The Health Education Assets Library (HEAL) is a collection of over 22,000 freely available digital materials for health sciences education. The collection is now housed at the University of Utah J. Willard Marriott Digital Library.
TO
Filters: Collection: ehsl_heal
| Title | Description | Subject | Collection | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
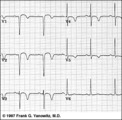 |
Anteroseptal MI, fully evolved: precordial leads | Anteroseptal MI, fully evolved: precordial leads | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 27 |
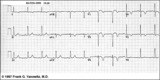 |
Anteroseptal MI: fully evolved | The QS complexes, resolving ST segment elevation and T wave inversions in V1-2 are evidence for a fully evolved anteroseptal MI. The inverted T waves in V3-5, I, aVL are also probably related to the MI. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 28 |
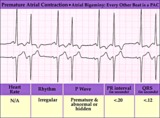 |
Atrial bigeminy - marquette | Atrial bigeminy - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 29 |
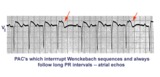 |
Atrial echos | In this example a typical Wenckebach sequence is interrupted by what looks like a PAC - indicated by red arrows. Atrial echos are more likely, however, because the preceding beat has a long PR interval, a condition that facilitates reentry and echo formation. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 30 |
 |
Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Atrial fibrillation with moderate ventricular response - Marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 31 |
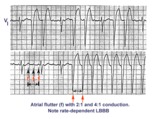 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 and 4:1 conduction and rate dependent LBBB | In this example of atrial flutter with variable AV conduction, the faster rates are associated with rate-related LBBB. Don't confuse this for ventricular tachycardia. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 32 |
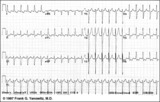 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | In this example of atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction the flutter waves are very hard to see. Atrial flutter with 2:1 block must be considered, however, because the heart rate is about 150 bpm. A careful look at V1 shows the two flutter waves for each QRS complex complex. One flutter wave imme... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 33 |
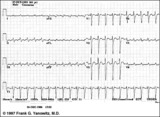 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | Flutter waves are best seen in lead V1; one immediately follows the QRS and the other precedes the next QRS. The regular ventricular rate of 150 bpm should always prompt us to condider this diagnosis. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 34 |
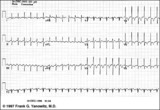 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction | Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV block is one of the most frequently missed ECG rhythm diagnoses because the flutter waves are often hard to find. In this example two flutter waves for each QRS are best seen in lead III and V1. The ventricular rate at 150 bpm should always prompt us to consider atrial fl... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 35 |
 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction: lead V1 | The arrows point to two flutter waves for each QRS complex. Atrial rate = 280; ventricular rate = 140. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 36 |
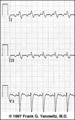 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 AV conduction: leads II, III, V1 | In leads II and III, the one of the flutter waves occurs at the end of the QRS complex and might be mistaken for part of the QRS itself; i.e., the S wave. In lead V1, the two flutter waves for every QRS are more easily identified. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 37 |
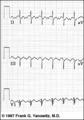 |
Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction: leads II, III, V1 | Atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction: leads II, III, V1 | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 38 |
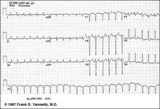 |
Atrial flutter with 3:2 AV conduction | This 12-lead ECG shows a subtle bigeminal rhythm resulting from atrial flutter with a 3:2 AV conduction ratio; RR intervals alternate by a small duration. This is uncommon! The impulses from the atrial flutter conduct through the AV junction in a Wenckebach sequence; for every 3 flutter waves the s... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 39 |
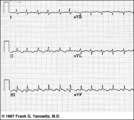 |
Atrial flutter with 3:2 conduction ratio: frontal plane leads | Note the subtle bigeminy in the RR intervals. The best way to identify the flutter waves in this example is to imagine what lead III would look like if the QRS complexs disappeared; what remains is a reasonable saw-tooth pattern characteristic of atrial flutter with a flutter rate of about 300 bpm... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 40 |
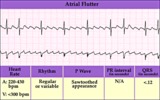 |
Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Atrial flutter with variable AV block - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 41 |
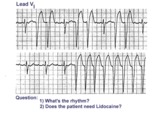 |
Atrial flutter with variable AV block and rate-dependent LBBB | The basic rhythm is atrial flutter with variable AV block. When 2:1 conduction ratios occur there is a rate-dependent LBBB. Don't be fooled by the wide QRS tachycardia on the bottom strip. It's not ventricular tachycardia, but atrial flutter with 2:1 conduction and LBBB. Lidocaine is not needed ... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 42 |
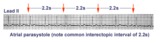 |
Atrial parasystole | Parasystolic rhythms involve an independent ectopic pacemaker resulting in nonfixed coupled premature beats. Parasystole may occur in the atria, as seen in this example, in the AV junction, and in the ventricles. Note the common inter-ectopic interval separating the parasystolic PAC's. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 43 |
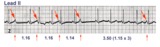 |
Atrial parasystole | In atrial parasystole non-fixed coupled PACs, shown by arrows, occur at a common inter-ectopic interval or at multiples of this interval. Atrial fusions, not shown here, may also occur when the PAC occurs in close temporal proximity to the sinus impulse. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 44 |
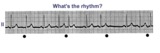 |
Atrial parasystole | The evenly spaced dots indicate ectopic atrial activity from a parasystolic atrial pacemaker. Non-fixed coupled PACs are seen having a common inter-ectopic interval. One of the PACs is nonconducted. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 45 |
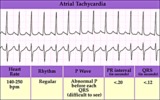 |
Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Atrial tachycardia - marquette | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 46 |
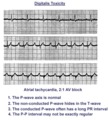 |
Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Atrial tachycardia with 2:1 AV block: a manifestation of digitalis intoxication | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 47 |
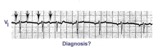 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 and 2:1 AV block | The ectopic atrial rate is 150 bpm. Some of the ectopic P waves are easily seen and indicated by the arrows. Other P waves are burried in the T waves and not so easily identified. Atrial tachycardia with AV block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. 3:2 and 2:1 AV block is seen in this examp... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 48 |
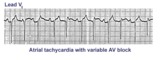 |
Atrial tachycardia with 3:2 AV block | In this rhythm the atrial rate from an ectopic focus is 160 bpm. Atrial activity can be seen on top of T waves, and before QRS's. Careful observation reveals a 3:2 Wenckebach relationship between P waves and QRS's. Atrial tachycardia with block is often a sign of digitalis intoxication. | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 49 |
 |
Atrial tachycardia with exit block and AV block | The ectopic P waves, easily seen in this example,occur in groups, separated by short pauses. This is likely due to an exit block just distal to the atrial pacemaker. Because not all of the P waves make it to the ventricles, there is also 2nd degree AV block. Therefore, two levels of block are pre... | Knowledge Weavers ECG | |
| 50 |
 |
Atypical LBBB with primary T wave abnormalities | Primary T wave abnormalities in LBBB refer to T waves in the same direction as the major deflection of the QRS. These are seen in leads I, III, aVL, V2-4. Most likely diagnosis is myocardial infarction. | Knowledge Weavers ECG |
