The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
Filters: Format: "video/mp4" Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 52 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Rebound (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Tap outstretched arms. Patient's arms should recoil to original position. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska Medical Center. Viewing... | Coordination Examination; Rebound | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 53 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 54 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Speech - Rapid Alternating Movements (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Having the patient say lah-pah-kah can test rapid alternating movements of the tongue, lips, and palate. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebr... | Coordination Examination; Rapid Alternating Movements | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 55 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 56 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Station (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Have the patient stand still. Note the position of the feet and how steady the patient is with eyes open. In the demonstrated exam, the patient is asked to hop and pat at the same time. This is a good way to test upper and lower extremity coordination and balance simultaneously. NeuroLogic Exam has ... | Coordination Examination; Station | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 57 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 58 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tandem Gait (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient is asked to walk heel-to-toe. Note steadiness. Tandem gait requires the patient to narrow the station and maintain balance over a 4-5 inch width. Patients with midline ataxias have difficulty with tandem gait. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Developme... | Coordination Examination; Tandem Gait; Heel-toe Gait | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 59 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 60 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Toe-to-finger (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | The patient touches her toe to the examiner's finger repetitively as the examiner moves his finger to new positions. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the Univer... | Coordination Examination; Toe-to-finger Test | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 61 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 62 |
 |
Coordination Exam: Normal Exam: Tremor (x2) (includes Spanish audio & captions) | Patient's arms are held outstretched and fingers extended. Watch for postural or essential tremor. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a grant from the Slice of Life Development Fund at the University of Utah, the Department of Pediatrics and the Office of Education at the University of Nebraska M... | Coordination Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 63 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 64 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 1 - Olfaction (x2) | This patient has difficulty identifying the smells presented. Loss of smell is anosmia. The most common cause is a cold (as in this patient) or nasal allergies. Other causes include trauma or a meningioma effecting the olfactory tracts. Anosmia is also seen in Kallman syndrome because of agenesis of... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 65 |
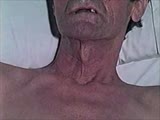 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 11 - Motor | When the patient contracts the muscles of the neck the left sternocleidomastoid muscle is easily seen but the right is absent. Looking at the back of the patient, the left trapezius muscle is outlined and present but the right is atrophic and hard to identify. These findings indicate a lesion of the... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 66 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 11 - Motor (x2) | When the patient contracts the muscles of the neck the left sternocleidomastoid muscle is easily seen but the right is absent. Looking at the back of the patient, the left trapezius muscle is outlined and present but the right is atrophic and hard to identify. These findings indicate a lesion of the... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 67 |
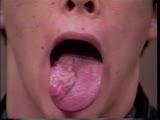 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 68 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 12 - Motor (x2) | Notice the atrophy and fasciculation of the right side of this patient's tongue. The tongue deviates to the right as well because of weakness of the right intrinsic tongue muscles. These findings are present because of a lesion of the right 12th cranial nerve. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 69 |
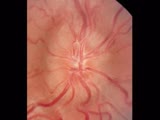 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Fundoscopy | The first photograph is of a fundus showing papilledema. The findings of papilledema include 1. Loss of venous pulsations 2. Swelling of the optic nerve head so there is loss of the disc margin 3. Venous engorgement 4. Disc hyperemia 5. Loss of the physiologic cup and 6. Flame shaped hemorrhages. Th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 70 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Fundoscopy (x2) | The first photograph is of a fundus showing papilledema. The findings of papilledema include 1. Loss of venous pulsations 2. Swelling of the optic nerve head so there is loss of the disc margin 3. Venous engorgement 4. Disc hyperemia 5. Loss of the physiologic cup and 6. Flame shaped hemorrhages. Th... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 71 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 72 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Acuity (x2) | This patient's visual acuity is being tested with a Rosenbaum chart. First the left eye is tested, then the right eye. He is tested with his glasses on so this represents corrected visual acuity. He has 20/70 vision in the left eye and 20/40 in the right. His decreased visual acuity is from optic ne... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 73 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 74 |
 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 2 - Visual Fields (x2) | The patient's visual fields are being tested with gross confrontation. A right sided visual field deficit for both eyes is shown. This is a right hemianopia from a lesion behind the optic chiasm involving the left optic tract, radiation or striate cortex. NeuroLogic Exam has been supported by a gran... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
| 75 |
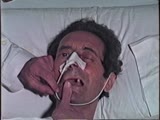 |
Cranial Nerve Exam: Abnormal Examples: Cranial Nerve 5 - Motor | The first patient shown has weakness of the pterygoids and the jaw deviates towards the side of the weakness. The second patient shown has a positive jaw jerk which indicates an upper motor lesion affecting the 5th cranial nerve. Video courtesy of Alejandro Stern, Stern Foundation. NeuroLogic Exam h... | Cranial Nerve Examination | NeuroLogic Exam: An Anatomical Approach |
