dendritic cell area; D. marginal zone; E. ... | white pulp; marginal zone; red pulp; antigen presenting cell (APC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
