The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
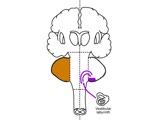 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Vestibulocerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The first subdivision of the cerebellum is the vestibulocerebellum. This consists of the connections between the vestibular system and the flocculonodular lobe. Dysfunction of this system results in nystagmus, truncal instability (titubation), and truncal ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported b... | Coordination Examination; Flocculonodular Lobe; Vestibulocerebellum | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 52 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Sensory (x2) | There is a sensory deficit for both light touch and pain on the left side of the face for all divisions of the 5th nerve. Note that the deficit is first recognized just to the left of the midline and not exactly at the midline. Patients with psychogenic sensory loss often identify the sensory change... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 53 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Sensory | There is a sensory deficit for both light touch and pain on the left side of the face for all divisions of the 5th nerve. Note that the deficit is first recognized just to the left of the midline and not exactly at the midline. Patients with psychogenic sensory loss often identify the sensory change... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 54 |
 |
Gait Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hemiplegic Gait Demonstration | The patient has unilateral weakness and spasticity with the upper extremity held in flexion and the lower extremity in extension. The foot is in extension so the leg is too long therefore, the patient will have to circumduct or swing the leg around to step forward. This type of gait is seen with a U... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 55 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Tandem Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patients with ataxia have difficulty narrowing the station in order to walk heel to toe. Tandem gait is helpful in identifying subtle or mild gait ataxia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 56 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 57 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Toe-to-finger (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Same as finger-to-nose except for the lower extremities. For both the upper and lower extremities, it is important to always compare right versus left. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and th... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 58 |
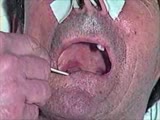 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 59 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 60 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Subdivisions of the Cerebellum (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The cerebellum has 3 functional subdivisions, which function as feedback and feed forward systems. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 61 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Vergence | Light-near dissociation occurs when the pupils don't react to light but constrict with convergence as part of the near reflex. This is what happens in the Argyll-Robertson pupil (usually seen with neurosyphilis) where there is a pretectal lesion affecting the retinomesencephalic afferents controllin... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 62 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Sensory & Motor: Gag Reflex (x2) | Using a tongue blade, the left side of the patient's palate is touched which results in a gag reflex with the left side of the palate elevating more then the right and the uvula deviating to the left consistent with a right CN 9 & 10 deficit. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. Neur... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 63 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Smooth Pursuit (x2) | The patient shown has progressive supranuclear palsy. As part of this disease there is disruption of fixation by square wave jerks and impairment of smooth pursuit movements. Saccadic eye movements are also impaired. Although not shown in this video, vertical saccadic eye movements are usually the i... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 64 |
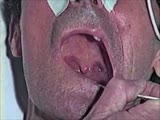 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor (x2) | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 65 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerves 9 & 10 - Motor | When the patient says ah there is excessive nasal air escape. The palate elevates more on the left side and the uvula deviates toward the left side because the right side is weak. This patient has a deficit of the right 9th & 10th cranial nerves. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. ... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 66 |
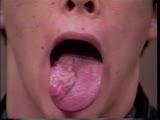 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor (x2) | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 67 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 68 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 7 - Sensory, Taste | The patient has difficulty correctly identifying taste on the right side of the tongue indicating a lesion of the sensory limb of the 7th nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Offic... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 69 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Anatomy: Midline Ataxia (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Clinically, the ataxic syndromes caused by vestibulocerebellar and spinocerebellar disease are lumped together and are called midline or equilibratory (gait) ataxias. The hallmarks of these midline ataxic syndromes are truncal instability manifested by titubation (tremor of the trunk in an anterior-... | Coordination Examination; Anterior Lobe of Cerebellum; Flocculonodular Lobe | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 70 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements - Dysarthria (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Impaired speech articulation of cerebellar origin is characterized by being slow, indistinct, and scanning (scanning refers to decomposition of words into monosyllabic parts and loss of normal phrasing and intonation). NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development ... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 71 |
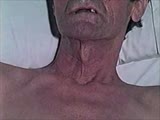 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 11 - Motor | When the patient contracts the muscles of the neck the left sternocleidomastoid muscle is easily seen but the right is absent. Looking at the back of the patient, the left trapezius muscle is outlined and present but the right is atrophic and hard to identify. These findings indicate a lesion of the... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 72 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Station (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's feet will be placed wider apart then usual in order to maintain balance (broad or wide-based station). Midline ataxias cause instability of station with eyes opened or closed. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, t... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 73 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hand - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Movements are slow and irregular with imprecise timing. Inability to perform repetitive movements in a rapid rhythmic fashion is called dysdiadochokinesia. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics an... | Coordination Examination; Dysdiadochokinesia | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 74 |
 |
Gait Exam: Abnormal Examples: Hemiplegic Gait Demonstration | The patient has unilateral weakness and spasticity with the upper extremity held in flexion and the lower extremity in extension. The foot is in extension so the leg is too long therefore, the patient will have to circumduct or swing the leg around to step forward. This type of gait is seen with a U... | Gait Examination; Hemiplegic Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 75 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Abnormal Examples: Natural Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Wide-based, unsteady, irregular steps with lateral veering| ataxia is most prominent when sudden changes are needed such as turning, standing up or stopping. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics ... | Coordination Examination; Natural Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
