A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Subject | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Complete Saccadic Palsy Due to Pulmonary Thrombectomy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 37-year-old woman who underwent pulmonary thrombectomy for a pulmonary embolus. Immediately following the procedure, she was unable to make normal eye movements. This video exam (she is the passenger in a car du... | Saccades; Horizontal Gaze Palsy; Vertical Gaze Palsy; Upgaze Palsy; Downgaze Palsy |
| 52 |
 |
Congenital Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Presented here are two patients with congenital nystagmus demonstrating characteristic features including: mixed pendular and jerk nystagmus (usually gaze-evoked) waveforms, stays horizontal even in vertical gaze, suppres... | Jerk Nystagmus; Pendular Nystagmus; Latent Nystagmus; Congenital Acquired Nystagmus |
| 53 |
 |
Convergence | Can bring out or change the direction of vertical nystagmus in Wernicke's, or cerebellar disease; may be impaired in Parkinson's disease, head trauma, elderly patients; may overcome an adduction deficit with an INO. Instructional ocular motor examination procedures. | Convergence; Exam; Abnormal Saccades |
| 54 |
 |
Convergence | Convergence: instruct the patient to focus on their thumb held at arm's length, and slowly move their thumb towards their nose. This may bring out or cause reversal of vertical nystagmus (e.g., transition from upbeat to downbeat nystagmus in Wernicke's encephalopathy [see example of transition from ... | Convergence |
| 55 |
 |
Convergence Insufficiency and Square Wave Jerks in PSP | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 70-yo-woman with progressive supranuclear palsy with complaints of difficulty reading. Her husband noticed that she would frequently close one eye when attempting to read, and words were not clear on the page, a... | Convergence; Alignment; Convergence Insufficiency; Square Wave Jerks |
| 56 |
 |
Curved Oblique Saccades and Saccadic Slowing in a Patient with an Anti-GAD Mediated Posterior Fossa Syndrome | This is a patient who developed muscle spasms especially involving the muscles of the trunk in addition to a progressive gait disorder. Examination demonstrated slow saccades, slower horizontally than vertically, in addition to gaze evoked nystagmus with a side pocket pattern. Side pocket nystagmu... | |
| 57 |
 |
Demonstration of HINTS Examination in a Normal Subject | In the acute vestibular syndrome - consisting of acute prolonged vertigo, spontaneous nystagmus, imbalance, nausea/vomiting, head motion intolerance which is typically due to vestibular neuritis or posterior fossa stroke - a 3 step test of ocular motor and vestibular function known as HINTS, has hig... | Acute Vestibular; Normal VOR; Vertigo; HINTS examination |
| 58 |
 |
Dissociated Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus in MS | This is a patient with multiple sclerosis who presented with oscillopsia. Seen in the video is an elliptical pendular nystagmus in both eyes that was dissociated. Here, the term "dissociated" refers to the fact that the nystagmus is (slightly) more intense in the left eye as compared to the right ... | |
| 59 |
 |
Divergence Insufficiency in Cerebellar Ataxia | This is a 65-yo woman with complaints of imbalance (progressive over years) and horizontal diplopia at distance. On her exam, there was a small symptomatic esotropia at distance, but only a small esophoria at near. There were no obvious abduction deficits, and the 6 prism diopter ET at distance was... | Abnormal Alignment; Divergence Insufficiency; OMS Cerebellar |
| 60 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike | The safety of the patient should be prioritized when completing this test virtually, and the examiner should avoid putting the patient in a position where a fall may occur. Floor (or bed) Dix-Hallpike: this test can be used for patients who are fully mobile and able to get down to the floor and up a... | Dix-Hallpike |
| 61 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver in Posterior BPPV with Reversal of Nystagmus on Sitting Up | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which is provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient is moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a brie... | BPPV Posterior; BPPV Diagnosis; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 62 |
 |
Dorsal Midbrain Syndrome from Stroke - Collier's Sign & Pseudoabducens | This is a 70-yo-man who suffered a right midline thalamic/rostral midbrain hemorrhagic stroke causing a pretectal (Parinaud's) syndrome. There was prominent eyelid retraction (Collier's sign), a left pseudo-abducens, and upgaze palsy with convergence retraction nystagmus. There was no light-near dis... | OMS Mesenecephalon; Convergence Reaction Nystagmus; Upgaze Palsy; Abnormal Range; Sixth Nerve Palsy; Vertical Gaze Palsy; Eyelid Retraction; OMS Dorsal Midbrain |
