John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
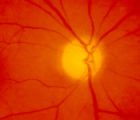 |
4-54a -Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 27 |
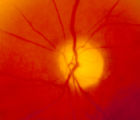 |
4-54b - Optic Neuropathy, Ischemic: Posterior | Image | |
| 28 |
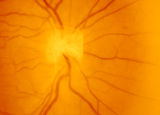 |
3-3 - Bergmeister Papilla | Image | |
| 29 |
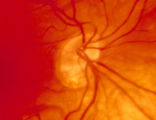 |
3-4 - Tilted Disc | Tilted discs are normal variants caused by oblique insertion of the optic nerve to the globe. They can be and frequently are mistaken for papilledema. In this case the superior edge of the disc is tilted and appears elevated. This disc exhibits a nasal inferior tilt. | Image |
| 30 |
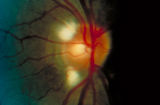 |
3-5b - Myelinated Nerve Fibers | Myelinated nerve fibers are frequently confused with papilledema. The feathery edge of the myelinated fibers that conceal the disc and vessel should provide the clue. These myelinated nerve fibers make the disc look blurred. | Image |
| 31 |
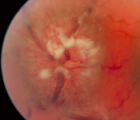 |
3-35a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 4 Stage 4 = Complete obliteration of the cup and complete obscuration of at least some vessels on the surface of the disc. There may be small dilated capillaries on the disc that resemble telangiectasia. It is not the NFL infarcts or hemorrhages but the obscuration of the ... | Image |
| 32 |
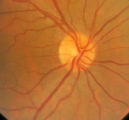 |
3-31b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 0 GRADING PAPILLEDEMA GRADING PAPILLEDEMA We grade papilledema in order to tell us how severe it is. The most sensible grading scheme has been provided by Lars Frisén. STAGE 0: This woman had documented increased intracranial pressure of 340 mm water. Very little if any ... | Image |
| 33 |
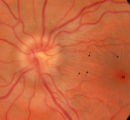 |
3-32b - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 1 Stage 1 = C shaped blurring of the nasal, superior and inferior borders. Usually the temporal margin is normal. Also notice the chorio-retinal folds (arrows) that eminate toward the macula (m) | Image |
| 34 |
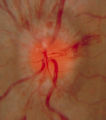 |
3-34c Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 3 Stage 3 = Elevation of the entire disc with partial obscuration of the retinal vessels at the disc margin. Here the vessels are partly obscured and make the development into stage 3 easier to call. | Image |
| 35 |
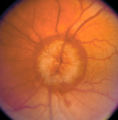 |
3-36a - Papilledema Stages | Grading Papilledema: Stage 5 Stage 5 = Dome-shaped appearance with all vessels being obscured. (Sometimes called "champagne cork" swelling--because of its dome shape.) | Image |
| 36 |
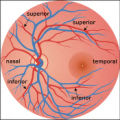 |
2-37a - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 37 |
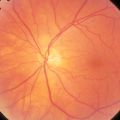 |
2-37b - Vascular Features | When looking at the disc, the central retinal artery and vein should be visible. The central retinal artery is usually slightly narrower than the vein. When the central retinal artery goes though the lamina cribrosa, the artery becomes smaller because of diminution of the muscular layer and loss of ... | Image |
| 38 |
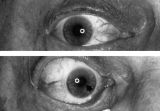 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Right Pupil | Aberrant regeneration of the right pupil in a man with a large intracavernous sinus meningioma causing a pupil-involving, incomplete third cranial nerve palsy. His pupil is round when he gazes straight ahead (top). When he tries to rotate the eye medially, the pupil constricts, but a segment of the ... | Image |
| 39 |
 |
Structures of the iris | Structures of the iris. The a indicates the anterior border layer that terminates at the pigmentary ruff of the pupillary border (b). The c indicates the iris sphincter muscle, which is oriented circumferentially within the stroma and located deep to the anterior border layer; d indicates vessels th... | Image |
| 40 |
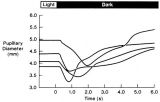 |
