The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Format: "image/png" Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 51 |
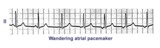 |
Wandering atrial pacemaker | Wandering atrial pacemaker is a benign rhythm change where the pacemaker site shifts from the sinus node into the atrial tissues. P-wave morphology varies with the pacemaker site. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 52 |
 |
QRS axis = +60 degrees | Lead aVL is isoelectric; leads II and III are mostly positive. The QRS axis, therefore, is +60 degrees. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 53 |
 |
Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Electronic ventricular pacemaker rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 54 |
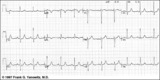 |
High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | High lateral wall MI (seen in aVL) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 55 |
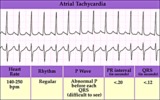 |
Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 56 |
 |
LVH with Strain | LVH with Strain | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 57 |
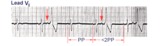 |
PAC's with RBBB aberrant conduction | PAC's are identified by the arrows. Note that the PP interval surrounding the PAC is less than 2x the basic sinus cycle indicating that the sinus node has been reset by the ectopic P wave. The pause after the PAC, therefore, is incomplete. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 58 |
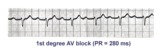 |
1st degree AV block | The normal PR interval is 0.12 - 0.20 sec, or 120 -to- 200 ms. 1st degree AV block is defined by PR intervals greater than 200 ms. This may be caused by drugs, such as digoxin; excessive vagal tone; ischemia; or intrinsic disease in the AV junction or bundle branch system. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 59 |
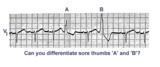 |
Sore thumbs | Two funny looking premature beats are seen in this rhythm strip. Beat A is preceded by a PAC which distorts the T wave, making this an aberrantly conducted PAC. Beat B is a PVC. The notch on the down slope of the QRS complex clearly identifies this as a PVC and not aberrancy. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 60 |
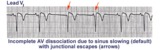 |
AV dissociation by default | If the sinus node slows too much a junctional escape pacemaker may take over as indicated by arrows. AV dissociation is incomplete, since the sinus node speeds up and recaptures the entricles. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 61 |
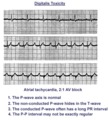 |
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 62 |
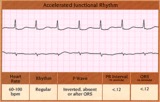 |
Accelerated junctional rhythm - marquette | Accelerated junctional rhythm - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 63 |
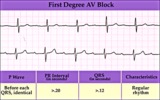 |
First degree AV block - marquette | First degree AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 64 |
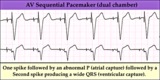 |
AV sequential pacemaker - marquette | (Summary) | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 65 |
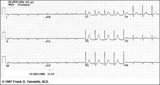 |
Postero-lateral MI: Fully Evolved | The true posterior MI is recognized by pathologic R waves in leads V1-2. These are the posterior equivalent of pathologic Q waves (seen from the perspective of the anterior leads). Tall T waves in these same leads are the posterior equivalent of inverted T waves in this fully evolved MI. The loss o... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 66 |
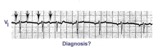 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 and 2:1 AV block | The ectopic atrial rate is 150 bpm. Some of the ectopic P waves are easily seen and indicated by the arrows. Other P waves are burried in the T waves and not so easily identified. Atrial tachycardia with AV block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. 3:2 and 2:1 AV block is seen in this examp... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 67 |
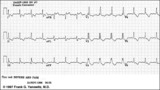 |
RBBB with primary ST-T wave abnormalities | RBBB is recognized by 1) rR' in V1; 2) QRS duration>0.12s; 3) terminal QRS forces oriented rightwards and anterior. In RBBB the ST-T waves should be oriented opposite to the terminal QRS forces. In this example there areprimary ST-T wave abnormalitiesin leads I, II, aVL, V5, V6. In these leads th... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 68 |
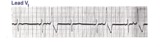 |
What are those funny looking beats???? | The differential diagnosis of funny-looking-beats, or FLB's, primarily considers beats of supraventricular origin with aberrant conduction and ventricular ectopic beats. In this example the two FLB's have an easily seen ectopic P wave before them; therefore these are PAC's with RBBB aberration. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 69 |
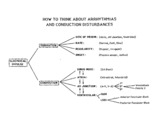 |
Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Conceptual framework: aArrhythmias and conduction abnormalities | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 70 |
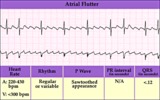 |
Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 71 |
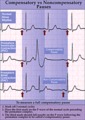 |
Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Compensatory vs. non-compensatory pauses - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 72 |
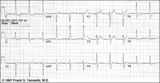 |
LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | LVH - best seen in the frontal plane leads! | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 73 |
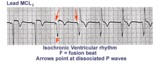 |
Isochronic ventricular rhythm | An isochronic ventricular rhythm is also called an accelerated ventricular rhythm because it represents an active ventricular focus. This arrhythmia is a common reperfusion arrhythmia in acute MI patients. It often begins and ends with fusion beats and there is AV dissociation. Treatment is usuall... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 74 |
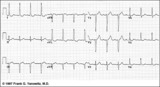 |
LVH: limb lead criteria | In this example of LVH, the precordial leads don't meet the usual voltage criteria or exhibit significant ST segment abnormalities. The frontal plane leads, however, show voltage criteria for LVH and significant ST segment depression in leads with tall R waves. The voltage criteria include 1) R in... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 75 |
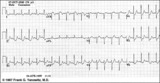 |
ST segment depression | ST segment depression is a nonspecific abnormality that must be evaluated in the clinical context in which it occurs. In a patient with angina pectoris ST depression usually means subendocardial ischemia and, unlike ST elevation, is not localizing to a particular coronary artery lesion. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
