John A. Moran Eye Center Neuro-Ophthalmology Collection: A variety of lectures, videos and images relating to topics in Neuro-Ophthalmology created by faculty at the Moran Eye Center, University of Utah, in Salt Lake City.
NOVEL: https://novel.utah.edu/
TO
Filters: Collection: "ehsl_novel_jmec"
| Title | Description | Type | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 26 |
 |
4-35 - Cupped Optic Nerve | Atrophic Glaucoma Atrophic glaucomatous discs show thinning of the neuro-retinal rim, "saucerization" (which is shallow cupping), evidence of peripapillary atrophy, and pallor of the very narrow neuroretinal rim. Notice that there is severe atrophy of the nerve fiber layer. | Image |
| 27 |
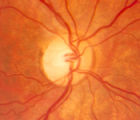 |
4-52b - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-52a mother, 4-52b son. | Image |
| 28 |
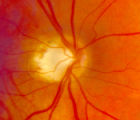 |
4-60a - Dominant Optic Neuropathy | A son presented with bilateral optic atrophy of unknown etiology after he failed a school visual exam. When looking for dominant optic atrophy, look at the parents. Mother was examined to find similar kind of atrophy. 4-60a mother, 4-60b son. | Image |
| 29 |
 |
Aberrant Regeneration of the Third | Patient with a right third nerve palsy demonstrates ptosis, anisocoria and ophthalmoplegia. During attempted downgaze, the right upper lid flutters back up (aberrant movement) and remains retracted. | Image/MovingImage |
| 30 |
 |
Basal Encephaloceles | Text | |
| 31 |
 |
Bilateral Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia | Example of patient with bilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia. Patient is led through instructions for direction and distance of gaze. | Image/MovingImage |
| 32 |
 |
Brainstem Trauma | Image/MovingImage | |
| 33 |
 |
Cogan's Lid Twitch | Image/MovingImage | |
| 34 |
 |
Cone Dystrophy | PPT covering Cone Dystrophy - An inherited degeneration that presents between 10 - 30 years of age. Symptoms are decreased visual acuity, poor color vision, and sometimes light sensitivity. | Text |
| 35 |
 |
Dissection of the Carotid Artery | ||
| 36 |
 |
Documenting the Neuro-ophthalmic Patient: External Photography | Description of documenting the neuro-ophthalmic patient using external photography. This covers pupils and extra ocular muscles. | |
| 37 |
 |
Facial Nerve Exam | Explanation of a facial nerve exam. | |
| 38 |
 |
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus with Third Nerve Palsy | Images showing presentation of Herpes Zoster (Zoster Ophthalmicus). | Text |
| 39 |
 |
Hydroxychloroquine Maculopathy (Plaquenil) | An overview of Chloroquine Maculopathy. | Text |
| 40 |
 |
Macula | Overview of the structure and viewing of the macula. | Text |
| 41 |
 |
Mimics of Atrophy | Text | |
| 42 |
 |
Near Reflex and Accomodation | Description of testing the near reflex and accomodation. | |
| 43 |
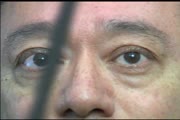 |
Normal Eye Movements | This is an examination of a person with normal eye movements. Notice the patient has normal excursions. He has normal pursuit and saccades (horizontally and vertically). | Text |
| 44 |
 |
Normal Optic Disc | Overview of the structure and function of the normal optic disc. | Text |
| 45 |
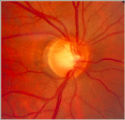 |
Notching of the Neuro-retinal Rim | The neuro-retinal rim becomes thinner; in particular the rim superotemporally and inferortemporally may develop a notch which is usually superior or inferior and rarely nasal or temporal. These notches are believed to be due to focal ischemic damage to the neuro-retinal rim. Glaucoma with Notching a... | Image |
| 46 |
 |
Optic Nerve Tumors Benign and Malignant | Discussion of optic nerve tumors including meningioma and glioma. | Text |
| 47 |
 |
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Progressive Supranuclear Palsy | Image/MovingImage |
| 48 |
 |
Retinal Fluorescein Angiography | This slide set provides a brief description of Retinal Fluorescein Angiography. First introduced in 1960, sodium fluorescein, a dye, is administered through an angiocatheter (3-5cc) by a nurse or technician. The dye reaches the central retinal artery after passing through the heart and lungs. | Text |
| 49 |
 |
Retinitis Pigmentosa Disease of Rods | Discussion of retinitis pigmentosa which is a retinal/choroidal degeneration caused by various genetic defects. | Text |
| 50 |
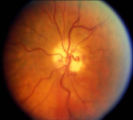 |
Shunt Vessel Meningioma | RETINO-CHOROIDAL (OPTO-CILIARY) COLLATERAL VESSELS: (also known as Retinal-choroidal venous collaterals, opticociliary veins or ciliary shunt vessels) Retino-choroidal collaterals are potential telangiectatic connections between the retina and choroidal circulation. Although sometimes called "shunts... | Image |