Pupillogram Demonstrating Paradoxical Pupillary Constriction to Darkness | Pupillogram demonstrating paradoxical pupillary constriction to darkness in four patients with congenital achromatopsia. Note that the pupils initially constrict when the light is extinguished. (Price MJ, Thompson HS, Judisch GF et al: Pupillary constriction to darkness. Br J Ophthalmol 1981;69:205-... | Image |
| 41 |
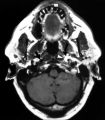 |
Left-sided Internal Carotid Artery Dissection | Left-sided internal carotid artery dissection identified on T-1 weighted magnetic resonance image from a 52-year-old man who suddenly developed left-sided neck and orbital pain along with a droopy left upper eyelid while dragging a deer out of the woods during hunting season. The normal dark flow vo... | Image |
| 42 |
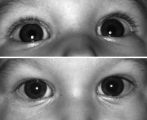 |
Right-sided Pseudo-Horner's Syndrome | Right-sided pseudo-Horner's syndrome in an 8-month-old infant referred because her mother had noted a larger pupil on the left for a few months and her pediatrician thought the right upper lid was droopy. Both pupils reacted normally to light and darkness, the degree of anisocoria was similar in bot... | Image |
| 43 |
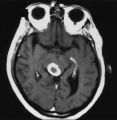 |
An Enhancing Bladder Metastasis Involving the Tectum of the Midbrain | Magnetic resonance image of an enhancing bladder metastasis involving the tectum of the midbrain of a 56-year-old man who developed double vision resulting from skew deviation and divergence insufficiency. He also had a left-sided relative afferent pupillary defect measuring 1.4 log units but showed... | Image |
| 44 |
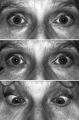 |
Light-near Dissociation | Light-near dissociation in a 51-year-old woman with multiple sclerosis who experienced double vision for 1 week. Her pupils are 5 mm in diameter in room light (top), react poorly in response to direct light reaction (middle), but constrict promptly in response to near stimulation (bottom). She also ... | Image |
| 45 |
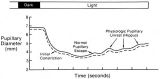 |
The Normal Pupillary Light Reflex | The normal pupillary light reflex is initiated following exposure to light. After a brief latency, both the right (solid line) and left (broken line) pupil constrict, then undergo a small amount of redilation (escape), followed by oscillations (hippus) if the light is sustained. Hippus is not a path... | Image |
| 46 |
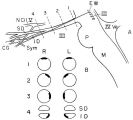 |
Location of Pupillomotor Fibers | Location of pupillomotor fibers are depicted as dark regions on cross-sections of the right (R) and left (L) oculomotor nerve at various locations along its course, including its emergence from the brain stem in the interpeduncular fossa (1), the midsubarachnoid segment (2), the level of the dorsum ... | Image |
| 47 |
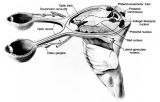 |
Anatomy of the Pupillary Light Reflex Pathway | Anatomy of the pupillary light reflex pathway. (Miller NR: Walsh And Hoyt's Clinical Neuro-Ophthalmology, p 421. Vol 2, 4th ed. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1985, with permission.) | Image |
| 48 |
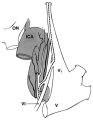 |
The Course of the Postganglionic Segment of the Oculosympathetic Fibers from the Internal Carotid Artery | The course of the postganglionic segment of the oculosympathetic fibers from the internal carotid artery (ICA) to the orbit is depicted as a dotted line. Note that they briefly join the abducens nerve (cranial nerve VI) before joining the nasociliary branch of the of the ophthalmic division of the t... | Image |
| 49 |
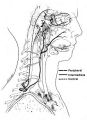 |
Anatomy of the Oculosympathetic Pathway | Anatomy of the oculosympathetic pathway. (Maloney WF, Younge BR, Moyer NJ: Evaluation of the causes and accuracy of pharmacologic localization in Horner's syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1980;90:394-402, Ophthalmic Publishing Company with permission.) | Image |
| 50 |
 |
Pupillogram of a Healthy Young Subject | Pupillogram of a healthy young subject showing continuous pupillary oscillations of both pupils when light is sustained, indicated by the dark arrow at the top of the recording. Note that the oscillations of the pupils are synchronous and demonstrate variable amplitude and frequency. This pattern of... | Image |
