The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
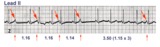 |
Atrial parasystole | In atrial parasystole non-fixed coupled PACs, shown by arrows, occur at a common inter-ectopic interval or at multiples of this interval. Atrial fusions, not shown here, may also occur when the PAC occurs in close temporal proximity to the sinus impulse. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 52 |
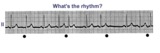 |
Atrial parasystole | The evenly spaced dots indicate ectopic atrial activity from a parasystolic atrial pacemaker. Non-fixed coupled PACs are seen having a common inter-ectopic interval. One of the PACs is nonconducted. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 53 |
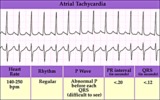 |
Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 54 |
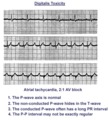 |
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
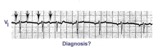
| 55 |
 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 AV block | In this rhythm the atrial rate from an ectopic focus is 160 bpm. Atrial activity can be seen on top of T waves, and before QRS's. Careful observation reveals a 3:2 Wenckebach relationship between P waves and QRS's. Atrial tachycardia with block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
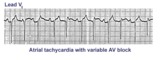
| 56 |
 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 and 2:1 AV block | The ectopic atrial rate is 150 bpm. Some of the ectopic P waves are easily seen and indicated by the arrows. Other P waves are burried in the T waves and not so easily identified. Atrial tachycardia with AV block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. 3:2 and 2:1 AV block is seen in this examp... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 57 |
 |
Atrial tachycardia with exit block and AV block | The ectopic P waves, easily seen in this example,occur in groups, separated by short pauses. This is likely due to an exit block just distal to the atrial pacemaker. Because not all of the P waves make it to the ventricles, there is also 2nd degree AV block. Therefore, two levels of block are pre... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 58 |
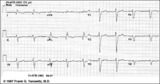 |
Atypical LBBB with Q waves in leads I and aVL | In typical LBBB, there are no initial Q waves in leads I, aVL, and V6. If Q waves are present in 2 or more of these leads, myocardial infarction is present. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 59 |
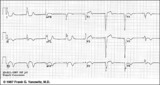 |
Atypical LBBB with primary T wave abnormalities | Primary T wave abnormalities in LBBB refer to T waves in the same direction as the major deflection of the QRS. These are seen in leads I, III, aVL, V2-4. Most likely diagnosis is myocardial infarction. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 60 |
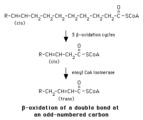 |
Beta-oxidation of a delta-9 fatty acyl CoA | Enoyl CoA isomerase is required to move the double bond in a Delta-9 fatty acyl CoA to a position where it can continue in beta-oxidation. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 61 |
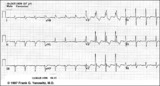 |
Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 62 |
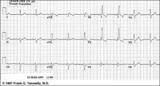 |
Bifascicular block: RBBB + LAFB | This is the most common of the bifascicular blocks. RBBB is most easily recognized in the precordial leads by the rSR' in V1 and the wide S wave in V6 (i.e., terminal QRS forces oriented rightwards and anterior). LAFB is best seen in the frontal plane leads as evidenced by left axis deviation (-50... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 63 |
 |
Bradycardia-dependent LBBB with carotid sinus massage | When carotid sinus massage slows the heart rate in this example, the QRS widens into a LBBB. This form of rate-dependent bundle branch block is thought to be due to latent pacemakers in the bundle undergoing phase 4 depolarization; when the sinus impulse enters the partially depolarized bundle, slow... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 64 |
 |
Calibration signal - marquette | Calibration signal - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 65 |
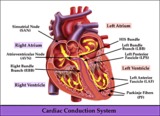 |
Cardiac conduction system diagram - marquette | Cardiac conduction system diagram - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 66 |
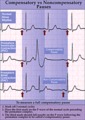 |
Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 67 |
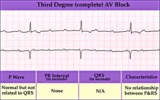 |
Complete AV block (3rd degree) with junctional rhythm | Complete AV block (3rd degree) with junctional rhythm | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 68 |
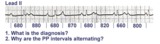 |
Complete AV block, junctional escape rhythm, and ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia | Complete AV block is seen as evidenced by the AV dissociation. A junctional escape rhythm sets the ventricular rate at 45 bpm. The PP intervals vary because of ventriculophasic sinus arrhythmia; this is defined when the PP interval that includes a QRS is shorter than a PP interval that excludes a ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 69 |
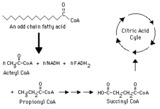 |
Complete oxidation of an odd-chain fatty acid -- overview | This diagram indicates production of propionyl CoA from an odd-chain fatty acid and the subsequent conversion of propionyl CoA to succinyl CoA, which can be metabolized through the citric (tricarboxylic) acid cycle. | Biosynthesis | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 70 |
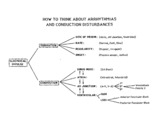 |
Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 71 |
 |
Condensation of an acyl group with a malonyl group | The acetyl group displaces the carboxyl of the malonyl group, forming a beta-ketoacyl group. This reaction is catalyzed by beta-ketoacyl Acyl Carrier Peptide synthase. The carboxyl released in the form of bicarbonate regenerates the bicarbonate used earlier in the acetyl CoA carboxylase reaction. | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids | |
| 72 |
 |
Contraception for women in their later years | Contraception for women in their later reproductive years. | Knowledge Weavers Human Reproduction | |
| 73 |
 |
Dehydrogenation of fatty acyl CoA | Fatty acyl CoA is dehydrogenated by FAD in a reaction catalyzed by one of the acyl CoA dehydrogenases. Note that the dehydrogenation occurs between the alpha- and beta-carbons. | FAD | Knowledge Weavers Fatty Acids |
| 74 |
 |
Diagram: frontal plane leads | Diagram: frontal plane leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 75 |
 |
Diagram: stages of acute Q-wave MI | Diagram: stages of acute Q-wave MI | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
