A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders. This collection includes many demonstrations of examination techniques.
Dan Gold, D.O., Associate Professor of Neurology, Ophthalmology, Neurosurgery, Otolaryngology - Head & Neck Surgery, Emergency Medicine, and Medicine, The Johns Hopkins School of Medicine.
A collection of videos relating to the diagnosis and treatment of eye movement disorders.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
Ocular Motor Signs in Early Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 64-year old man who experienced imbalance and falls (usually backwards) for the last 6 months. He experienced difficulty navigating stairs and had become a messy eater (thought to be in large part due to his ver... | Image/MovingImage |
| 27 |
 |
Spontaneous Upbeat Nystagmus in Acute Wernicke's Encephalopathy | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 40-year-old woman presenting with imbalance, confusion and oscillopsia. Exam demonstrated upbeat nystagmus (UBN) in primary gaze that remained UB in all directions of gaze, with a slight torsional component (top... | Image/MovingImage |
| 28 |
 |
Gaze-Evoked, Rebound, and Centripetal Nystagmus in Cerebellar Degeneration | A 68-year-old female reported a 2-year history of progressive gait imbalance, falls, dizziness and vertical oscillopsia. She described that dizziness and oscillopsia were worst when looking down. There was no family history of ataxia. Composite gaze with fixation was recorded with video-oculography ... | Image/MovingImage |
| 29 |
 |
Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, & Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS): Impaired Visually-Enhanced VOR and Abnormal Head Impulse Testing | A 67 year old woman presented with 1 year of progressive numbness, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bilateral horizontal gaze-evoked nystagmus, impairment of the visually-enhanced vestibular ocular reflex (vVOR - s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 30 |
 |
Five Common Ocular Motor Signs in Cerebellar Disorders - Saccadic Hypermetria, Saccadic Pursuit & VOR Suppression, Gaze-evoked & Rebound Nystagmus | (1) Saccadic hypermetria - an overshoot of the visual target (2) Saccadic smooth pursuit - due to impaired pursuit and low gain, saccades are needed to keep up with the visual target. This gives it a ‘choppy' appearance. (3) Saccadic vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) suppression - another... | Image/MovingImage |
| 31 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV Pre- and Post-Epley Maneuver | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical right posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which was provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient was moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a b... | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
+ HIT, + Skew, Unidirectional Nystagmus: Central Acute Vestibular Syndrome Due to Wallenberg Syndrome | This is a 45-year-old woman who presented to the ED with acute prolonged vertigo and vertical diplopia. She was seen as an outpatient 1 month after her ED visit, and double vision and balance were improving by that time. Her HINTS testing showed the following (seen in the video): 1) Head Impulse - A... | Image/MovingImage |
| 33 |
 |
Abnormal Visually-enhanced Vestibulo-ocular Reflex (vVOR) in Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This patient complained of chronic (unexplained cough), progressive numbness in the legs and feet, gait instability, and oscillopsia when walking or with head movements. Examination showed excessive square-wave jerks, bil... | Image/MovingImage |
| 34 |
 |
Ocular Alignment | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: These tests allow for detection of eso-, exo- or hyperdeviations (phorias (one eye viewing) or tropias (both eyes viewing) that can be seen with ocular motor palsy, skew deviation, or with cerebellar disease (commonly eso... | Image/MovingImage |
| 35 |
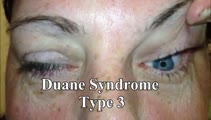 |
Duane's Syndrome Type III | This is a 40-yo-woman seen in neurology clinic for a complaint unrelated to her eyes. On exam, there was impaired adduction and abduction OS. In adduction, there was narrowing of the palpebral fissure OS, a result of her globe retraction due to co-contraction of the medial and lateral rectus muscles... | Image/MovingImage |
| 36 |
 |
Assessing Utricle Pathway Function and the Effects of Convergence on Nystagmus in Acute Vestibular Neuritis | A 35-year-old woman presented a few days after the onset of room-spinning vertigo. She denied diplopia, dysarthria, dysphagia, dysphonia, incoordination, numbness, and weakness. On examination, she had subtle spontaneous right-beat nystagmus (RBN). This nystagmus increased in amplitude and frequency... | Image/MovingImage |
| 37 |
 |
Upbeat Transitioning to Downbeat Nystagmus in Wernicke's Encephalopathy | This is a 30-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse who presented to the hospital with inability to walk after several weeks of heavy drinking and malnutrition. While in the hospital, he noted that when he would look straight ahead, everything he saw would appear to be bouncing up and down - a... | Image/MovingImage |
