The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
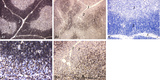 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the CD8-thymocytes in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days, i.e. the darkly stained cortex and the lightly stained medulla in normal thymus ... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 27 |
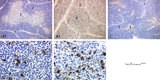 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide on the resident macrophages in thymus (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP, 70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution after 4 days. The darkly stained cortex of th normal thymus (A1, A2) decreases its dark stain... | cyclophosphamide; ED1 macrophages ; immunosuppression; lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 28 |
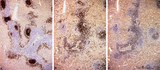 |
The effect of cyclophosphamide treatment on the B and T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with antibodies to B cells (Mark 1), CD3 and CD8 T cells. (A): B cells in the follicles, germinal centres (2) and corona are stained positive brown, while the PALS area (1) is negative (blue)... | CD3 lymphocytes; CD8 lymphocytes; B lymphocytes; cyclophosphamide | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 29 |
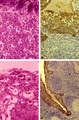 |
Follow-up of the process of diapedesis through stratified epithelium of the palatine tonsil (gut-associated lymphatic tissue or GALT) (human) | Stain: (A, C) Azan and (B, D) anti-keratin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB) on frozen section, counterstained with hematoxylin. (1) (keratinized) stratified squamous epithelial cells. (2) between desquamated epithelial cells the spaces are filled with infiltrated l... | stratified squamous epithelial cells; GALT | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 30 |
 |
Hassall's corpuscle in thymus (human, puberty) | Stain: Hematoxylin. A larger magnification of the thymic medulla reveals the purple-stained structures in the centre of a so-called Hassall's (or thymic) corpuscle consisting of keratinized (*) epithelial cells. It is surrounded by recognizable flattened cells showing keratohyalin granules (-->). T... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); epithelioreticular cell (ERC); lymphoid tissue | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 31 |
 |
Hassall's corpuscle in thymus (mouse) | Electron microscopy. The centre of a small Hassall's corpuscle consists of darker-stained cells (1) which are keratinizing and represent degenerating cytoplasmic remnants (2). (3) is an infiltrating monocyte and (*) indicate the presence of free keratohyalin granules from disintegrated epithelial ce... | thymic corpuscle (Hassalls); lymphoid tissue ; epithelioreticular cell (ERC) | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 32 |
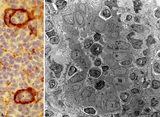 |
High endothelial venules (HEV) (rat lymph node, human palatine tonsil) | Stain: (A) Anti-laminin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section of lymph node; (B) electron microscopy (palatine tonsil). (A): Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes are outlined demonstrating postc... | palatine tonsil; high endothelial venule (HEV); laminin; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 33 |
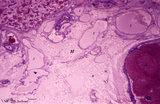 |
Hilum side of lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Site of the hilum of a lymph node includes part of the medulla and medullary cords (1) and medullar sinuses (2). In the hilum (H) dilated efferent lymphatic vessels (3) and draining veins (4) and entering arteries (5) are present. (6) represents adipose tissue embedding the efferent ves... | hilum; lymphatic vessels; medullary cords; paracortex | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 34 |
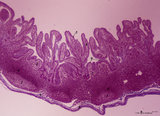 |
Ileum with Peyer's patches ('gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. Survey ileum (see also Digestive System: Ileum) A large amount of non-encapsulated diffuse lymphatic tissue or mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT) is located in the subepithelial lamina propria/submucosa of the ileum and called 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' (GALT). These so-c... | follicle; lymph node; germinal center | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 35 |
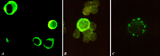 |
Immunohistochemical identification of splenic B cells (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of FITC-labeled anti-Mark-1 antibody against rat B cells, carried out on spleen cells after fixation (A, B) or non-fixated spleen cells (C). (A) shows (young) plasma cells producing antibodies. (B) a green-stained B cell. The surrounding negative cells are likely T cells.... | immunofluorescence; B lymphocyte; capping | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 36 |
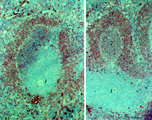 |
Immunohistochemistry of B cells in splenic white pulp (rat) | Stain: Immunohistochemistry of Vector red for Mark-1-antibody-stained B cells. (1) indicates the PALS area populated with unstained T cells located around the central artery of the white pulp. (2) indicates the positively red stained B cells in the germinal centre of the follicle. (3) the B-cells i... | marginal zone; immunohistochemistry; follicle | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 37 |
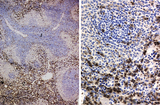 |
Immunohistochemistry of ED1-positive subset of macrophages in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with the anti-macrophage antibody ED1. Most of the labeled (brown) macrophages are found in the red pulp (2) up to the marginal zone border (B). The PALS area (1) contains sparsely spread ED1 ... | ED1 ; macrophages; immunohistochemistry; marginal zone | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 38 |
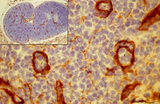 |