| 63 |
 |
Downbeat (Perverted) Head Shaking Nystagmus in a Patient with Spontaneous Torsional Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with vascular risk factors who experienced abrupt onset imbalance and dizziness. Symptoms were maximal at onset, and she denied progression over 6 months. Clinically, it was felt that she had s... | Torsional Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; Headshaking; Downbeat Nystagmus; Cerebellar Pathology |
| 64 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old man with 2 years of progressive ataxia and oscillopsia. On examination, he had downbeat nystagmus (DBN), an ocular motor finding that is usually (but not always) associated with flocculus/parafloccul... | Downbeat Nystagmus; OMS Cerebellar; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 65 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus and Cerebellar Atrophy | This is a 40-year-old man with 2 years of progressive ataxia and oscillopsia. On examination, he had downbeat nystagmus (DBN), an ocular motor finding that is usually (but not always) associated with flocculus/paraflocculus dysfunction, which causes overaction of the anterior canal (upward or anti-g... | Downbeat Nystagmus; OMS Cerebellar; Jerk Nystagmus; Vestibular Nystagmus |
| 66 |
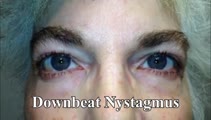 |
Downbeat Nystagmus and Convergence Spasm | This is a 60-yo-woman with vertical oscillopsia related to her downbeat nystagmus, and diplopia related to an intermittent esotropia. When the esotropia was present, with versions there were bilateral abduction deficits. With ductions and the vestibulo-ocular reflex, it was apparent that the range o... | Convergence-abnormal; Range-abnormal; Sixth Nerve Palsy; Convergence Spasm; Cerebellar Pathology; Jerk Nystagmus; Downbeat Nystagmus |
| 67 |
 |
Downbeat Nystagmus with Active Horizontal Head Shaking | This is a 70-year-old man who presented with one single complaint for 10 years - if he moved his head too quickly (even one single horizontal head movement to the right or the left), he would experience the abrupt loss of balance and dizziness. His typical episodes were reproducible, and interesting... | Downbeat Nystagmus; Jerk Nystagmus; OMS Cerebellar; Abnormal Headshaking; Gaze-Evoked Nystagmus |
| 68 |
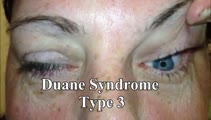 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Duane's Syndrome; Type 3 |
| 69 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: After assessing static binocular visual acuity, dynamic visual acuity (DVA) is determined by repeating the test during horizontal and vertical head shaking at 2-3 Hz. Dynamic visual acuity is most important to test when ... | Dynamic Visual Acuity |
| 70 |
 |
Dynamic Visual Acuity | Dynamic Visual Acuity: the examiner can use screen-sharing to provide a visual acuity chart. Instruct the patient to sit at the appropriate distance from their screen at which the lowest line on the visual acuity chart is just readable. Have the patient move their head (horizontally to evaluate the ... | Dynamic Visual Acuity |
| 71 |
 |
Elliptical Pendular Nystagmus in MS | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-yo-woman with MS and bilateral optic nerve disease who presented with a year's long history of oscillopsia, which was related to elliptical pendular nystagmus. The appearance of elliptical nystagmus is the re... | Pendular Nystagmus; Multiple Sclerosis |
| 72 |
 |
Enhanced Ptosis in Myasthenia Gravis | This is a 20-yo-woman who presented with generalized weakness, ptosis and ophthalmoplegia. She had severe ptosis OU at baseline, but when one eyelid was manually elevated, there was marked enhanced ptosis of the opposite eyelid. This was in accordance with Hering's law of equal innervation of the le... | Myasthenia Gravis |
| 73 |
 |
Evaluation of Auditory Function Using Rinne and Weber Tests | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The Rinne test is an assessment of auditory thresholds to air and bone conduction of sound. The Weber test is a comparison of bone conducted sound of either ear. Conductive hearing loss results in a loss of air conducte... | Auditory Testing |
| 74 |
 |
Evaluation of Convergence | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: The assessment of convergence includes measuring alignment at near versus distance (see video, https://collections.lib.utah.edu/details?id=187677), near point of convergence and convergence amplitude. Near point of conve... | Normal Convergence |
| 75 |
 |
Examples of Patients with Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks) | Seen here are patients with saccadic intrusions that do have an intersaccadic interval. Square wave jerks are commonly seen in degenerative conditions, mainly involving the posterior fossa (e.g., cerebellar degeneration) and basal ganglia (e.g., progressive supranuclear palsy). | Square Wave Jerks |