| 38 |
 |
Provocative Maneuvers (Removal of Fixation, Vibration, Head-Shaking) to Accentuate Peripheral Vestibular Nystagmus) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: With an acute destructive process like vestibular neuritis that causes significant unilateral vestibular loss, spontaneous nystagmus is always present. However, over days to months, spontaneous nystagmus should resolve co... | Image/MovingImage |
| 39 |
 |
Oculopalatal Tremor with Prominent Nystagmus, Bilateral Horizontal Gaze Palsy, and Bilateral Facial Palsies | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 50-year-old woman who experienced the acute onset of right sixth and seventh nerve palsies and left hemiparesis. Two cavernomas within the right pons (one in the region of the facial colliculus) were demonstrat... | Image/MovingImage |
| 40 |
 |
PSP with Vertical Gaze Palsy, Abnormal Optokinetic Nystagmus and Inability to Suppress Blinking to Light | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 75-year-old woman with a diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Examination demonstrated vertical supranuclear gaze palsy (i.e., it could be overcome by the vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex [VOR]), s... | Image/MovingImage |
| 41 |
 |
Slow Volitional Saccades and Poor Fast Phases to an Optokinetic Stimulus, with Preserved Head Impulse Testing | This is a 67-year-old woman presenting with imbalance and binocular horizontal diplopia at near. On examination there were frequent square wave jerks, limited supraduction OU and convergence insufficiency, which explained her diplopia. Pursuit and suppression of the vestibulo-ocular reflex were sa... | Image/MovingImage |
| 42 |
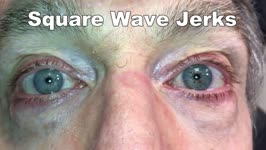 |
Saccadic Intrusions (Square Wave Jerks, SWJ) | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Seen here are SWJ, which is the most common example of a saccadic intrusion. Here the patient is fixating on the camera, and all of the sudden a saccade takes the eyes off the fixation target, there's a brief intersaccadi... | Image/MovingImage |
| 43 |
 |
Trigeminal, Facial (with Aberrant Regeneration), and Vestibulocochlear Nerve Palsies Following Tumor Resection | This is a 30-yo-woman who underwent resection of a right trigeminal schwannoma. Post-operatively, she was vertiginous with a clearly + head impulse test to the right (and spontaneous left-beating nystagmus), had lost hearing in the right ear, had no facial sensation on the right, and had a right low... | Image/MovingImage |
| 44 |
 |
Slow Horizontal, Vertical, Oblique Saccades and Gaze-evoked Nystagmus in Anti-AGNA-1 Encephalitis | This is a patient who presented subacutely with imbalance and dizziness. On examination, she had evidence of gaze evoked nystagmus, right internuclear ophthalmoplegia, as well as slow saccades horizontally and vertically. She was diagnosed with a rare antibody-mediated disorder, anti-AGNA-1 (antig... | Image/MovingImage |
| 45 |
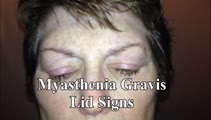 |
Typical Lid Signs (Cogan's Lid Twitch, Lid Hopping, Enhanced Ptosis) in Myasthenia Gravis | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a 60-yo-woman with MG who displays typical eyelid signs including Cogan's lid twitch, lid hopping (appreciated during horizontal smooth pursuit in this patient), and enhanced ptosis in accordance with Hering's law... | Image/MovingImage |
| 46 |
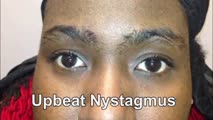 |
Upbeating and Gaze-evoked Nystagmus, V-pattern Esotropia from Bilateral 4th Nerve Palsies | Video example of a patient with upbeating and gaze-evoked nystagmus, V-pattern esotropia from bilateral 4th nerve palsies. | Image/MovingImage |
| 47 |
 |
Anterior Canal BPPV | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Although the anterior canal (AC) variant of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is rare, mainly owing to its orientation relative to gravity (which makes otoconial debris much less likely to enter it), it can occu... | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Dix-Hallpike Maneuver in Posterior BPPV with Reversal of Nystagmus on Sitting Up | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: This is a patient with typical posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), which is provoked by the Dix-Hallpike maneuver. When the patient is moved into the right Dix-Hallpike maneuver, after a brie... | Image/MovingImage |
| 49 |
 |
Posterior Canal BPPV Treated with Semont Maneuver | This is a patient with left posterior canal (PC) benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV), and upbeat-torsional (towards the left ear) nystagmus was provoked by left Dix-Hallpike maneuver and left side-lying maneuver. This video demonstrates treatment of her left PC BPPV with the Semont maneuver.... | Image/MovingImage |
| 50 |
 |
Test Your Knowledge - Monocular Oscillopsia | 𝗢𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻𝗮𝗹 𝗗𝗲𝘀𝗰𝗿𝗶𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: Which of the following associated signs is most likely to be seen in this patient presenting with oscillopsia? A. Optic nerve pallor B. Palatal tremor C. Severe unilateral cataract D. Head bobbing E. Neurovascular contact... | Image/MovingImage |