Immunohistochemistry of laminin in cortex lymph node (rat) | Anti-laminin-antibody and immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section. Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes (BM) are outlined demonstrating postcapillary venules (1) in the paracortical areas, as well as larger b... | paracortex; high endothelial venule (HEV); laminin; immunohistochemistry | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 39 |
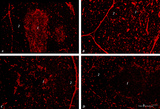 |
Immunohistochemistry of thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) Medulla. (2) Cortex. (A): Staining with a monoclonal antibody against vimentin illustrates that vimentin is localised in the stromal cells of the connective tissue of the capsule, of the septa or trabeculae that invade the cortex (2) and overwhelmingly ... | vimentin; laminin; fibronectin; ED2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 40 |
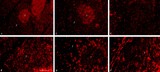 |
Immunohistochemistry with cellular markers in thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence. (1) medulla. (2) cortex. (A-survey, B-cortex): ER13 antibody stains for MHC-class II antigens on reticular cell types in medulla and cortex. (C): ED1 monoclonal antibody stains a single chain glycoprotein of 110 kDa on the lysosomal membrane of myeloid cel... | ER13 antibody; ED1 monoclonal antibody; ED2 monoclonal antibody; ER2 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 41 |
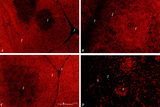 |
Immunohistochemistry with cellular markers in thymus (rat) | Stain: Alexa 594 red immunofluorescence. (1) medulla; (2) cortex; (3) septa. (A): Strong CD8 staining of the thymic cortical lymphocytes (single CD8+ and double positive CD4+CD8+ thymocytes). (B): OX19 staining for almost all T cells, equivalent to T1 human marker and Ly-1 mouse marker. Note that... | cyclophosphamide; CD8 monoclonal antibody; OX19 monoclonal antibody; ER1 monoclonal antibody | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 42 |
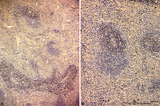 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD3 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti CD3 antibodies. Survey (A) and detail (B) show that CD3 marker for mature T cells stains positively (brown) in the PALS area (1) around the central arteries, while the adjacent follic... | CD3 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 43 |
 |
Immunoperoxidase stained CD8 positive T cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunoperoxidase staining using diaminobenzidin (DAB)/ hematoxylin counterstained on frozen section with anti-CD8 antibodies. A, B and C show brown-stained CD8-positive T cells or Tc cells at different enlargements. The CD8 Tc/s cells are localised predominantly in the PALS area (1), while th... | CD8 lymphocytes; immunohistochemistry; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 44 |
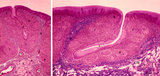 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Survey; B: detail of the crypt. The lingual tonsil consists of accumulations of bulging lingual lymphatic follicles in the dorsal part of the tongue behind the terminal sulcus, and belongs to the so-called Waldeyer's ring of pharyngeal lymphatic tissue. The left (A) and right (B) ... | lingual tonsil; GALT; Non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; crypt | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 45 |
 |
Lingual tonsil ('lymphoepithelial tissue', 'gut-associated lymphatic tissue' or GALT) (human) | Stain: Azan. A: Left side shows a secondary lymphatic follicle (1) separated by the connective tissue of the proper lamina (2) from the lining non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium (3). The mantle zone (4) is indicated by the peripheral dense aggregations of (memory) B lymphocytes. (5) diff... | lingual tonsil; GALT; non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 46 |
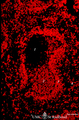 |
Localization of B cells in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Vector red using Mark-1 antibody against B cells. The T cells in the PALS (periarteriolar lymphatic sheath) remain unstained (1, dark). The red-stained B cells are packed in the germinal centre (2), the corona (3) or mantle layer that diffuses into the marginal zone and... | B lymphocytes; immunofluorescence; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 47 |
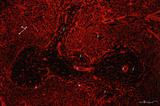 |
Localization of heparan sulfate (HS) in spleen (rat) | Stain: Immunofluorescence of Alexa 594 red labeled single chain antibody 3C3 for heparan sulfate (HS). The antibody stains HS epitopes of the meshwork of reticulum cells and the basal membrane of blood vessels. (1) central arteries in the T cell area of the PALS (2). The B cell area in the follic... | white pulp; heparan sulfate; PALS | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 48 |
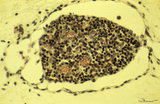 |
Lymph node (fetus, human) | Stain: Trichrome (Goldner). Along the course of lymphatic vessels lymph nodes develop. Lymphatic vessels dilate and form lymphatic sacs and lymphocytes aggregate around these sacs. A tiny developing lymph node with dense-stained thymocyte nuclei is closely associated with dilated lymph capillaries. ... | fetal lymph node; development | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 49 |
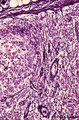 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Silver stain (Gomori). Due to the argyrophilia of reticular fibres the reticular network is black-stained among others such as collagen type I, III, IV. From the fibrous capsule (1) a meshwork of fine reticular fibres penetrates into the cortex of a lymph node crossing the subcapsular (or m... | germinal center; argyrophilia; reticular fibers | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
| 50 |
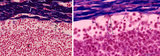 |
Lymph node (human) | Stain: Azan. Left: subcapsular (or marginal) sinus in lymph node. Right: higher magnification. Both pictures show a thick capsule (1), at (2) subcapsular (or marginal) sinus filled with lymphocytes indicate (lining) littoral cells (?). Reticular cells (3) are localized perpendicularly through sin... | subcapsular sinus; reticular cell | Poja Histology Collection - Lymphatic Tissues and Organs Subset |
